Forsythia dwarf planting and care. Types and varieties of forsythia. Forsythia: landing, care
Forsythia (Forsythia) is a plant from the Olive family.
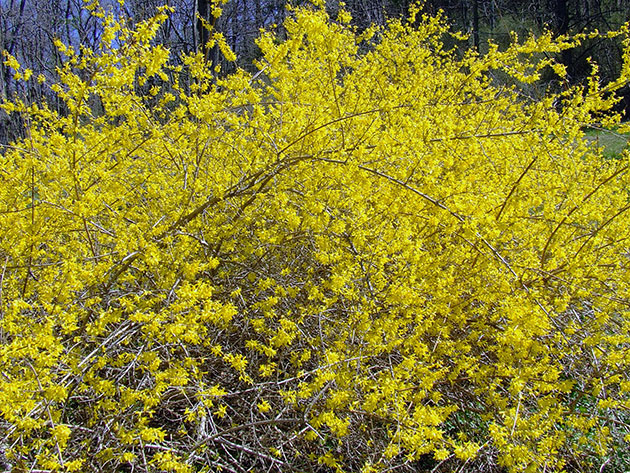
It is remarkable in that it begins to bloom in early spring, when other plants are just beginning to “wake up” after hibernation. Forsythia is especially popular in Europe - its bright yellow flowering bushes are an excellent decoration of city streets.
Forsythia got its name from the Scottish botanist W. Forsyth, who first brought it to Europe from China.
Due to the unpretentiousness of forsythia, it can be easily grown on suburban area, besides, it is decorative not only in spring. but also in autumn (its leaves acquire a golden or purple-purple color).
Bushes look especially impressive in the "company" with coniferous plants.
Types and varieties of forsythia
Among the species forms of forsythia, there are both dwarf forms and tall tree-like forms, reaching a height of up to 3 m, with straight and drooping branches, green, yellow or variegated foliage.
For cultivation in a temperate climate zone are suitable:
European Forsythia is one of the most winter-hardy species. It reaches a height of 2-3 m. It blooms with bright yellow bell-shaped flowers;
Forsythia Giralda - outwardly similar to European forsythia. The flowers have a twisted shape, abundantly cover the branches;
Forsythia ovoid is a small spreading shrub (up to 1.5 m high). The most spectacular varieties: Tetragold, Goldsauber, Dresdner Forfrueling, Spring Gloria;
Forsythia intermediate is an erect shrub with a spreading crown up to 3 m in height. The species is cold-resistant (with shelter it can withstand up to -25 ° C). Popular varieties: Golden Time, Fiesta, Fensiflora, Beatriks.
More thermophilic and suitable for cultivation only in the southern regions:
Forsythia greenest - shrub with powerful erect branches. It blooms with bright yellow flowers with a greenish tinge, arranged 1-3 in the axils of the leaves;
Forsythia drooping or hanging - a tree-like shrub, reaching up to 3 m in height. It has a high decorative effect: in autumn, its green foliage turns yellow or purple (depending on the variety).
Forsythia: Landing
This shrub can be planted both in early spring and in autumn (before the onset of stable frosts). Although the forsythia is shade-tolerant, it is better to choose a place for it sunny and protected from strong winds. Soils prefer alkaline, permeable. If the site has heavy clay soils, they are pre-drained and limed.
A landing hole is dug 0.5x0.5x0.6 m. At the bottom, drainage is made 15-20 cm thick from large pebbles, crushed stone or broken bricks. A layer of coarse sand (10 cm) is poured on it, and on top of it is a mixture of leafy soil and peat (2: 1). Add a glass of wood ash to each well. After that, bushes are planted and watered. If the planting was carried out in the fall, then the ground around the seedlings is mulched, and the plants themselves are covered with breathable material.
If forsythia is supposed to be planted in a row, then a distance of 1.5-2 m is left between the bushes.
Forsythia: growing methods (photo)
Forsythia is grown mainly vegetatively (by cuttings and layering).
In the middle climatic zone, forsythia is grown mainly by summer cuttings. After the flowering of the bush (in June - early July), green shoots with short internodes are selected and cut into cuttings of about 15 cm. The lower leaves are cut off, and the upper ones are shortened by half. For more reliable rooting, the cuttings are soaked in a solution of a root formation stimulator (Kornevin, heteroauxin) in accordance with the instructions for the preparation. Prepared cuttings are planted in perlite or sand in a greenhouse.
In autumn (October), lignified cuttings are rooted. They are planted immediately in the ground to such a depth that 2-3 buds remain above the surface. So that the seedlings do not freeze in winter, they must be covered with a layer of dry leaves. In the spring, the shelter is removed. By autumn, the surviving seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place.
Rooting forsythia cuttings
Forsythia is also grown by layering. To do this, after flowering, the lower young shoots are used. In several places of the branches, cuts are made from the underside, the shoots are bent to the ground and pinned. The incised places are sprinkled with soil and periodically moistened. The following spring, rooted shoots are separated from the mother bush and transplanted to a permanent place. Young plants will bloom in a year. https://mtdata.ru/u16/photo6D59/20770717304-0/original.jpg Reproduction of forsythia by layering
You can try to grow forsythia from seeds, you just have to be patient - the process takes a long time. In addition, the percentage of germination of forsythia seeds is quite low and amounts to 35-50%. Seeds are harvested after they are fully ripe in autumn. At the end of March, they are planted in boxes with nutrient soil, watered and placed in a greenhouse or covered with glass. Periodically, crops are ventilated and moistened. The first shoots appear in about a month. When the seedlings reach 4-5 cm in height, they dive into separate pots. The following year, young plants are planted in open ground. For the winter they are covered with a 15-20 cm layer of dry leaves. Bushes will bloom in 4-6 years.
Forsythia: care (photo)
Due to the unpretentiousness of forsythia, care for it is simple.
With a sufficient norm of precipitation in the summer, additional watering of the forsythia is not required. In a dry summer, this shrub is watered 1-2 times a month, 10 liters of water for each adult bush. Immediately after watering, the soil under the plants is loosened to a depth of 15-20 cm to improve air access to the root system.
The forsythia feeding schedule includes three stages:
In the spring (after the snow has melted), organic fertilizers (rotted manure or compost) are applied under the trunk circle, after which they are watered abundantly;
In April, mineral fertilizers are applied (60-70g/m2);
After flowering (at this time the plants begin to lay flower buds for the next year), the shrub is fed again with a complex mineral fertilizer (for example, Kemira-Universal, Agricola, Bona Forte, etc.).
On a note!Dry fertilizers are applied along the contour of the crown of the bush - this will ensure their maximum consumption by the root system of the plant.
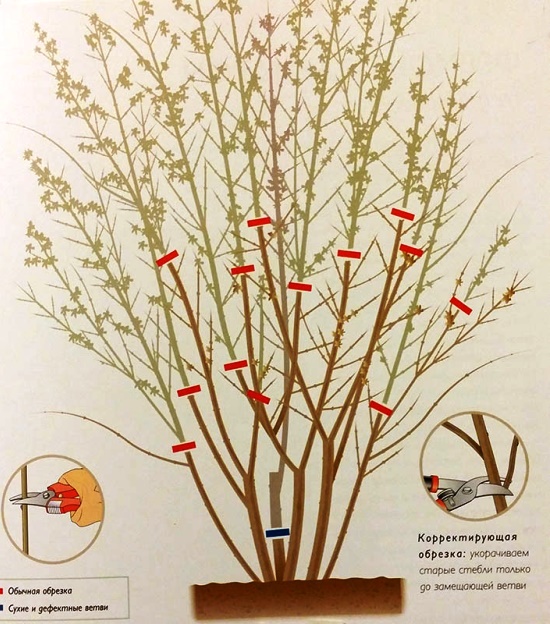
Pruning is an essential part of forsythia care. With the help of pruning, the bush is given the desired shape, the density and height of the crown are adjusted. Sanitary pruning is carried out annually. At the same time, broken, dried, frozen branches in winter are removed.
After the end of flowering in adult bushes, the branches are shortened by half.
Once every 3-5 years, anti-aging pruning is carried out on old bushes. In this case, all branches are cut to a height of 4-6 cm from ground level. This procedure activates the growth of new shoots.
Forsythia pruning
Forsythia is covered for the winter: the trunk circle is covered with dry leaves (10 cm layer), the branches are bent to the ground and covered with spruce branches.
Problems when cultivating forsythia
Forsythia is resistant to many diseases. Problems in its cultivation arise with improper care of it.
If the plant looks stunted and withered, despite abundant watering, then most likely there is a problem with the roots - they have rotted. Forsythia does not tolerate waterlogging. In this case, you should dig up a bush, inspect the root system: cut out rotten areas, and disinfect the remaining living roots in an antifungal drug (hamair, fundazol). The plant is transplanted to a new place.
Massive premature yellowing of the leaves of forsythia, and subsequently the wilting of the bush, indicates that the plant is affected by bacteriosis. At the same time, dark affected vessels are visible on the transverse section of the branch. It is impossible to save the plant - it must be uprooted and burned.
"Forsythia" (or "forsythia", named after the English botanist Forsyth) is an extremely unusual plant. It belongs to the genus of deciduous ornamental shrubs, and, moreover, is considered one of the earliest, primroses. This means that in early spring, against a gray background of nature that has not yet awakened, bare trees, forsythia bushes are already beginning to bloom and brighten up the landscape with their bright golden bell-shaped flowers.
Popular varieties of forsythia with photographs and their birthplace










It was first discovered in the South-Eastern part of Europe, namely: on the slopes of the mountains of the Balkan Peninsula.
This shrub is not very tall, about 2 m tall (12 years -3.5 m). Leaves up to 7 cm long. The flowers are golden yellow, have a slightly pronounced bell shape.
Origin: northern part of China.
Special characteristics: slightly curved branches, leaves up to 10 cm long, light yellow flowers, large, with slightly twisted openwork petals. Compared to European forsythia, this plant is more sensitive to low temperatures.

A photo. Forsythia ovoid
It comes from the deciduous forests of the Korean Peninsula. It is considered the most winter-hardy and drought-resistant, and therefore extremely popular in Central Russia, since it is possible to grow it without shelter.
Varieties and their features:
- "Melisa" (dwarf and very compact crown)
- 'Tetragold' (dark yellow flowers)
- 'Spring Glory' (longest flowering period, color varies from yellow to crimson depending on flowering time)
The wild hanging forsythia is still found in the Northern and Central regions of China.
Branches arched, drooping. The flowers are golden yellow, small, growing in bunches along the shoots.
- motley (leaves with a golden tint);
- purple stem;
- deceptive;
- Fortune (dark yellow flowers);
- Siebold;

A photo. Forsythia greenest
Origin: Eastern China. Wild forsythia loves the slopes of the mountains and covers them with whole thickets.
Features: very dark, long (up to 15 cm long), serrated, oblong leaves. The flowers may also have a greenish sheen.
Forsythia intermediate is a hybrid between dark green and drooping. It is characterized by a wide choice of various decorative forms. Here are some of them:
- Fiesta
- "Beatrix Farrand"
- "Lindwood" (formed as a standard plant)
- Variegata
It should be noted that there is another species - Forsythia Snow, or Abeliophyllum. Unfortunately, this species is endangered, listed in the Red Book and is extremely rare.
Features of growing forsythia in open ground
It is known that forsythia is extremely popular in the landscaping of European cities. It can often be found on the streets and in parks. This is due not only to the attractive appearance of the plant, but also to the fact that it is unpretentious and undemanding. Caring for forsythia does not require special gardening skills and will not cause trouble even for the inexperienced.
planting season
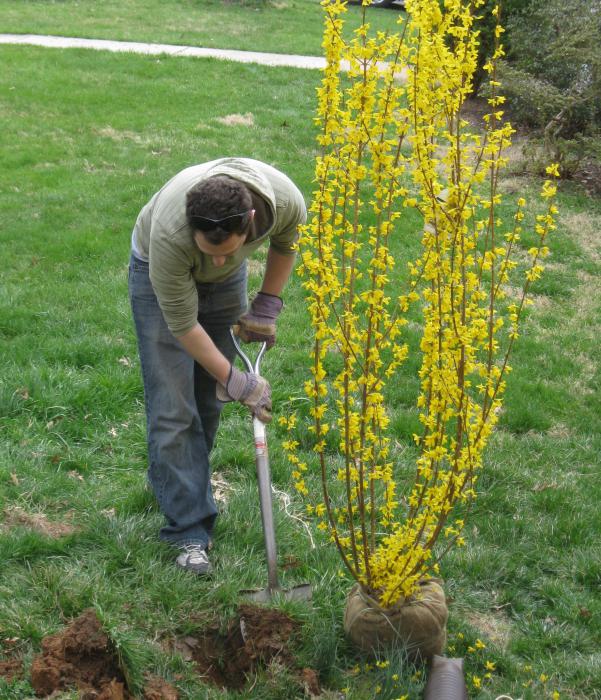

Forsythia is planted in spring or early autumn until frost.
Planting is done either in early autumn, before frost, or in spring.
Reference: Remember to mulch the soil with dry leaves, especially when planting in early fall.
Planting Forsythia on your own
Soil requirements are as follows: light loam or calcareous, slightly alkaline dry soils.
Reference: The site must be protected from the wind!
The planting pattern is as follows: 0.7 - 1.5 m between plants in group planting, the pit for each plant should be 50x50x60 cm.
Packing the hole before planting:
- 12 cm of drainage (crushed stone, broken brick);
- 10 cm of sand;
- a mixture of leafy soil and peat in a ratio of 2: 1;
- 200 grams of wood ash;
After planting, the ground should be in without fail compacted.
Forsythia outdoor care
The plant is unpretentious, caring for it does not require special care. It should only be noted that forsythia is photophilous, therefore, constantly shaded landing areas are undesirable for it. Watering is moderate, in dry weather the plant needs no more than 10-12 liters of water per month.
Fertilizer three times per season:
- For the first time, rotted manure along the trunk circle (not close) with abundant watering (period: early spring);
- Then with a full-fledged mineral fertilizer at the rate of 60-70 grams per 1 m² (April);
- Top dressing "Kemira-universal" 100-120 grams per 1 m² (period after flowering);
Forsythia propagation methods

The most successful forsythia propagation method is cuttings.
There are two ways to propagate forsythia: seed and vegetative (i.e. root offspring, dividing the bush and cuttings).
In horticulture, vegetative methods are, of course, popular.
If you prefer to grow forsythia from cuttings, then:
Cuttings are cut about 15 cm long, preferably in June. Further, the lower leaves must be cut off, the branch itself is treated with a root formation stimulator (Kornevin, Epin, heteroauxin), after which it can be planted. Older and lignified cuttings can also be planted in early autumn, before the onset of frost, it is only necessary to form a cover of dry leaves in order for the plant to overwinter and take root.
If you decide to grow forsythia by layering, then:
The young shoot should be bent to the ground and secured. Having previously cut the bark, cover it with fertile soil on top. Thus, the shoot will take root very soon and a new plant will form. The old branch can be cut off after a year.
Forsythia seeds do not reproduce well, so this method is not popular among gardeners.
Pests, shrub diseases and how to deal with them
Forsythia is exposed to bacteriosis and moniliosis, the effects of nematodes. In the first case, the plant can no longer be helped, and it can only be dug up with roots and thrown away.
miniliosis is a fungal disease characterized by brown spots on the leaves. Not to be confused with simple wilting, since funds such as Fundazol or Tseneb (2-5% solution) save from wilting, while miniliosis can only be cured by cutting out all damaged tissues. With the harmful effects of nematodes, the soil under the plant is disinfected with Carbation.
Pruning bushes

As usual, forsythia is pruned to remove dried and frozen branches.
Forsythia undergoes only sanitary pruning, i.e. no special requirements. Dried branches are cut, in adult shrubs - frozen ends of branches. Sometimes, after the flowering period, all forsythia branches are shortened by one third, if desired, giving the bush a spherical or cupped shape. But such radical methods are used, as a rule, to “rejuvenate” the bush, that is, to enable new shoots to germinate. This procedure should be done no more than once every 4 years.
Preparing for winter forsythia
For young plants, a cover of spruce branches should be prepared in advance. Otherwise, the branches of the bush bend down to the ground and, if possible, strengthen in this position. The trunk and the trunk circle are covered with dry branches and leaves, from above the entire bush is covered with spruce branches. Please note: as mentioned above, some types of plants, such as Forsythia ovoid, are able to overwinter without any shelter.
Landscaping: ideas for the garden
It has long been established that forsythia looks best against a background of dark green coniferous plants, so that as companions they usually go to her: spruce, thuja, and also juniper. Forsythia itself is most often planted as a tapeworm (i.e. a single plant), or as part of mixborders (flower beds of free combinations). Hanging forsythia looks very impressive on the trellises of buildings, is used when decorating slopes, in hedges.
forsythia
In the literature, these plants have many similar-sounding names. - forsythia, forsythia, forsythia, forsythia. Such inconsistency arose due to differences in the spelling and pronunciation of the same word in Russian, English and Latin.
The fact is that the genus Forsythia of the olive family was named after the famous English gardener W. Forsyth (1737-1800). The genus is very small, and includes only 8 species of beautifully flowering deciduous shrubs, most of which are of subtropical origin. These are relics of the Tertiary period, 6 of them grow in East Asia, 1 - in Europe. And only five have been introduced into culture.
Forsythia european, homeland - the mountains of Albania. It is a shrub up to 2 m tall. Green shoots. Leaves up to 8 cm long. The flowers are smaller, and the plant itself is less decorative than other types of forsythia, moreover, the most not winter-hardy of them. In our country it can be grown in open field only in the foothills of the Caucasus (Krasnodar Territory). However, in the arboretum of the Botanical Garden. V. L. Komarova grow several specimens of this species, which annually freeze heavily. In view of the less decorative than other species, and insufficient winter hardiness- in conditions middle lane and north- little prospect.
Forsythia green, or the greenest is a bush up to 3 m tall. Motherland- China. Shoots are green, tetrahedral. Foliage is shiny, dark green. The species is very decorative, but thermophilic, therefore it can be grown in open ground not north of Rostov-on-Don.
Forsythia Giralda(or Giralda) is also from China. Blossoms in June, later than other species, pale yellow flowers. In the North-West, without shelter, it freezes a lot, but still sometimes blooms. In the Chernozem zone, it is quite winter-hardy.
Forsythia hanging down, or drooping. Motherland- mountainous regions of China. the species is very variable, it is a bush up to 4 m tall. The branches are thick, tetrahedral, drooping, sometimes creeping, with yellow or gray-brown, warty bark. Buds are tetrahedral, yellow-brown. Leaves trifoliate or three-lobed, occasionally entire. Flowers about 2.5 cm in diameter, collected in corymbose inflorescences of 1-6 pcs. Corolla golden yellow or bright orange-yellow. Flower tube inside with orange-yellow stripes. Calyx teeth ovate-lanceolate, up to 8 mm long. The species is characterized by rapid growth, early and abundant flowering, endurance to urban conditions; loves calcareous soils. Moreover, inside the species there is a particularly winter-hardy form- forsythia Siebold, which can be successfully grown without shelter for the winter, even in Leningrad region. Her bushes have a lower growth, and the petals of the corolla are bent back.
Forsythia oval, or ovoid- homeland Korea, shrub up to 1.5 m in height, blooms beautifully with single amber-yellow wide-flowered flowers. The most winter-hardy type of forsythia, however, in culture it is still quite rare. Abroad, on its basis, an even more decorative cultivar was bred- Tetragol d , but, unfortunately, it is not winter-hardy.
In addition, a hybrid view- forsythia medium, or intermediate, obtained from crossing f. drooping and f. the greenest. It has the appearance of a widely spreading bush up to 3 m tall, the branches are not as drooping as those of the mother plant, only some of them are curved and hang down to the ground in an arcuate manner, the rest are directed upwards. Very decorative. The leaves are mostly entire, only occasionally lobed. The flowers are bright yellow, the petals are narrow, slightly twisted. The species is fairly drought tolerant. It has a higher winter hardiness than both parents, therefore it is successfully grown in the Moscow region and in the North-West of the country. Only in particularly severe winters do the tips of the shoots freeze slightly in plants. AT Western Europe on its basis, ornamental varieties with huge flowers more than 5 cm in diameter have been bred, but, unfortunately, they are not winter-hardy enough in our country. In addition, several decorative hybrid forms and varieties of forsythia with variegated and purple leaves have been bred by selection and hybridization ( cv. variegata, cv. atrocaulis), creeping and climbing shoots, but, unfortunately, without proper shelter, they are also not winter hardy enough.
Forsythia are photophilous, prefer a sunny location, but can withstand a little shading, so they can grow in partial shade. They are not demanding on soil fertility; any garden soil is suitable for their cultivation. They can grow even on heavy ones. Responsive to liming. They do not like strong pruning, it causes excessive branching to the detriment of flowering, but old faded branches should be shortened by about 1/3. In addition, it is imperative to remove the ends of last year's frozen shoots, and bushes that are too thick- thin out, removing frail, broken, rubbing and intertwined branches. To increase winter hardiness, at the end of August- in early September, it is useful to lightly shorten, or pinch (pinching) the non-lignified tips of the shoots. Leaves opposite, petiolate, unequally serrate, entire, ovate-oblong; in some species, trifoliate or three-lobed. The flowers are large, bisexual, look like shallow bells; calyx four-petalled, with widely spread petals, corolla sympetalous, tubular; fragrant, their aroma is somewhat reminiscent of the smell of jasmine. The color of the flowers, depending on the species and variety, varies from pale yellow to bright canary and amber. Forsythia bloom in May, before the leaves appear. Flowering is regular and very abundant. To obtain seeds, cross-pollination of different generative forms is necessary, with self-pollination, seed setting is weak. Fetus- cracking oblong, narrowed towards the base, slightly flattened box containing several winged seeds.
Forsythia are propagated by root offspring, horizontal and arcuate layering, lignified, semi-lignified and green cuttings. East Asian species are especially well replicated last, their root formation reaches almost 100%. The distance between seedlings when they are planted in a permanent place should be at least 45 cm.
Forsythia are one of those first ornamental shrubs that brighten up the rather dull look of the garden areas immediately after the snow melts. They look good both singly and in groups. AT landscape design used as a tapeworm (single), in biogroups, border plantings, as well as for decorating slopes. In the latter case, they look especially natural, since they grow in the mountains at home. In summer, the greenery of their bushes is in perfect harmony with roses, so they are often used to frame the latter. All types of forsythia are suitable for growing in tub culture (in flowerpots) and creating portable winter gardens. Their branches can be used for winter forcing in December - January for bouquets. As you can see, forsythia are very unpretentious, require almost no maintenance, decorative, beautiful, bloom magnificently and very profusely, so our amateur gardeners should not only breed more widely their most winter-hardy types and forms (oval, medium and Siebold), but also on their based on trying to develop their own, local, more beautiful and original varieties.
V. Shpagin , Ph.D. Sciences
Forsythia: landing, care
 Forsythia is known to many people, you can guess a riddle that absolutely everyone will answer - which shrub blooms very early, has bright yellow flowers and elegant greenery, is not afraid of shade and is resistant to frost - of course, this is forsythia!
Forsythia is known to many people, you can guess a riddle that absolutely everyone will answer - which shrub blooms very early, has bright yellow flowers and elegant greenery, is not afraid of shade and is resistant to frost - of course, this is forsythia!
Forsythia is like a butterfly to a tuxedo, no garden will be complete without it, already in April - or early May in colder regions, you can admire its charming yellow flowers, imperceptibly replacing each other for a month.
Forsythia has several names, this is a rare naming for Russia - forsythia and forsythia - as the nerds of botany call it. The genus of forsythia belongs to a very interesting family - olive, interesting because all its representatives are quite beautiful during the flowering period.
There are many types of forsythia, but all are the same siblings, they are close and appearance and for a number of biological characteristics, but their purpose is exactly the same - decorative.
Golden-yellow forsythia flowers, reminiscent of a little bells, bloom, as if, chaotically and unexpectedly. On young seedlings there are much fewer of them than on adult plants, they are like small spring butterflies sitting on shoots, it seems that you just need to clap your hands and they will scatter in all directions.
Close to us in spirit and able to grow in our climate, not all types of forsythia, often only in the collections of fans of this culture can be seen in addition to the familiar ovoid forsythia - oval, drooping, hanging and intermediate. Being well sheltered for the winter, European forsythia, as well as dark green, will grow on our site with you.
But whatever view you have in your hands, the first thing to start with is to select the most well-lit and wind-protected area, and the second is much more important than the first. In the shade, forsythia will be able to survive and even bloom well, but in a place open to all winds it can freeze to the level of the snow cover. Here, as they say, either a tit in the hands or ...
Having chosen a place, dig deeper, it is advisable to replace the earth layer with a more nutritious substrate. Ideally, it can be a mixture of humus, leafy soil and sand in equal proportions. You can lime the soil a little, especially if the soils of your site are acidic, forsythia does not like them.
When planting plants, try not to thicken the plantings, why oppress such beauty. Forsythia needs a lot of space to unfold its festive outfit, so leave two, preferably three meters between seedlings.
Before planting a seedling, dig a small hole, its size is not important, the main thing is that the roots in it are located freely. Place some broken brick at the bottom of the hole for drainage, and sprinkle the roots with nutrient soil, so you will ensure the plants take root quickly and actively grow. By the way, for planting in the middle part of Russia, choose autumn, but in more northern regions, the best time is spring.
Immediately after planting the plants in the spring, they can be fed, absolutely any complex mineral fertilizer, the volume of which is 60-80 g per m², is suitable for this.
Further care is absolutely standard, this is loosening the soil, removing weeds while the seedling is still young, mulching the soil with peat, as well as watering and pruning. Speaking of watering - do not flood the plant, forsythia belongs to the category of crops that feel better on a dry substrate than on a too waterlogged one. However, if there is a strong heat outside and the soil is too dry, this crop must also be watered. Usually one watering every 15-20 days is enough, but it should be plentiful, so you need to pour at least a bucket of water under each plant, and preferably a couple of buckets.
Every spring, a couple of weeks before the flowering of the crop, it is necessary to carry out sanitary pruning. It is not difficult and involves the removal of all diseased, frozen, broken and dried shoots, as well as those that are too thin and those that grow inside the crown, thickening it greatly.
For the winter in the central regions of Russia, forsythia can not be covered, it is enough to mulch the soil with peat or humus, but in colder regions, shelter is necessary. Most often, this is spruce spruce branches - it perfectly retains snow, dry leaves or non-woven material, the shelter of which provides for bending the shoots to the ground.
As for reproduction, everyone can duplicate this culture - any of the indicated methods will do - with green cuttings (in the presence of greenhouses), lignified cuttings (on a moist and nutritious substrate), as well as horizontal layering.
Maybe not everyone knows, but forsythia can be made to bloom even in winter! Of course, not on the street, but in the room and not a whole tree, but only its individual shoots. To do this, cut them at the beginning of winter, wrap them in plastic and place them in the refrigerator. And in winter, remove it from the film and put it in warm water with sugar dissolved in it (for nutrition), in five to seven days the shoots will wake up, and after a couple more they will bloom!
N. Khromov , candidate of biological sciences
Plant forsythia (lat. Forsythia), or forsythia- a genus of small trees and shrubs of the Olive family, blooming in early spring with bright yellow flowers. The genus of forsythia is very ancient, and this is confirmed by the dispersion of the natural habitat: six species of forsythia grow in East Asia (in Japan, Korea, China), while in Europe, forsythia flowers, represented by the only species of European forsythia (Forsythia europaea), bloom mainly in the Balkans, although I was first struck by the blooming forsythia in mid-March in Germany. The forsythia flower was named after William Forsythe, a Scottish botanist, head gardener at Kensington Palace and one of the founders of the Royal Horticultural Society. It was Forsyth who brought the first forsythia bush to Europe from China.
Listen to article
Forsythia shrub - description
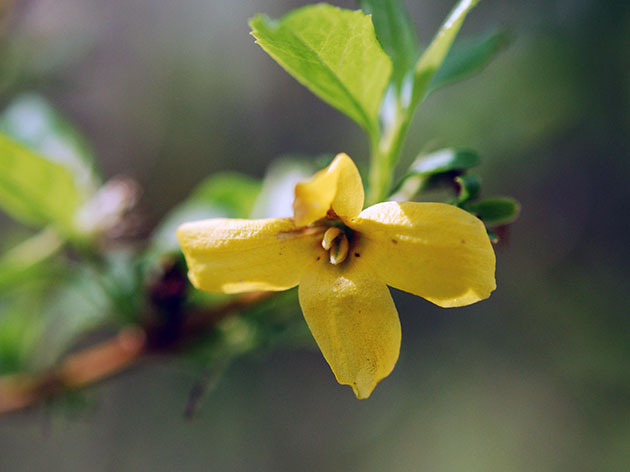
Forsythia, as already mentioned, is a small tree or bush with a height of one to three meters. The bark is coarse in texture and grey-brown in color. The leaves of some species are trifoliate, but in most forsythia they are simple, without stipules, opposite, oval in shape with notches along the edges, from two to fifteen centimeters long. Bell-shaped flowers are bright yellow. Forsythia blooms in early spring and lasts up to three weeks, sometimes even longer. The fruit is a capsule with winged seeds.
Features of growing forsythia
Today it is impossible to imagine city streets, squares and private gardens in Europe without forsythia, primarily because it is the symbol of the coming of spring. On the gray, still winter streets, the yellow flame of forsythia flowers suddenly begins to blaze, and the townspeople, longing for warmth and greenery, perk up, begin to prepare for spring. Such early flowering of forsythia is a property that distinguishes it from other shrubs. Undemanding to care and location adds to its popularity. What are the features in the care and cultivation of this shrub popular with flower growers?
- - Forsythia are photophilous, but grow in the shade.
- - The soil for the plant needs lime.
- - Forsythia looks most spectacular against the background of dark green coniferous plants.
- - In autumn, the green leaves of the forsythia turn golden or purple-purple, and it again attracts attention with its bright motley flame.

Forsythia planting
When to plant forsythia.
Planting and transplanting of forsythia is carried out in spring or early autumn, before the onset of frost, so that the plant has time to take root before winter. For this, they choose a site protected from the wind in the sun or in partial shade - although forsythia is shade-tolerant, it loves light. The plant is undemanding to the composition of the soil, but it grows best on slightly alkaline dry soils. If at the site the pH is shifted to the acid side, it is better to dig the soil with wood ash in advance.

How to plant forsythia.
Forsythia holes should be 50x50x60 so that the root ball is at a depth of 30-40 cm after planting. If you plant several bushes, then dig holes for them at a distance of one and a half meters from each other. Before planting, it is necessary to fill the pits with a layer of drainage made of broken brick or crushed stone 15-20 cm thick, then a ten-centimeter layer of sand, then a mixture of leafy soil, sand and peat in a ratio of 2: 1: 1 and 200 g of wood ash. Forsythia seedlings are lowered into a hole, dug in with earth, which is then necessarily compacted, and watered abundantly. If you planted forsythia in the spring, then in the future it will require your usual care. Autumn planting and caring for forsythia is somewhat more complicated: they require mandatory mulching of the site, regardless of the variety of plant you plant. The covering material must be breathable so that in winter, during short thaws, flower buds do not swell under it.

Forsythia - care
How to care for forsythia.
Caring for forsythia is not much different from caring for any garden bush. With sufficient rainfall in summer time the plant does not need watering, but if the summer turns out to be dry, then forsythia will have to be watered at least once or twice a month at the rate of 10-12 liters for each bush. After watering, you need to loosen the soil and remove weeds, and you need to loosen to the depth of a spade bayonet to provide air access to the roots of the plant. After loosening, the trunk circle is mulched with compost or dry earth. Forsythia is fertilized three times a season: in early spring, a thick layer of rotted manure is laid out along the trunk circle, but not close to the branches and trunk, then watered abundantly. Manure will become both mulch and organic food for the plant. In April, full mineral fertilizer is applied to the soil at the rate of 60-70 g per 1 m². After flowering, when the plant lays flower buds for the next year, forsythia is fed with Kemira-universal at the rate of 100-120 g per 1 m².

Forsythia reproduction.
Forsythia is most often propagated vegetatively. For example, green cuttings about 15 cm long, which are best cut in June. The lower leaves are removed, and the cuttings, having previously been treated with a root formation stimulator (root, epin or heteroauxin), are planted under a greenhouse in perlite or sand. You can also root lignified cuttings cut in October, and plant them directly in the ground in the garden, leaving two or three buds above the surface. It is only necessary to cover the cuttings for the winter with dry leaves. In the spring, when you remove the cover, the adopted cuttings will grow, and by autumn you will have beautiful seedlings. Forsythia is also propagated by layering: in summer or autumn, bend the lower young shoot to the ground, after pulling it at the base with a wire and cutting the bark on the side that lies on the ground, fix it, sprinkle it with fertile soil, and the shoot will soon form roots. In the spring, cut this branch from the bush, and the next year the young plant will bloom.

Forsythia also reproduces in a generative way, that is, by seeds, but this is already a conversation for specialists.
Forsythia cutting.
Young forsythia bushes are subjected only to sanitary pruning - frozen, shrunken or broken shoots are removed. In adult plants, the frozen ends of the branches are cut in the spring, while the main pruning is carried out in the summer, when flowering ends: the faded branches are shortened by half, the old and dried ones are cut at a height of 4-6 cm from the soil level, and then side shoots will come from them. Pruning also helps to regulate the density, height and shape of the bush - cupped or spherical. If you have a need to rejuvenate your mature forsythia, then it is best to cut all branches to a height of 4-6 cm, or at least 2/3, in order to activate the growth of young shoots. But you should not abuse such haircuts, because as a result the bush will grow stronger, but it will stop blooming. Forsythia should be rejuvenated so that it does not lose its decorative qualities no more than once every 3-4 years.

Pests and diseases of forsythia.
This shrub is resistant to both pests and diseases, but is sometimes affected by wilting, moniliosis and bacteriosis. Withering is treated by spraying with a two to five percent solution of foundationazole, but there is no salvation from bacteriosis, and the bush will have to be dug up along with the roots and destroyed. Moniliosis is expressed by the appearance of brown spots on the leaves. In case of illness, you need to cut and clean all the affected areas to healthy tissue. Forsythia has troubles due to nematodes, then you have to disinfect the soil with carbation.

Forsythia after flowering and wilting
To protect the forsythia from winter frosts, the trunk circle is covered with a ten-centimeter layer of dry foliage, the branches are bent to the ground and pinned, and they are thrown from above with spruce branches. In early spring, the shelter is removed, the branches are unfastened, the dry leaves are removed from the trunk. Young plants for the winter are completely covered with spruce branches. AT snowy winters forsythia winters well even without shelter, but who knows in advance what kind of winter it will be?

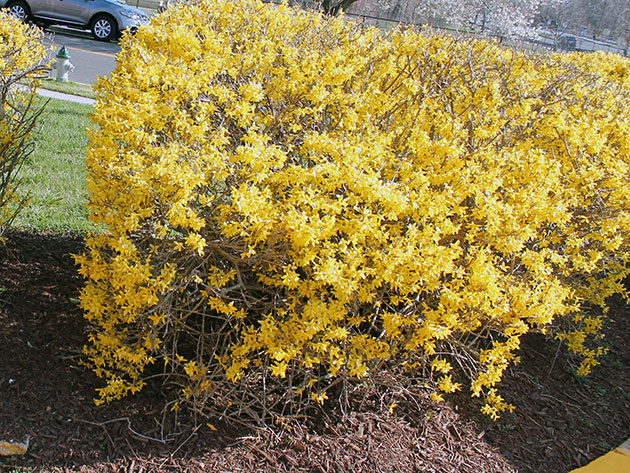
Types and varieties of forsythia
The most common species in culture in our latitudes is European forsythia (Forsythia europaea). This is a low (up to two meters) upright shrub with entire oblong leaves up to 7 cm long. Its flowers are solitary, bell-shaped, golden yellow.

Forsythia Giralda (Forsythia giraldiana)
very similar to European, but more sensitive to low temperatures. She is the same height, her stems are also mostly straight, but tetrahedral, yellow-brown. The leaves are elliptical, dark green, up to 10 cm long. It blooms in May with large graceful light yellow flowers with twisted petals.

Forsythia hanging, or drooping, or drooping (Forsythia suspensa)
taller shrub - up to three meters tall, with a spreading crown, arcuate, drooping, thin tetrahedral branches of reddish-brown or olive color. Leaves on old shoots are simple, on growth ones - trifoliate. The flowers are large, up to 2.5 cm in diameter, golden yellow, collected in bunches of several. In culture, several forms of hanging forsythia are grown:
- – motley (forsythia variegata)- bright yellow flowers, yellowish variegated leaves;
- – Fortuna (forsythia fortunei) with narrow trifoliate leaves, dark yellow flowers collected in bunches;
- – purple stem (forsythia artocaulis)- with dark red shoots and leaves at the time of opening;
- - and others: Simbold's forsythia, deceptive forsythia, Forsythia hanging Fortune.

Dark green forsythia (Forsythia viridissima)
- tall, up to three meters tall, shrub with green branches directed upwards. The leaves are densely growing, simple, oblong-lanceolate, serrated in the upper part, very dark green, up to 15 cm long, up to 4 cm wide. Bright flowers of a greenish-yellow hue are collected in small bunches. Drought-resistant.

Forsythia intermediate (Forsythia x intermedia)
is a hybrid of forsythia drooping and forsythia dark green. It grows up to three meters in height, blooms in the fourth year of life. Its leaves are oblong with a jagged edge, but there are also trifoliate, up to 10 cm long. The dark green color of the leaves persists until late autumn. Bright yellow flowers are collected in bunches of several pieces. Blooms in April-May. Winter-hardy, drought-resistant, very fast growing. Varieties:
- – Beatrix Farrand- bush height up to 4 m, bright yellow flowers with dark yellow stripes at the base;
- – Denziflora- a low bush up to one and a half meters tall and about the same in volume, the flowers are pale yellow, twisted. Blooms in May for two to three weeks. Afraid of frost;
- – Spectabilis- one of the most beautiful varieties: the bush is only a meter high, but the crown in diameter reaches 120 cm. The leaves are green in warm weather, in autumn they are purple and bright yellow. The flowers are dark yellow, up to 4.5 cm in diameter, bloom in late April.

Forsythia snow, or white (Forsythia abeliophyllum)
reaches a height of 1.5-2 m. The leaves are oval, up to 8 cm long, in summer the underside of the leaves acquires a purple hue. The flowers, as the name implies, are white, with a yellow throat, pale pinkish in buds.

Forsythia ovoid (Forsythia ovata)
low shrub - from one and a half to two meters tall. The branches are spreading, grayish-yellow. Leaves up to 7 cm long, bright green in summer, turn purple in autumn. Single flowers of bright yellow color up to two centimeters in diameter. It blooms earlier than all other types of forsythia, grows quickly, is winter-hardy and drought-resistant. Popular varieties:

- – Spring Glory- up to three meters high, green in summer, the leaves become variegated in autumn - from pale yellow to dark purple. Blooms profusely in May with bright yellow large flowers;



