The device of a fluorescent lamp is a choke. What is a starter for fluorescent lamps
Every day the popularity of lamps daylight as a source of illumination only grows. This is due to their high duration of work and high-quality glow.
Fluorescent lamps do not work directly from a 220 volt network. For their operation, a special unit is required, called ballasts (ballasts). The design of the unit includes three main elements, which include: a choke (core inductor), a smoothing capacitor and a starter. Here's how we'll talk about the latest device today.
Greetings to all my friends on the website "Electrician in the House", I recently had to look for the cause of a malfunction of luminaires with fluorescent lamps, which consisted in a malfunction of the control gear element, so the next issue will be devoted specifically to fluorescent lamp starter. We will analyze its purpose, device and functions.
Fluorescent lamp starter device
The design of this element is quite simple. Each model released by a certain manufacturer has its own specifications. This should be taken into account when choosing lamps. The starter is a glass container with an inert gas inside. It can be a mixture of helium and hydrogen or neon. Fixed metal electrodes are soldered into the balloon. Their conclusions pass through the plinths.

The cylinder is located inside a plastic or metal case with an opening at the top. The most popular body material is plastic. deal with high temperature special impregnation allows such a case. Any has only two legs (contact).

If you remove the structure from the body, you can see the flask itself. It is also seen that some element is connected in parallel to the electrodes of the bulb - this is a capacitor. Its capacity is about 0.003-0.1 microfarads. The capacitor is designed to perform two functions at once:
- - fights radio interference that occurs due to the contact of the electrodes by reducing their level.
- - participates in the process of ignition of the lamp.



The capacitor reduces the voltage pulse, which is formed when the electrodes open, and increases its duration.

Due parallel connection with electrodes, the capacitor reduces the likelihood of their welding (sticking). Similar phenomenon can occur during the opening of the electrodes due to the formation of an electric arc. The capacitor extinguishes the arc in the shortest possible time.
Why do you need a starter in fluorescent lamps
This element is the main one in the design fluorescent lamps. Without it, electromagnetic ballasts will not be able to function. The main purpose of the starter is to start the mechanism and ignite the inert gas in the gas discharge flask. The starter works like a switch - it opens and closes the electrical circuit.

Starter installation is dictated by the need to perform two important functions:
- - circuit closure. Allows you to heat the lamp electrodes, thereby facilitating the ignition process;
- - chain break. Occurs immediately after heating the electrodes. As a result of the opening, an increased voltage pulse is formed, which is the cause of the breakdown of the gas gap of the flask.
The inductor plays the role of a stabilizer and a transformer. It maintains the required current of the lamp filaments, creates a voltage pulse necessary for the breakdown of the lamp and stabilizes the arcing process.
How does a fluorescent lamp work
When the circuit is connected to electrical circuit all voltage is applied to . In the normal position, the electrodes are in the open position. A glow discharge begins to appear on the starter electrodes. A small current (30-50 mA) passes through the circuit.
This current is sufficient to heat the electrodes. When a certain temperature is reached, they begin to bend and close the circuit. After the contacts close, the glow discharge stops.
Let's take a look at the main parts of the lamp itself.

When the circuit is closed (through the starter electrodes), a current begins to flow through it, the value of which is 1.5 times greater than the rated current of the lamp. The amount of current is limited by the resistance of the inductor. The lamp and starter electrodes cannot perform this function, since the former have insufficient resistance, and the latter are in a closed position.

The heating of the electrodes up to 8000C occurs within 1-2 seconds. As a result of an increase in temperature, an increase in electron emission occurs, which facilitates the simplification of the process of breakdown of the gas gap. There is no discharge in the starter electrodes and they gradually cool down.


After the starter cools down, the electrodes open, taking their original position, and break the circuit. An open circuit is accompanied by the appearance of self-inductance EMF in the inductor. Its value is directly proportional to the inductance of the inductor and the rate of change in the magnitude of the current when the circuit is broken.


The emergence of self-induction EMF is the reason for the creation increased voltage value of 800-1000 V, which in the form of a pulse is applied to the lamp. Its electrodes are preheated and it is ready to be ignited. At this moment, a breakdown occurs and the glow begins.
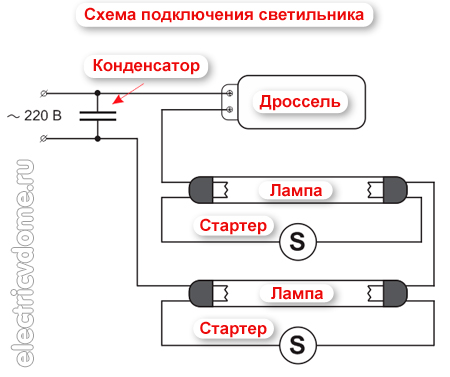
A voltage is now applied to the starter, which is connected in parallel with the lamp, the value of which is two times lower than the mains voltage. It is not able to break through a neon light bulb, therefore, its ignition is no longer carried out. The entire ignition cycle lasts no more than 10 seconds.
How to test a fluorescent lamp starter
This question very often arises before specialists in the process of repairing fluorescent lamps. Although the detail is small, it can cause serious problems.
You can identify a breakdown of the starter by replacing it with a serviceable one, if one is at hand. But what to do in cases where there are no more lamps nearby, and the nearest specialized store is more than one kilometer away? How to test a fluorescent lamp starter at home? You can check the performance of this device according to the standard scheme.
In series with the starter, an ordinary lamp with an incandescent filament is connected to the network. It is desirable that its power does not exceed 40 watts.
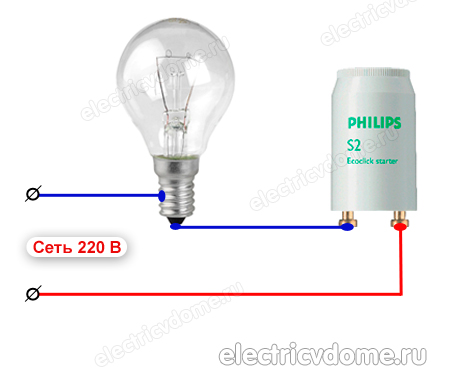
It is not difficult to assemble such a scheme. If the starter is in good condition, the lamp will burn and periodically go out for a moment. This process will be accompanied by characteristic clicks that indicate the work of contacts. If the light does not light or glows constantly (without blinking), then the starter may be damaged.
In this simple way, you can check starter for fluorescent lamps. Although, to tell the truth, I have not yet seen them tested anywhere in production. This is probably due to their low cost. It usually happens like if the lamp does not work or starts flashing, just change the starter to a new one, it turned out to eliminate the cause well, no, the problem is different.
Why is the fluorescent lamp flashing
Dear friends, you have probably noticed that luminaires with fluorescent lamps begin to blink over time. And this is not due to the use of backlit switches that cause energy-saving lamps to flicker.
During the operation of the lamps, the operating voltage of the ignition of the glow discharge in the starter drops. This is the reason why the starter will operate even when the lamp is on. After opening the electrodes, the glow is restored. The human eye perceives this as a flashing process. A similar phenomenon is the cause of damage to the lamp and failure of the inductor as a result of its overheating.

Therefore, if you notice a constant flashing of the lamp, you must replace the starter with a new one. In 90% of cases, it is he who is the cause of this phenomenon.
If flashing occurs, it is necessary to replace the starter as soon as possible, since in this mode of operation the resource of the components of the lamp will decrease and the bulb or choke may already fail.
The throttle is characterized by certain parameters. Since it is sometimes an essentially non-linear element, its parameters are not unique. They can be divided into two groups: nominal, characterizing the inductor as an independent product, and calculated, characterizing it as an element of a specific circuit.
The nominal parameters of the throttle should be found or determined under strictly specified conditions. We will determine them with a sinusoidal voltage at the terminals of the winding, indicating the magnitude of the voltage and frequency.
Ratings must fully guarantee the service life of the inductor and its reliable operation in a particular circuit. Although the nominal parameters of the inductor do not determine the electrical regime in the circuit in which it can be included, however, they fully characterize the inductor as a product and, at the same time, are associated with its design parameters.
The main nominal parameters of the throttle, which must be indicated in its passport, are as follows:
Current frequency f, Hz.
Nominal (maximum allowable) value of the inductor current I, a.
Choke inductance at rated
Winding resistance of the "cold" choke
Choke core loss
Throttle weight G, kg.
Other nominal parameters of the inductor are: maximum permissible value of the harmonic coefficient in the rated current curve maximum permissible overheating of the inductor winding deg (at a certain temperature environment); overall power of the throttle and its reactive power quality factor D; technical and economic indicator of the inductor screening factor of the inductor .
Let us explain the parameters and D; throttle parameters will be discussed in § 1.5 and 1.6.
1. Nominal choke inductance
The rated inductance of the inductor is determined by the expression
![]()
where f and - frequency and effective value of the sinusoidal voltage applied to the inductor winding;
I - effective value of the rated current;
Phase angle between voltage and equivalent current sinusoid.
For small values of the ohmic resistance of the inductor winding and losses in its core, the nominal inductance can be approximately determined by the formula
![]()
The value of the inductance (1.1) of the non-linear choke is not constant, but depends on the magnitude of the applied voltage and current frequency. Therefore, the choke as an independent product must be characterized precisely by the value of its nominal inductance, measured under completely defined conditions and indicated in the passport. Only such inductance is a characteristic parameter of the inductor. The value of the inductance of the inductor is recommended to be indicated in the passport indicating in the form of indices the effective value of the sinusoidal voltage at which it is determined, for example, etc.
2. Harmonic rated current curve
Due to the non-linearity of the inductor, due to the properties of its ferromagnetic core, the current in the winding is not sinusoidal. The current curve, even with a sinusoidal voltage, has a distorted, pointed shape (Fig. 1.3). The presence of higher current harmonics can in some cases have a detrimental effect on the operation of certain devices, while in others this property of chokes is beneficial.
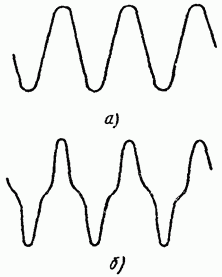
Rice. 1.3. Oscillograms of voltage at the terminals of the inductor (a) and current in the winding (b).
To quantify the distortion of the current curve at a non-sinusoidal voltage, the coefficient of non-linear distortion is used. It is defined as the ratio of the square root of the sum of the squared amplitudes of all harmonics to the amplitude of the useful component of the entire spectrum of harmonics.
With a sinusoidal voltage, the distortion factor is called the harmonic coefficient. It is the ratio of the square root of the sum of the squares of the effective values of all harmonics, with the exception of the useful harmonic, to the effective value of the useful harmonic. If the fundamental, first, harmonic is useful, then the harmonic coefficient
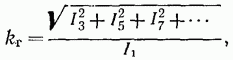
where is the effective value of the harmonic current.
If not the first, but some harmonic (or the sum of harmonics) is useful, then the numerator of the fraction should contain the root mean square value of all harmonics, with the exception of , and the denominator should contain the effective value of the corresponding harmonic.
The harmonic coefficient is measured using special instruments at the rated current of the inductor. Typically, chokes are designed with a value
3. Voltage waveform factor
The voltage applied to the clamps is estimated by the curve shape factor; it is understood as the ratio
![]()
where are the effective and average voltage values, respectively.
4. Throttle power
Two choke powers should be distinguished - the overall power and the calculated reactive power Q. The overall choke power is understood as the value
![]()
under the calculated reactive power - the value
![]()
where is the current waveform distortion factor.
The value determines the dimensions of the inductor core. Knowing the required overall power of the designed inductor, it is possible to choose a normalized core for it. Note that for conventional chokes, the values and Q differ slightly. Rated values and Q should be measured at nominal voltage and frequency.
5. Choke quality factor and loss angle
These parameters characterize the quality of the inductor in terms of losses in it. The higher the quality factor and the smaller the loss angle, the better the quality of the inductor. Note, however, that the greater the quality factor of the inductor, the greater its size and weight.
The quality factor of the inductor is equal to the ratio of the reactive power of the inductor to the sum of losses in its core and winding:
It is convenient to introduce the concept of partial quality factors or, in other words, about the quality factor in the core and the quality factor in the winding
![]()
The quality factors and are interconnected by the following relation.
Fluorescent lamps are now at the peak of popularity. They are used in hospitals, schools, kindergartens and other public institutions. Fluorescent lamps have many advantages over conventional lamps:
The device of starters and chokes and the principle of their operation
Starter consists of a small glass flask filled with gas. The flask is placed inside a metal or plastic case. There are two electrodes on the underside of the starter that come into direct contact with the lamp wires during operation. There is sometimes a window on top of the starter. Starters often fail, but they are very easy to replace because they are removable.
Throttle is a coil in a metal shell. The power is set to the same as the lamp itself. Without a choke, the lamp will not work. The inductor ignites the mercury vapor in the lamp and limits the current supply. The inductor stabilizes the voltage in the network if it is higher than the nominal one.
The principle of operation of the starter and throttle is that one element (starter) starts the electrodes, and the throttle supports this work. When the current is turned on in the circuit, the starter is turned on first. It warms up the electrodes, the current supply to the device increases, the starter bimetallic plate heats up. After the electrodes have warmed up, the contact opens and the current is transferred to the inductor. For some time, the throttle accumulates voltage, the gas in the flask breaks through, and the lamp lights up.
During operation, the current is evenly distributed between the inductor and the lamp, which ensures stable operation even under conditions of increased voltage. The inductor does not consume energy for itself, it only accumulates it and converts it.
Without a starter, it is basically impossible to turn on a lamp using certain chokes. It just won't light up. Whereas during the further operation of the lamp, the starter is not needed. You can even pull it out if necessary and check it or replace it while the lamp is on. But the subsequent inclusion will require a starter. It is also possible to operate the lamp without a starter, directly. In this case, the lamp is ignited by a cold start, which significantly reduces its service life. The choke ensures the operation of the lamp. Without it, the lamp will not work.
Varieties of starters
- Glow starters - a lamp with bimetallic electrodes. Such starters are more often used, as they have a simplified design and a relatively short ignition time.
- Thermal starters - characterized by an increased ignition time, due to which the electrodes heat up longer, which has a positive effect on the operation of the lamp. However, such starters have a more complex structure, additionally consume energy for themselves, their connection scheme has a complex structure.
- semiconductor starters. Their work is built on the principle of a key. After heating the electrodes, the voltage opens, and a pulse occurs in the flask.
Varieties of chokes for fluorescent lamps
- Electromagnetic chokes - connected in series with the lamp. For the operation of the electromagnetic throttle, a starter is required, that is, a cold start will no longer be possible. They have a very big drawback - during operation, the lamp flickers.
- Electronic chokes are a relatively recent invention. Its incomparable advantage is a simplified wiring diagram, since a starter is not needed for its operation. Thanks to such chokes, the flickering of the lamp is reduced; at start-up, the lamp does not pulsate. Reduces lamp noise.
Which manufacturer is better?
 It is impossible to give a definite answer here. Each manufacturer of elements for the operation of fluorescent lamps is trying to produce good products. Therefore, the choice will be based on the results of personal experience or the experience of acquaintances. The most famous manufacturers of chokes are Chilisin, Luxe, Vossloh schwabe, Navigator, starters: perhaps the most popular manufacturer is Philips. Basically, chokes and starters come with a lamp. If you need to buy spare elements, or replace burned-out ones, you can choose one of these manufacturers.
It is impossible to give a definite answer here. Each manufacturer of elements for the operation of fluorescent lamps is trying to produce good products. Therefore, the choice will be based on the results of personal experience or the experience of acquaintances. The most famous manufacturers of chokes are Chilisin, Luxe, Vossloh schwabe, Navigator, starters: perhaps the most popular manufacturer is Philips. Basically, chokes and starters come with a lamp. If you need to buy spare elements, or replace burned-out ones, you can choose one of these manufacturers.
Service life of starters and chokes
According to the manufacturers, the starter must withstand at least 6,000 lamp starts. In this case, the operating range should be from + 5 ° C to + 55 ° C. Chokes under normal operating conditions should work for about 3 years. Again, it all depends on the manufacturer and the likelihood of getting a marriage.
How to choose a starter and choke
First you need to decide what type of launch you will have. If you use electronic throttles, then the starter will not be needed. When choosing electromagnetic chokes, you need to think about buying a starter, because without it the lamp will not burn.
- Choose a trusted manufacturer, do not chase cheapness.
- Take immediately with a margin - suddenly you come across a defective or poorly working part.
- If you do not understand anything about electricity, entrust this matter to professionals. Or consult with people who have had experience with fluorescent lamps.
How to replace the starter
Perhaps even a beginner can easily cope with this work. Sometimes it happens that the lamp burns for a while and goes out. So you need to check the starter. To replace the starter, you need to turn off the lamp and remove the cover. The damaged starter is pulled out of the lamp by turning it counterclockwise. To connect a new starter, just insert it into the grooves and turn it clockwise. That's all - the starter is firmly in place.
How to replace the throttle
Most craftsmen prefer to repair the choke, but this will require technical skills. Therefore, it is easier to replace the throttle. Before replacing the inductor, you need to turn off the electricity in the entire house, since simply turning off the lamp will not relieve the voltage on the lamp. After that, you can dismantle the failed throttle. We remove the fasteners and disconnect the wires through which the current goes to the lamp. Now it remains to connect the wires in the order in which they were connected initially, and put the throttle in its place.



