Manufacture of industrial and technological equipment. Technological equipment
Technological equipment for automated production.
The production of engineering products is approximately 80% small- and medium-scale in nature. The rapid renewal of a wide range of manufactured machines with a simultaneous increase in the complexity of their design and accuracy necessitates a quick and efficient restructuring of production at enterprises based on highly automated machine tools. Rapidly readjustable automated production pays off in a reasonable time only if it works in two or three shifts. Automated production is serviced by workers only in the first shift; in the second and third shifts, it operates practically without service personnel. During the day shift, automated production operates in the mode of adjustment and preparation for work (picking and incoming control of workpieces to be processed, adjustment, condition monitoring and assembly of cutting tools, checking and adjusting control programs, condition monitoring, equipment maintenance, etc.); in the evening and night shifts, production works automatically under the supervision of on-duty personnel. The principle of such work is embedded in flexible production systems of varying complexity.
Machine System (SS) is a set of machine tools and auxiliary equipment that is used to process one or more identical workpieces, as well as workpieces of a wide range based on one or several different route technological processes.
Automated or automatic SS- a set of interacting machines and auxiliary equipment, united by automated or automatic subsystems: transport and storage, instrumentation and control. Automated SS function with the participation of a person in the implementation of some production functions, and automatic SS - without human participation or with minimal participation.
Depending on the type of production, SS is divided into special (non-reconfigurable), specialized (reconfigurable) and universal (flexible).
To special SS includes reconfigurable automatic lines (AL) for processing blanks of 1-2 items. The annual program of production of parts of the same name is more than 75,000 pcs. on one route technological process. The flow of processed workpieces follows the "machine - machine" scheme. The structure of special SS, which is the main means of automation of large-scale and mass production, includes various combinations of special, specialized systems and other mechanisms. Due to the presence of branched transport systems and intermediate positions for the accumulation of parts, setting and Maintenance individual machines in AL can be performed without a significant reduction in product output. In the manufacture of small-sized and homogeneous parts, rotary lines are the most productive, in which the processes of processing and transporting parts are combined in time.
To specialized SS include reconfigurable AL (PAL), which include universal and specialized machines, transport and storage systems and other mechanisms. PAL perform processing of blanks from 2 to 15 items. Universal SS includes only universal machines; the flow of workpieces being processed according to the scheme "machine - warehouse - machine". This group includes SS (HMS), which are used to process a wide range of workpieces with different technological routes.
GPS- a set of various combinations of CNC equipment, robotic technological complexes (RTC), flexible production modules (FPM), individual units of technological equipment and systems for ensuring their functioning in automatic mode for a given time interval. The GPS provides for automated changeover in the manufacture of products of arbitrary nomenclature within the established limits of values and their characteristics.
Robotic technological complex (RTK)- a set of a unit of technological equipment, industrial robots (IR) and equipment. The RTK functions autonomously and performs multiple cycles. The complex is equipped with devices for accumulation, orientation, piece-by-piece issuance of production objects and other devices that ensure the functioning of the RTK. PR can be used as technological equipment. The RTK designed to work in the GPS should be provided with automated readjustment and the possibility of embedding in the system.
Flexible Manufacturing Module (FPM)- a unit of technological equipment with program management for the production of products of an arbitrary range within the established limits of the values of their characteristics. The GPM, which functions autonomously and automatically performs all the functions associated with the manufacture of products, can be integrated into the GPS.
Robotic production line (RTL)- a set of RTCs interconnected by vehicles and a control system, or several units of technological equipment serviced by one or more PRs to perform operations in the applied technological sequence.
System for ensuring the functioning (SOF) of the GPS- a set of interconnected automatic systems that provide product design, technological preparation of production, control of the FMS, automatic movement of production facilities and technological equipment. in SOF in general case includes: automated transport and storage system (ATSS); automated instrumentation system (ASIO); automated control system (ACS); automated waste disposal system (AWS); automated process control system (APCS); automated system of scientific research (ASNI); computer-aided design system (CAD); automated system for technological preparation of production (ASTPP); automated control system (ACS) and a number of others.
According to the organizational features of the State Border Service subdivided into a flexible automated line (GAL), a flexible automated section (GAU), a flexible automated workshop (GAC) and a flexible automated plant (GAZ).
Currently, the production requires a rapid transition from the manufacture of one type of product to another. This property is called mobility or flexibility. There are two types of flexibility: with unscheduled changes in the production task; with a planned change in the task or the range of products.
The first type of flexibility is typical for a short-term failure of individual machines. In this case, tasks are performed by transferring workpieces to similar machines from among interchangeable ones, i.e., complete specialization of equipment is excluded.
With this form of flexibility, it is possible to somewhat expand the number of workpieces processed on each machine and ensure timely delivery of finished parts. In this case, the specified productivity is achieved by optimizing the structure and composition of the productive system for a different (by type, number and labor intensity), but clearly limited range of products. This form of flexibility can be quantified as the number of workpiece items that can be processed on a given SS.
The second type of flexibility of the equipment of the complex is to efficiently manufacture parts of both a given nomenclature with a variable sequence of their launch into production, and a modified nomenclature.
The concept of production system flexibility refers to two main areas: production (management and organization); production planning (technology, structure, capacity).
Technological flexibility is defined as versatility, i.e., the ability to perform several technological tasks on existing SS, such as mobility - the ability of the complex to perform various technological tasks with little time spent on readjustment.
Structural flexibility is characterized by freedom in choosing the sequence of processing operations. In this case, a contradiction arises between the desire for the maximum load of equipment and the desire for a minimum production cycle.
The desire to reduce the production cycle leads to the construction of a product-oriented production structure (subject principle). In this case, the machines are arranged in the sequence of the technological process of manufacturing products.
The desire to increase the load of equipment leads to the construction of a production structure focused on the means of production (technological principle). In this case, the failure of one SS is easily compensated by loading similar, neighboring SSs. Such a structure requires intermediate storage of production objects.
The flexibility of the production capacity of the system is characterized by its ability to expand, compensatory ability, storage capacity. The ability to expand is determined by the quantitative reserves of the system's production capacity (change in shifts, increase in output). The compensatory possibility lies in the ability of the system to equalize the quantitative shifts in the production program. Cumulative capacity - the ability of the system to equalize quantitative fluctuations in the structure of orders due to the medium-term time shift in the start of work. The smaller the storage capacity of the system, the more flexible the production.
Depending on the type of production, the timing of the replacement of manufactured products, technical, economic and social requirements, all main areas of automation are used in mechanical engineering. GPS machining are created for serial, and in some cases for mass production.
Automatic lines.
Automatic line (AL) called a system of automatically operating machine tools connected by transporting devices and having a single control device. AL carries out a given sequence of a number of technological operations without the participation of operators. Periodic control of the equipment and its adjustment is performed by the adjuster. Loading blanks and unloading finished parts is carried out by the operator or PR. The number of equipment installed in AL usually does not exceed 12 units.
AL is created on the basis of aggregate machines (AS). The design of AL and AU is based on the principle of aggregation, which makes it possible to reduce the time for designing and manufacturing the specified equipment. The arrangement of AS and AL and unified nodes increases their reliability, as there is a continuous improvement of unified nodes.
Workpieces processed on the AL must be technologically advanced, have a stable design, and provide a minimum number of installations. The operations of the technological process must be synchronized in time to fulfill a given cycle of product release. This is carried out by using a combined tool, coordinating cutting conditions for individual operations and other measures.
Technological unit1 AL(picture) is a machine that performs one or more completed parts of the technological process, except for the accumulation and transportation of workpieces 3. transport unit 2 AL is a machine that performs interoperational transport operations of the technological process.
Storage device4 touched AL (Fig. in)- a device for receiving, storing and issuing an interoperational backlog located between two machines or AL sections.
structural construction of automatic lines
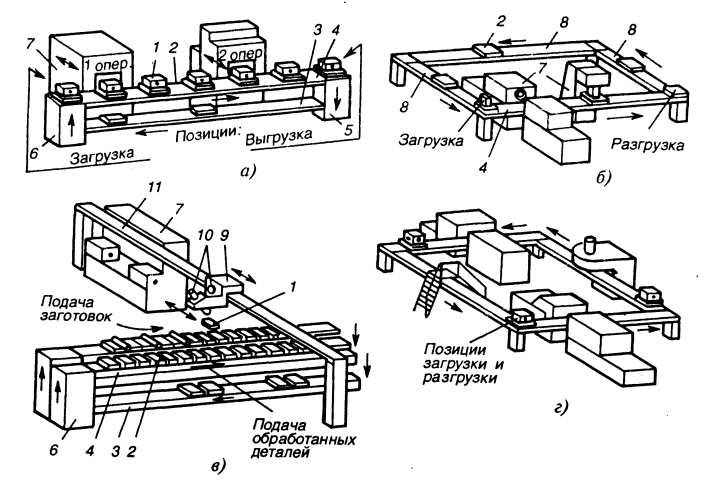
Plot AL is its part, connected to the rest of the technological equipment by means of a storage device or a transport device with a container for blanks and semi-finished products (Fig. in).One-subject(single item) AL is a line in which blanks of the same standard size and name are processed (Fig. a).Multidisciplinary(multi-product) AL - a line in which workpieces of many items are processed simultaneously or different sizes of the same name (Fig. b).
The connection between the technological units of the AL is determined by the nature traffic movements between their processing areas and the presence or the absence of interoperational backlogs between them. In AL with these backlogs are absent by a rigid connection, and if one afegate fails, the entire AL stops (Fig. a). In AL with flexible connection between individual units and sections have interoperational backlogs, placed in storage tanks or in the transport system, there is no rigid coordination in the time of operation of the units: failure of any unit or section does not cause downtime of the others until as long as the stock of blanks has not been exhausted or the container has not been filled for finished parts (Fig. c - g).
AL classification. The structure and design of the AL is determined by its purpose, adopted equipment and specific operating conditions. AL is classified according to various criteria:
By type of technological equipment AL are divided into the following groups: 1. From modular machines; 2. From modernized universal machines, semi-automatic machines and automatic machines general purpose(for processing shafts, disks, gears, etc.); 3. From specialized and special machines made only for this AL; four . From CNC machines and a transport system with PU, which are controlled by a single UE.
According to the type of transport systems and the method of transferring workpieces from machine to machine, AL is distinguished:
1. With end-to-end transportation through the working area (Fig. b-d). They are mainly used for processing body blanks at the AU; 2. With top transport (fig. in). Are applied to processing of preparations of gear wheels, flanges, shaft and other details; 3. With lateral (frontal) transportation (Fig. b). They are used in the processing of blanks for crankshafts and camshafts, sleeves, large wheels; 4. With combined transportation (Fig. h); 5. With rotary transportation used in rotary AL, in which the processes of processing and transportation of workpieces are partially
or completely coincide in time.
According to the type of equipment location, they are distinguished closed (Fig. h) and open (Fig. a - g) AL. In closed AL, loading of blanks and removal of finished parts is carried out in one place, which is convenient, but access to the units is difficult. Therefore, non-closed ALs with straight, L-shaped, U-shaped and other arrangements of equipment are most common.
According to the structural construction, AL is distinguished:
1. With a serial arrangement of equipment (Fig. a); 2. With a parallel-serial arrangement (Fig. e) when several machines work in the AL sections, performing the same operation in parallel, and the sections in the AL work in series.
According to the type of workpieces being processed, AL is distinguished for processing body blanks, blanks of rotation bodies, etc.
Reconfiguration possible AL is divided into reconfigurable and
non-adjustable. At the first, the equipment is periodically changed from processing one type of workpiece to another, slightly different in size and geometric shape.
In order to reduce downtime, long ALs are divided into several independently functioning sections (Fig. d), between which drives are installed. In the AL of high-performance machines, storage devices can be installed after each machine (Fig. in). The expediency of installing the drive and its capacity is determined on the basis of technical and economic calculations. Accumulators reduce AL downtime, but increase its cost. The storage capacity is usually chosen to provide 15-120 minutes of non-failure operation of the AL, based on the productivity of adjacent machines or sections.
The storage can be a special device in the form of a store, a bunker, or the transport system itself. 2 (rice. d- and). To simplify the installation and fastening of non-rigid blanks of housings and other parts of complex configuration, special satellite devices are used. , which ensure the preservation of the orientation of the workpieces located on them during transportation and processing, during which the satellite is automatically fixed and fixed in the working positions of the AL.
In such ALs, the return of satellites to their working position after removal
of the finished part / can be performed in various ways: 1. In the vertical plane by the return conveyor 3 (Fig. a), located above the working conveyor 4. 6 4 to the machine 7 and back is produced by the loading device; 2. In the horizontal plane behind the machines with return conveyors 8 (Fig. b), located at the same height as the working conveyor 4. The movement of the satellite in the vertical plane is carried out by a lift 6 and lowerer 5. Feeding the pallet with the workpiece from the working conveyor 4 to the machine 7 and back is produced by the loading device; 3. In the horizontal plane behind the machines, return conveyors 8 (Fig. b), located at the same height as the working conveyor 4. There are AL, in which the return conveyor 3 is located above the working conveyor. In this case, the transfer conveyors are made inclined. 4. Horizontal return conveyors 3 and devices 6 for satellite transmission 2 between conveyors 3 and 4 (rice. in). According to the working positions of the AL, where there is no return of unloaded satellites (Fig. G).
schemes for working with devices-satellites
In a number of ALs designed for processing workpieces of a very complex shape (for example, crankshafts or eccentric shafts), satellites 2 are used only for transporting workpieces 1 between machines 7. In this case, the workpiece is removed from the satellite and transferred to the machine for processing by a portal manipulator that moves along the traverse 11 carriage 9 with two grips 10 for transporting workpieces and parts (Fig. in)
Rotary AL. In terms of structure, rotary ALs used in mass production have significant differences from ALs assembled from AU and other machine tools connected by a transport system. Rotary AL are completed from rotary automatic machines in which all technological operations are carried out in the process of continuous transport movement of the processed workpiece together with the tool. The trajectory of the transport movement of the manufactured part on all machines is provided by transport rotors. The high productivity of rotary AL is ensured by the number of positions of rotary machines and the rotational speed of the rotors.

rotary automatic line
Rotary AL consists of multi-spindle rotary automatic machines 1, which are interconnected by transport rotors 4, which, by means of tongs, load workpieces onto the first machine, transfer them between machines and unload finished parts. In a rotary machine, workpieces are transferred by pushers 2 from tongs to chucks 6 work spindles. The spindles, together with calipers 5 and the cutting tool attached to them, are mounted on a drum that slowly rotates on a central fixed column 8. The calipers receive the necessary movement through the rods from the fixed copier 7.
The use of AL reduces the cost of manufacturing parts, reduces the number of workers and the space occupied. Compared to separately operating NPPs, ALs assembled from them are several times more efficient: the volume of work in progress is reduced. In AL, to perform various operations for loading blanks, unloading finished parts, for interoperational storage, orientation and movement in the manufacturing process, various automatic loading, orienting, turning, transport devices, control mechanisms, and chip removal devices are used.
![]()
diagrams of automatic loading devices
Boot devices AL. According to the location, automatic loading devices are divided into built-in ones, which are integral parts of the machines and operate from a common drive (Fig. a), and on the AL located near the machines and between the sections, operating from an independent drive (Fig. b). According to the nature of the feed of the workpieces, the loading devices are divided into continuous devices (Fig. G) and cyclic action (Fig. in). They are mechanical, hydraulic or pneumatic driven.

Loading devices carry out the accumulation and issuance of the workpiece, semi-finished products or products in an oriented position and consist of a container and target mechanisms: capture; cutter; ejector; drive. Depending on the method of accumulation, the devices are divided into bunker, store and stack. In bunker devices, the production objects in the tank are in an unoriented position. By means of a special mechanism, they are oriented and issued from the bunker device (Fig. a, e - h). In store devices, production objects are placed in a container in an oriented position in one row (Fig. b, c) and in stacking devices - in several rows or layers (Fig. in, d, f).
By design, loading devices are divided into chain, friction, tubular, disk and tray. Workpieces can move in a hopper or magazine under the action of a chain, a feed disc, a pusher of rotating brushes of a vibrating mechanism and other mechanisms, as well as under the influence of gravitational forces (mass). The movement of workpieces can be intermittent and continuous.
Transport systems AL. Systems are classified according to various criteria:
1. According to the nature of the transport connection between the technological equipment of the AL, transport systems are distinguished as synchronous (rigid) and non-synchronous (flexible). In AL from AS, for the manufacture of body parts, transport systems with a rigid connection of technological equipment are most often used, which include conveyors with retractable pawls or rotating flanges. . To reduce equipment downtime in AL with rigid connection, conveyors with control pawls are used (Fig. e ), performing a small inter-operational accumulation of production objects between machines. In AL with flexible connection, which are used mainly for processing workpieces of bodies of revolution, transport systems are most often used.
in the form of chain, roller, screw, vibration conveyors (Fig. c, 3, g, i, e), lifts (Fig. to, l), trays (Fig. G). With flexible communication, there is no coordination of movement of production objects in the AL.
2. According to the nature of the movement of production objects in the AL, cyclic transport devices are distinguished (Fig. a, b, e, l) and continuous action (217, a, e, g, h, i, j).
3. According to the method of moving production objects, transport systems are divided into systems with movement under the action of gravity (Fig. d), with forced movement (Fig. a - h, k, l) and With moving in a mixed way.
4. According to the intended purpose, transport systems are divided into systems for inter-operational and inter-machine maintenance (Fig. i, d, etc.) and for waste disposal - chips (Fig. and).
Mechanisms for changing the orientation of the AL rotate the workpieces by 90 and 180°. To change the orientation of body blanks, drums are used to rotate around a horizontal axis, tables to rotate around an inclined axis. A change in the orientation of the blanks of bodies of revolution occurs when they are transported in trays.
AL control systems. The execution of a given cycle of operation of individual built-in pieces of equipment in the AL is carried out by automatic control systems. The specified sequence of operation of the AL equipment is ensured by the timely supply of unambiguous commands to the drive and executive bodies of machine tools and mechanisms. In the general case, the AL control system consists of three types of devices that serve to receive information, convert and transmit it, and use information by additional mechanisms. The AL control system includes a number of subsystems: blocking, control of the size of workpieces being processed, signaling, etc. The tasks of the AL control system include automatically finding the location of the failure and determining its nature, obtaining information for managing the operation of equipment, data on the performance of the AL, accounting and analysis of downtime, control of the state of the cutting tool.
To control the AL, track control based on relay-contact equipment is often used. AL control systems are also built on the basis of command devices - programmable controllers (PC), which are small control machines made on the elements of computer technology. Two types of PCs are produced: 1. Small PC-PCM, which serve only to control the cycle of equipment operation; 2. Large PC-PCBs providing cycle control and equipment maintenance organization.
basis of industrial production. The release of essential goods, foodstuffs, medicines and other products depends on technological equipment. Enterprises are interested in buying high-quality, easily integrated and intuitive technical equipment for production.
The equipment can be divided into ready-made production lines, the installation of which on a turnkey basis solves the problem of releasing new products or changing the range, and industrial units, machines, pipelines and individual devices that allow upgrading, improving or updating the existing production line.
Buy technological equipment:
|
pharmaceutical industry. Reactors, separation systems, component mixers, drying, granulating, tableting and homogenizing machines are equipment designed for the production of products. For packaging, bottling, scattering, capping and checking, complete lines are provided that guarantee the presentation of the finished product. |
Food industry. As in the pharmaceutical industry, in this industry the main role is given to materials for the manufacture of components, reactor vessels and pumping devices that come into contact with the food product. Technological equipment for food enterprises is made of AISI 304 sanitary steel, which guarantees the absence of corrosion and oxidation. Pasteurizers, heat exchangers, emulsifiers, reactors and mixers allow you to expand the product line and increase the productivity of companies. |
|
Chemical industry. A branch of production engaged in the processing of natural raw materials and obtaining a chemical product suitable for further use in industry. This is the production of solvents, plastics, polyethylene or organic compounds. During installation, the possibility of a fire or explosion of process equipment due to work with hazardous reagents must be taken into account. Accordingly, technological lines are made of hard chemical steel AISI 316 resistant to aggressive environments. Explosive sensors are installed on the equipment, and the device of the machines is adapted to work with hazardous vapors and gases. |
Auxiliary equipment. Manifolds, trolleys, vacuum loading systems, heat exchangers, scrubbers, gate valves, viewing windows, agitators and other technical equipment that can be removed from the line, added or changed if necessary. According to SNiP, platforms, fencing or protection are provided for the main equipment - a reactor, a distillation column or a CIP station, and the installation of auxiliary machines has no building restrictions. |
Why is it profitable to order from us?
Our company has been actively working in the market of technological equipment and laboratory equipment for more than 10 years. Same way:
- We have the ability to independently prepare or implement on our own finished project without intermediaries and foreign specialists.
- Our specialists are trained at the enterprises of manufacturers, have certificates and can carry out a complete assembly, installation, start-up of lines and technical equipment purchased from us.
- We work directly with manufacturers of process equipment, we specialize in engineering and design of production.
All this reduces the cost of installation and preparation of production lines.
What guarantees do we provide to customers?
Buying from us, you can count on free delivery and installation of technical means. We guarantee:
- Service support for 5 years.
- Availability of documentation in Russian.
- Familiarization of your personnel with the operation of technological equipment.
Technological equipment is the basis of any catering establishment or food industry enterprise. As you know, high-quality modern technology is the key to high production efficiency and, accordingly, prompt execution of orders. If you are going to open your own restaurant, cafe, snack bar or confectionery, then the technological equipment of enterprises can help you a lot. As a rule, these are complex systems designed for a particular type of production. The company "Prof-Master" has rich experience in the sale and maintenance of such lines, so we are always ready to provide you with valuable advice on choosing the necessary equipment.
Installation of technological equipment
Installation of technological equipment is carried out by us at the highest and professional level, this can always be confirmed by our regular customers. Moreover, we do not just help customers choose and correctly install the main technological equipment. Also, our specialists are ready to provide you with design services for industrial, commercial or any other premises with the competent placement of the necessary equipment there.
Production of technological equipment
The company "Prof-Master" is a full-cycle enterprise, so the production of technological equipment occupies an important place in the overall spectrum of our activities. Any technological equipment of enterprises placed in our catalog is a reliable and durable equipment that perfectly copes with the most intensive work schedule.
Repair of technological equipment
Naturally, even the most reliable technological equipment can break down sooner or later, especially with active round-the-clock use. We took care of this problem by providing our customers with such an important service as the prompt fixing of equipment problems. The staff of our company consists of experienced and qualified specialists who are willing to do everything possible to quickly and efficiently return your equipment to operation, as well as to carry out the installation of technological equipment.
Technological equipment of enterprises
"Prof-Master" offers you to purchase the best basic technological equipment - for bars, canteens, restaurants and cafes, bakery, meat processing equipment, etc. We have established the production of technological equipment at the highest level, so we provide customers with guarantees for the quality of our products. And in case of rare, but possible malfunctions, such a service as repair and maintenance of equipment will always come to your aid.



