What corresponds to the power of an energy-saving lamp. LED lamps and incandescent lamps. Dimensions and appearance
| Ordinary lamps | LED lamp | ||
| Name | Name | ||
| Incandescent lamp. | 40W | LED | 3W |
| Incandescent lamp. | 60W | LED | 5W |
| Incandescent lamp. | 75W | LED | 7W |
| Incandescent lamp. | 100W | LED | 11W |
| Incandescent lamp. | 150W | LED | 15W |
| Energy saving. | 9W | LED | 3W |
| Energy saving. | 11W | LED | 5W |
| Energy saving. | 15W | LED | 7W |
| Energy saving. | 20W | LED | 11W |
| Energy saving. | 30W | LED | 15W |
| Halogen lamp | 35W | LED | 3W |
| Halogen lamp | 50W | LED | 4W |
| Fluorescent lamp T8 | 18W | LED T8 | 8W |
| Fluorescent lamp T8 | 36W | LED T8 | 15W |
Ratio Comparison Table luminous flux(lumen) to luminaire power (W)
| incandescent lamp, | Fluorescent Lamp, | LED lamp, | Luminous flux, Lm |
| 20 W | 5-7W | 2-3 W | About 250 lm |
| 40 W | 10-13 W | 4-5W | About 400 lm |
| 60 W | 15-16 W | 8-10 W | About 700 lm |
| 75 W | 18-20 W | 10-12 W | About 900 lm |
| 100 W | 25-30W | 12-15W | About 1200 lm |
| 150 W | 40-50W | 18-20 W | About 1800 lm |
| 200 W | 60-80W | 25-30W | About 2500 lm |
As can be seen from the table, on average, LED lamps are 10 times more efficient than incandescent lamps, and fluorescent lamps are 2 times more efficient.
Savings calculator LED lamps:
| Lamp costs |
|||
| Number of working lamps | |||
| Lamp type | Energy saving | incandescent |
|
| Power consumption (W) | |||
| Electricity cost (1KW) | $0.093 (14 tg.) | $0.093 (14 tg.) | $0.093 (14 tg.) |
| luminous flux (Lumen) | |||
| service life (hours) | |||
| lamp cost ($) | |||
| electricity consumption energy per day (W) | |||
| electricity consumption energy per year (W) | |||
| electricity costs for 1 year ($) | |||
| electricity costs for 2 years ($) | |||
| electricity costs for 5 years ($) | |||
| number of lamps for 5 years | |||
| lamp costs over 5 years ($) | |||
| Total cost over 5 years ($) | |||
Arc mercury lamps(DRL)
The most common type of lamp currently used in street and industrial lighting. Developed earlier than other lamps and the least labor-intensive to manufacture, DRL lamps are widely used for indoor and outdoor lighting. DRL lamps have a lower light output compared to HPS lamps, but unlike them, they do not require additional high-voltage triggering devices for ignition. The ergonomic indicators of illumination of DRL lamps (the pulsation coefficient of the light flux, the correspondence of the emission spectrum to the solar spectrum) are slightly worse than, for example, DRI lamps, but much better than HPS lamps.
Arc sodium tubular lamps (HSS)
Currently, they are widely used for lighting streets, highways, public buildings, etc. HPS lamps have the highest luminous efficiency among gas discharge lamps and a lower value of luminous flux reduction with long service life. Due to the very high ripple factor and the large deviation of the lamp emission spectrum towards the red region, which violates the color rendering of objects, it is not recommended to use HPS lamps for lighting inside industrial and residential premises. The large dependence of the light output and ignition voltage of HPS lamps on the composition and pressure of the internal gas, on the current passing through the lamp and on the burner temperature place very high demands on the quality of manufacture and operating conditions of HPS lamps. Therefore, for effective work for HPS lamps, it is necessary to provide "comfortable" operating conditions - high stability of the supply voltage, temperature environment from -20оС to +30оС. Deviation from "comfortable" operating conditions leads to a sharp reduction in lamp life and a decrease in light output. The service life of HPS lamps is also affected by the quality of the pulse triggers used. Currently, there is a widespread misconception that replacing DRL lamps with more efficient HPS lamps leads to improved lighting quality and energy savings. This does not take into account that a HPS lamp of similar power with a higher luminous flux has a higher current consumption. In addition, the predominance of the red spectrum from HPS lamps worsens the overall picture of the visibility of illuminated objects, which is especially dangerous for lighting high-speed highways.
LED lamps (LED or LED)
By themselves, LEDs have been used for a long time, mainly for indication. Emission of light by an LED by recombination of photons in area p-n transition of a semiconductor during the passage of current. The breakthrough in the field of LEDs, which occurred several years ago, was primarily associated with the development of new semiconductor materials that increase the brightness of LEDs by more than 20 times. Unlike other technologies, LEDs have a very high efficiency - at least 90% (95-98%). In most existing technologies, there is a heating of a body or area, which requires a decent amount of energy. Thanks to its high efficiency, LED technology ensures low power consumption and low heat generation. In addition, due to the very nature of receiving radiation, LEDs have a set of characteristics that are unattainable for other technologies. Mechanical and thermal stability, resistance to voltage drops, long service life, excellent contrast and color reproduction. Plus, environmental friendliness, no flicker and even light. This is the quality modern technology.
Parameters of the considered types of lamps:
| Rated power, W | Consumed active power, W | Average burning time, hours | Luminous flux, Lm |
||
| DRL-125 | |||||
| DRL-250 | |||||
| DRL-400 | |||||
| DNAT | DNAT-100 | ||||
| DNAT-150 | |||||
| DNAT-250 | |||||
| DNAT-400 | |||||
| analog DRL-125 | |||||
| analog DRL-250 |
* The LED analogue of the DRL-250 lamp can surprise with a luminous flux of 5000 lumens. In fact, it is quite enough due to the strong directivity of the LEDs. When used indoors, where light scattering is important, this factor affects much less than outdoors, where the height of the suspension is usually 6m and above. An experimental comparison of lamp types can clearly demonstrate this. In addition, USS LED luminaires use an innovation that increases the efficiency of the luminaire without increasing the cost. Some manufacturers have a more technological implementation of this idea, but in their case this affects the cost.
When choosing DRL analogs on your own, it is important to remember:
The DRL lamp loses its luminous flux exponentially, and after about 2-3 months. work falls twice from the declared.
In a luminaire with a DRL lamp, at least 30% of the luminous flux is lost on the reflectors and the lamp's own dimming.
The declared luminous flux of a DRL lamp and the luminous flux of a lamp with a DRL lamp are two different things.
The actual power consumption of a luminaire with a DRL lamp is 20-50% higher than the declared power of the DRL lamp, due to losses in the ballast.
With equal luminous fluxes, LED lamps visually shine brighter due to: no stroboscopic effect, high contrast ratio, high color rendering index (Ra) and daylight(4700K).
Based on the foregoing, when replacing luminaires with DRL lamps with an LED analogue, it should be taken into account that adjusting the luminous flux of the LED luminaire to the declared luminous flux of the new DRL lamp will lead to a visual increase in brightness by 3-6 times, and unnecessary costs. Also, it should be noted that in accordance with the new SNiP and GOST, the luminous flux of LED lamps is taken one step lower than for DRL.
| Lamp type | DRL-250 | DNAT-150 | LED lamp |
| Luminous flux, Lm | 5000 |
||
| Consumption, W | 65 |
||
| Service life, hours | up to 100 thousand |
||
| Contrast and color reproduction | very weak | excellent |
|
| Mechanical strength | excellent |
||
| Temperature stability | very weak | excellent |
|
| Drop resistance | excellent |
||
| Startup time | 10-15 minutes | 10-15 minutes | instantly |
| heated up | weakly |
||
| Environmental Safety | the lamp contains up to 100 mg of mercury vapor | the lamp contains sodium-mercury amalgam and xenon | absolutely harmless |
Note: Under temperature stability it implies how much both the operation of the lamp and its service life depend on critical temperature values. For example, it is known that the HPS lamp is extremely sensitive to deviations from "comfortable" temperature values. Such deviations adversely affect the light output and lead to a sharp reduction in service life.
How many lumens are there in a lamp with a DRL lamp, DNAt and LEDs?
The luminaire, unlike the lamp, has an optical system for more efficient use of the luminous flux. In cheap luminaires that do not have special reflectors and high-quality diffusers, the luminous flux when using powerful DRL and Dnat lamps is much lower and can drop to 50-60% of the total luminous flux of an individual lamp, while for LED luminaires with a more directional luminous flux, these losses will be much less - up to 5% depending on the optical system.
| Lamp with DRL lamp | Lamp with lamp Dnat | LED lamp | Luminous flux, Lm |
| 125 W | 70 W | 30-40W | About 3,500 lm |
| 250 W | 100 W | 40-60W | About 8,000 lm |
| 400 W | 150 W | 80-120W | About 12,000 lm |
| 700 W | 250 W | 140-160W | About 20,000 lm |
| 1000 W | 400 W | 180-200W | About 30,000 lm |
*Approximate ratios based on Dialux calculations.
Analysis:
It is important to point out one more point, which was not mentioned above. DRL and HPS lamps have an aging effect. It is reliably known that after 400 hours of operation, the drop in the luminous flux of DRL lamps is more than 20%, and by the end of their life, more than 50%. For most of its life, the lamp emits only 50-60% of the rated luminous flux. This is clearly seen from the decay curve of the luminous flux. With HPS, the situation is even sadder, due to their lower temperature stability. LEDs don't have that. LEDs throughout their entire service life retain their parameters at their original level. Only by the end of the term can there be a slight drop. This is where an interesting and important point comes to light. It turns out that if you measure the parameters, for example, every month during the entire service life, and then calculate the average, then it will be about (!) 60% of the nominal value. The declared values of the parameters refer only to the initial period of operation and will constantly fall along the curve from the very beginning. This is nothing more than the costs of existing technologies. The above can be interpreted as follows. For the declared characteristics (first of all, the luminous flux is meant), you pay more or pay 100% for the characteristics in reality, ~ 40% lower.
Efficiency of using these types of fixtures.
DRL.
The most simple and affordable technology. The low initial cost, provided there are no stringent lighting requirements, justifies its use.
DNAT.
The best light output among gas-discharge lamps is the only serious advantage over DRL. But a very weak color rendering index and a high sensitivity to temperature cast doubt on the feasibility of a replacement. HPS is not recommended for indoor lighting and is even banned in some countries. Lighting of roads, especially high-speed ones, is also not recommended. When illuminating any other areas, the use of HPS lamps can be considered justified in comparison with DRL.
SD.
It may seem incredible, but LED lamps have no technical flaws. They are the best in everything. In addition to the above, we can add that LED lamps do not require inrush currents, and therefore require a smaller cable section. The only downside is that they are way ahead in price. How justified is their use? Taking into account all the factors related to the operating costs of DRL or HPS lamps, the payback period for LED analogues starts from 3 years. That is - 3 years (or more) the LED lamp pays for itself, and in all subsequent years it makes a profit. At the same time, all the time giving out the highest quality light compared to other technologies.
LEDs and short circuit.
The LED as such cannot be energized because of its CVC (voltage-ampere characteristic). Either it won't light up or it will burn out, so the LED is current driven. The easiest way is through a resistor. In the lamp for supplying "edible" current to the LED circuit, a so-called driver is provided. The driver not only acts as a converter (adapter), but also protects the LEDs from a short circuit (short circuit). In the event of a short circuit, it is the driver that takes the blow.
Advantages of LED lamps:
Low power consumption - no more than 10% of consumption when using incandescent lamps;
- long service life - from 50,000 hours (10-15 years), (up to 100,000 hours);
- high strength resource - shock and vibration resistance;
- purity and variety of colors, directivity of radiation;
- adjustable intensity;
- low operating voltage;
- environmental and fire safety.


The rise in electricity prices is forcing us to save where we had not even thought about spending before. For example, the replacement of incandescent lamps has become massive. There are much more economical light sources - fluorescent and LED. But how to decide which ones to put - energy-saving or LED lamps? To make a decision, you need to compare their characteristics. And it's better to do it objectively.
Which are more economical
The name "energy-saving" has stuck with us in relation to compact fluorescent lamps (CCL). At the time of their widespread use, they were the most economical. Especially if you compare them with the usual incandescent lamps - housekeepers consume 3-4 times less energy. Later they began to "promote" LED light sources. They consume even less electricity, which means they are the most economical.
To see the difference, see the table. It shows the power consumption of LED, fluorescent lamps and familiar to us with a tungsten filament. They all have the same (or almost) luminous flux, but as you can see, the power consumption is very different. A 3 W LED lamp is equal in light power to a 7 W energy-saving lamp or a 20 W incandescent lamp. diode lamp 5 W will replace the 12-13 watt "housekeeper" or 40 watt incandescent. These are averaged data, since the indicators vary somewhat for different manufacturers, but, in general, the proportions remain the same.
| Incandescent lamps | Luminescent and energy saving | LED | Light flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 W | 5-7W | 2-3 W | 250 lm |
| 40 W | 10-13 W | 4-5W | 400 lm |
| 60 W | 15-16 W | 6-10W | 700 lm |
| 75 W | 18-20 W | 10-12 W | 900 lm |
| 100 W | 25-30W | 12-15W | 1200 lm |
| 150 W | 40-50W | 18-20 W | 1800 lm |
| 200 W | 60-80W | 25-30W | 2500 lm |
Already by this table alone, it is easy to say that energy-saving or LED lamps are the most economical. But that's not all the advantages of LED technology. We will talk about them further (as well as about the shortcomings, however).
Life time
If we talk about service life, then the average for energy-saving ones is on average 10,000 hours. For LED, this figure is higher: on average - 30,000 hours, but there are requests from manufacturers for 50-60 thousand hours of operation.
It seems that LED lamps are among the leaders here, but there is one caveat. Both technologies have a rather significant drawback: over time, their glow intensity gradually decreases. There is a so-called "burnout". In this regard, it is worth focusing not on the declared time of work, but on the warranty period. It more accurately reflects the actual position. After all, if something happens to the lamp at this time, the manufacturer will have to replace the device with a new one. The less often such cases happen, the better. That is why manufacturers tend to underestimate the warranty period, as they bear financial responsibility.
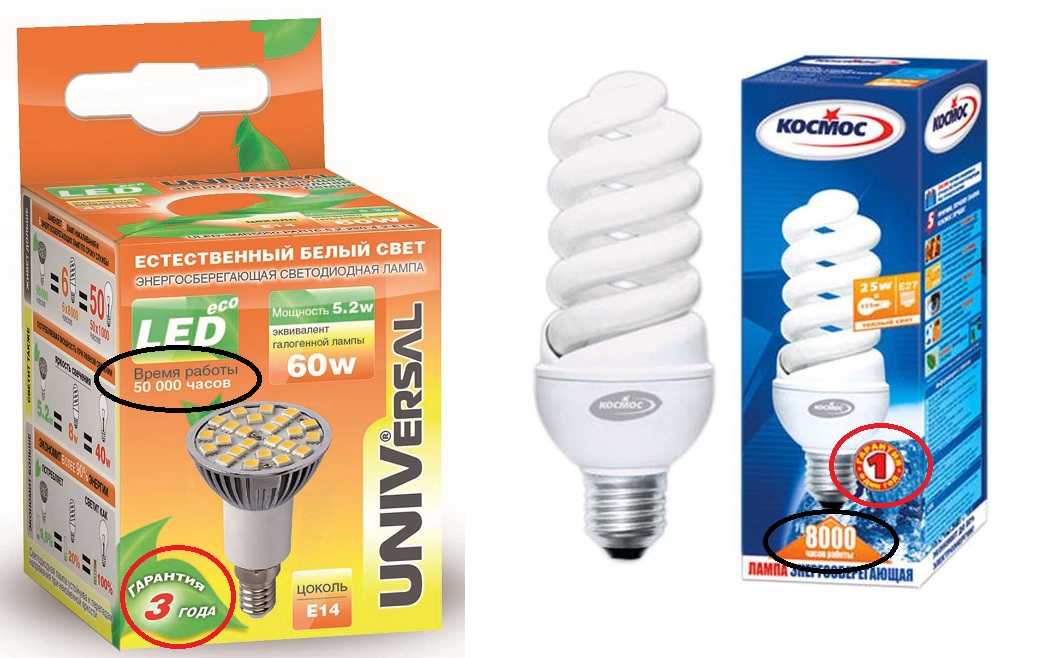

And if we compare energy-saving and LED lamps by the warranty period, there is also a difference. For LEDs, the average is 3 years, for housekeepers - 1 year. There are more / less, but these are particulars. So here, comparing, energy-saving or LED lamps are better, LED technology is the best.
Dimensions and appearance
Everyone knows the type and size of energy-saving lamps. This is a tube with a phosphor twisted into a complex spiral. The most compact ones can fit into a medium-sized ceiling, but in most cases they stick out of ordinary lamps, and with built-in ones they look “not so hot” at all.

LED lamps can be quite small. A three-watt crystal can be made in the form of a circle with a diameter of 1.5-2 cm. And this is the equivalent of a 7 W energy-saving device, which has a minimum size of 32 * 79 mm. Such miniature sizes of LEDs make it possible to make recessed fixtures of very small thickness - 2 cm or less. And this is with a heatsink to remove the heat that the LEDs emit during operation. Such small dimensions allow them to be built into furniture or lowered suspended and stretch ceiling to a very low height.

If we talk about a more familiar format - with a flask, then the shape and size of the flask can be completely different. This detail is optional - the LED does not require a vacuum or a specific gas environment. So it's more of a tribute to tradition. There are bulbless lamps, which are called "corn" for their characteristic appearance. Their service life is determined by the quality of the LEDs, and not by the integrity of the shell, which, in fact, does not exist. You can even assemble lighting in general from individual LEDs on a metal heatsink plate or even without it. In general, both the size and appearance of LED lamps can be different. And here, when deciding which energy-saving or LED lamps are better, we certainly come to the conclusion that LED lamps are better - they can be almost invisible, they can have any shape and size.
Convenience and safety of use
Everyone knows that in fluorescent lamps the tubes are filled with a phosphor, which begins to glow under certain conditions. It takes some time to create these conditions. Sometimes it is almost imperceptible, and sometimes the delay after switching on can be a second or even a little more. This is not the most pleasant phenomenon that you have to put up with. LED lamps light up immediately after the voltage is applied. In this they are definitely better.
Today, more and more people are trying to make lighting with the ability to change the intensity of light. Is this achieved or complex scheme with a large number of switches, or - a small device that allows you to smoothly change the level of glow. But the fact is that not all lamps can work with a dimmer. Energy savers can't. They need a certain level of voltage and its shape, and the dimmer just distorts the shape. But some LED lamps can work with this device. Just look for dimmable ones when choosing LED bulbs. This ability is indicated in technical specifications. Minus - such light sources with equal characteristics are more expensive.

Another point in favor of LED lamps. Their flask (if any) is made of impact-resistant plastic. Energy-saving fluorescent - made of glass. Moreover, damage to the tube is fatal - the light source stops working. In addition, some (cheap) housekeepers contain mercury vapor, so that a glass tube damaged by a phosphor can cause serious harm to health. This also leads to difficulties with disposal - special enterprises are needed for the processing of such lighting fixtures.
And the last point regarding ease of use - neither an incandescent nor a fluorescent lamp can be restored after a failure. When damaged, they completely lose their functionality. LED lamps usually consist of a number of crystals located on the body. When one or more crystals fail, the luminous flux decreases, but the light is still emitted, albeit in a smaller amount. In addition, if desired, you can replace the burned-out elements, restoring the previous brightness.
So, deciding whether energy-saving or LED lamps are better in terms of ease of use, we see that LED lamps are more practical and safer.
Prices and yet what is better ...
Everyone knows that LED lamps are more expensive. This is perhaps the only point on which fluorescent lamps are ahead. But today the difference in price is not as great as before. They are already almost equal. If we take, for example, light sources of the same manufacturer with the same equivalent (or almost the same) in relation to incandescent lamps, then the prices are almost identical.

Here, even the LED price is lower. True, the color temperature is different ...
For example, Camelion lamps (Chamelion). Energy-saving lamp - LH15-FS-T2-M / 864 / E14 is the equivalent of a 75 W incandescent lamp, costs 160-225 rubles. LED lamp - Camelion LED8-C35 / 830 / E27 (also equivalent to 75 W incandescent) - 170-230 rubles. Both series are basic, without any special “bells and whistles”, and if we take into account the savings on electricity (8 W vs. LED lamps" does not occur. The solution is probably unequivocal - more economical, easy to use and durable LED. They are the best to install instead of incandescent lamps.
But in the press and the Internet there is a lot of recent times there was information that LEDs are harmful - they emit a harmful spectrum and flicker. As for the spectrum, there is no confirmed data, but flicker, flicker and luminescent. But they always flicker, and there are LEDs without pulsations, they just cost a lot more. In general, the decision is yours.
Recently popular energy-saving lamps are one of the best recent inventions. Compact in size, they do not require a starter to start the lighting, they work without sound, they are easy to connect (the threaded base is simply installed in the lighting equipment), they save energy by 80%, they are reliable, these are some of the main advantages of these devices.
The principle of operation of an energy-saving fluorescent lamp lies in its content of mercury vapor, argon, neon, and sometimes krypton gases. When electricity enters the lamp, the cathode heats up, from which electrons begin to radiate. They ionize the gas mixture to produce a plasma that emits ultraviolet light invisible to the human eye. Due to this light, the phosphor covering the walls of the tube is illuminated and as a result, the phosphor produces the usual visible light.
Main characteristics
Power
 The most important distinguishing characteristic of energy-saving lamps from others is their low power consumption. All the power they receive is converted into light. The power of such bulbs is 3 - 85 watts.
The most important distinguishing characteristic of energy-saving lamps from others is their low power consumption. All the power they receive is converted into light. The power of such bulbs is 3 - 85 watts.
Energy-saving lamp power table
The table below shows the ratios energy saving lamp and incandescent lamps: numbers - the average indicates that the same light is supplied by lamps with different powers (a difference of approximately 5 times). So, for example, a 100-watt incandescent light bulb works the same as a 20-watt energy-saving light bulb.
| incandescent lamp | Energy saving lamp |
| 25 | 5 |
| 40 | 9 |
| 60 | 11 |
| 75 | 15 |
| 100 | 20 |
| 120 | 23 |
Light flow
 The efficiency of the lamp is also determined by another important characteristic feature of energy lamps - light movement, with a unit of measurement lm (lumen). It depends on how bright the device shines. Human eyes do not perceive even the most powerful ultraviolet or infrared radiation.
The efficiency of the lamp is also determined by another important characteristic feature of energy lamps - light movement, with a unit of measurement lm (lumen). It depends on how bright the device shines. Human eyes do not perceive even the most powerful ultraviolet or infrared radiation.
Plinth type
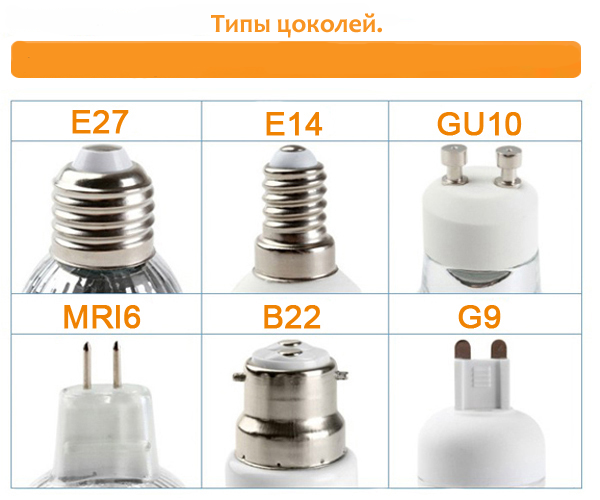 The base is the most important part and feature of energy-saving lamps. When buying it, you should consider the base, it must match the cartridge.
The base is the most important part and feature of energy-saving lamps. When buying it, you should consider the base, it must match the cartridge.
There are various brands of plinths on the market: pin and threaded, with sealed contact and non-standard. The table below gives general information about the types of socles.
light temperature
 Qualitative parameters include color temperature (measured using the Kelvin temperature scale (denoted by "K")), which determines the naturalness (whiteness) of the illumination emanating from the lamp.
Qualitative parameters include color temperature (measured using the Kelvin temperature scale (denoted by "K")), which determines the naturalness (whiteness) of the illumination emanating from the lamp.
There are the following color temperatures:
- warm white (less than 3000 K),
- neutral white (from 3000 to 5000 K)
- day white (more than 5000 K).
 For residential premises it is better to use lamps with warm shades. They relax and soothe. AT office space cold tones are better suited. The color temperature from 2800 to 3500 K is considered natural and most pleasant for a person.
For residential premises it is better to use lamps with warm shades. They relax and soothe. AT office space cold tones are better suited. The color temperature from 2800 to 3500 K is considered natural and most pleasant for a person.
Light output
 In the matter of energy saving, the main parameter of electricity performance is considered to be luminous efficiency, measured in lm / W. Through this indicator, the amount of light produced by the device is set.
In the matter of energy saving, the main parameter of electricity performance is considered to be luminous efficiency, measured in lm / W. Through this indicator, the amount of light produced by the device is set.

The maximum level of light output is 683 lm/W. Previously, the output was 10-15 lm / W, and now it is 100 lm / W.
Light level
An indicator that determines the illumination of a certain surface is called the level of illumination (measured in lux (lux)). The norm of illumination of the working surface in Russia is 200 lux, in Europe it is 800 lux.
Color rendering index
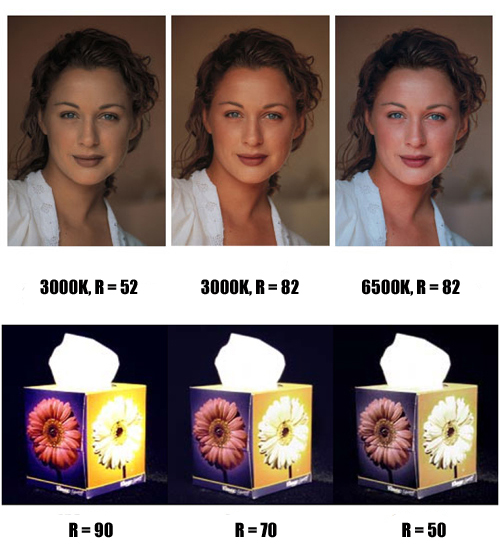 The color rendering index determines the figure of the natural transmission of the tone of the illuminated objects. The color rendering of light bulbs depends on the spectral radiation. A lamp with an absolutely correct reproduction of the color spectrum of objects is assigned the Ra index. A decrease in the Ra index indicates a deterioration in color rendering properties.
The color rendering index determines the figure of the natural transmission of the tone of the illuminated objects. The color rendering of light bulbs depends on the spectral radiation. A lamp with an absolutely correct reproduction of the color spectrum of objects is assigned the Ra index. A decrease in the Ra index indicates a deterioration in color rendering properties.
Term of the work
 The performance characteristics include the duration of the lamp, the speed of switching on and their number (guaranteed), design parameters. These characteristics show the cost of use, which determines the benefit of buying a lamp.
The performance characteristics include the duration of the lamp, the speed of switching on and their number (guaranteed), design parameters. These characteristics show the cost of use, which determines the benefit of buying a lamp.
Labeling of energy-saving lamps
 Before buying an energy-saving lamp, you should pay attention to the markings on the packaging. Russian manufacturers, following legal standards, use a letter as a marking for fluorescent lamps, foreign manufacturers use numerical values. The table below shows the markings of domestic and foreign lamps:
Before buying an energy-saving lamp, you should pay attention to the markings on the packaging. Russian manufacturers, following legal standards, use a letter as a marking for fluorescent lamps, foreign manufacturers use numerical values. The table below shows the markings of domestic and foreign lamps:
| RF marking | Foreign marking | Characteristic |
| L | luminescent; | |
| B | 835 | white color; |
| 33 | Cold white | |
| LD | 54 | Cold daylight (in blue) |
| TB | 29,827830/930 | warm white; yellowish |
| D | 765/865/965 | daytime color; |
| C | 880 SKYWHITE | with improved color rendering; |
| E | with improved environmental friendliness; | |
| 76/79 | for meat counters | |
| 89 | for aquarium | |
| 77 | for plants | |
| 08 | for checking banknotes and interior lighting | |
| 15 | red | |
| 16 | yellow | |
| 17 | green | |
| 18 | blue |
In addition, the labeling of energy-saving lamps indicates:
- power strength (20 W),
- color temperature (85w 6400k),
- plinth type (gu3),
- halogen lamp (mr 16),
- reflector lamp (r 80).
Countries producing energy-saving lamps
| Producing country | The name of the company that produces energy-saving lamps |
| Russian Federation | Space |
| Germany | Osram |
| Denmark | Comtech |
| USA | General Electric |
| Japan | Hitachi |
| PRC | Zeon |
| Netherlands | Philips |
Scheme of the energy-saving lamp
 The main part of energy-saving lamps is a bulb, inside of which spirals are soldered on both sides. They are covered with an oxide layer in order to create thermionic emission (when voltage is applied, the spirals begin to heat up to the desired temperature, from which electrons appear). The flask contains mercury vapor, which collides with electrons, forming ultraviolet radiation. It leads to a bright glow of the phosphor and a person sees the electric light that is familiar to him.
The main part of energy-saving lamps is a bulb, inside of which spirals are soldered on both sides. They are covered with an oxide layer in order to create thermionic emission (when voltage is applied, the spirals begin to heat up to the desired temperature, from which electrons appear). The flask contains mercury vapor, which collides with electrons, forming ultraviolet radiation. It leads to a bright glow of the phosphor and a person sees the electric light that is familiar to him.
For longer lamp life, it is better to use non-constant voltage. The electrons moving in the bulb are the cathode and the anode. With a long lamp operation, the electrons will overheat, due to which the oxide layer will quickly collapse. After the destruction of the oxide layer, the resistance of the electrodes will increase and the luminous flux of the lamp will decrease. When the electrodes are destroyed the lamp stops working.
Energy-saving lamp failures

| № | Energy-saving lamp failure | Solving the lamp breakage problem |
| 1. | Increasing the voltage leads to swelling and leakage of the capacitor, the lamp will stop working. | Such damage requires replacement of all semiconductors. |
| 2. | Increasing the voltage breaks the capacitor. The device begins to glow in places where the filaments are left. | This damage is corrected by replacing the capacitor. |
| 3. | Improper operation leads to an uneven distribution of the light flux. The flask is partially sealed. | In this situation, the lamp is defective. |
| 4. | When the filament burns out (one is enough), the lamp does not work. First you need to check the capacitor. | In place of a broken glow, the diode is replaced by a resistor by soldering. |
| 5. | A malfunction of the diode thyristor leads to a breakdown of the device. | The defective element must be replaced. |
Repair of energy-saving lamps
You can start repairing energy-saving lamps by finding out the cause of the malfunction and making sure that there are spare parts that will be installed in place of the damaged ones.
Next, using a screwdriver, disassemble the bulb housing. Then disconnect the wires coming from the flask. Cut both wires supplying the electrical device. Digital pliers check the spirals of the flask. If at least one filament burns out, the bulb is considered defective and the lamp must be disposed of.
With working spirals, you can restore the device. When purchasing parts to replace burnt ones, you need to choose models of the same marking as the faulty device.
The main task of any lighting device is to create the appropriate level of lighting. But, since the lamp consumes electric current, and it is not cheap, the second important parameter when choosing is power. As far as incandescent or halogen lamps are concerned, the ratio of power and luminous flux intensity was connected by a simple correspondence.
But when it comes to energy-saving devices, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarity of their design.
Fixture device
- The light source in an incandescent lamp is a wire conductor. Under the influence electric current it gets hot and starts glowing. The conductor is placed in a glass flask filled with an inert gas and halogens. The design contains a fuse that prevents the destruction of the bulb when the filament breaks.
There are a great many varieties of the device and, despite the relatively low efficiency of work and fragility, they are unlikely to leave the market soon. The fact is that such a lamp is insensitive to voltage drops, which compares very favorably with modern advanced devices that are sensitive to this indicator.

- LED lamps have a fundamentally different structure. Here, the incandescent body is a semiconductor that generates optical radiation when an electric current is passed. The color of the light flux - red, blue, determined chemical composition LEDs. To get a white familiar light, different LEDs are combined in the lamp and light filters are installed.
The power of the luminous flux is much superior to that of an incandescent lamp, as well as durability. However, this device also has its weak point - ballasts. The fact is that a semiconductor needs D.C., while the power grid supplies AC. And the converters, the better, the more dependent on the quality of the source current. Pictured is an LED lamp.

Basic concepts
For conventional lighting devices, the power consumption is equivalent to the intensity of the light flux. But as soon as the lamps began to improve, the direct relationship began to change. And now main characteristic is the luminous flux power.
This value corresponds to the amount of light energy in the measured light flux. The unit of measurement is lumens. This characteristic exactly indicates what level of illumination will be when installing an LED lamp or any other with a specified value.

The correspondence between the power consumption, that is, the amount of electric current that is necessary for the operation of the device, and the intensity of the light flux for different devices is different.
Value ratio
The correspondence between the power of LED lamps and energy-saving lamps to incandescent lamps is approximately considered as 1:10, which is not true. Firstly, the bulb on such devices is matte, since the light in a powerful diode device is dazzling and resembles welding. And, therefore, the intensity of the light flux that enters the room is reduced by 20%. Secondly, approximately 1W is required to ensure the operation of the electronic driver.
The correspondence table looks like this.
| Incandescent lamp, W | Energy saving, W | LED lamp, W | Stream of light, Lm |
| 20 | 4 | 3 | 250 |
| 40 | 9 | 5 | 400 |
| 60 | 15 | 10 | 950 |
| 100 | 20 | 14 | 1300 |
| 200 | 30 | 22 | 2100 |
A simple comparison of the values demonstrates the efficiency of LED lamps: at the same level of light output, they consume 7 times less electric current. However, when replacing conventional appliances with LEDs, there are several other factors to consider.
A semiconductor generates directional radiation, which is why it is considered the best option for street lighting: all the luminous flux is directed to the sidewalk and the road, and not to the surrounding air. However, when lighting a room, this feature is not always useful. Manufacturers for household appliances offer products in which the diodes form a pyramid or even a cylinder: here the lighting will be the most uniform.

The durability of the device is determined not so much by the quality of the semiconductor - it is extremely difficult to destroy it, but by the operating time of the control gear. And the latter does not like voltage drops or low voltage and can fail long before the expiration of the specified period.
The main advantage of LED light sources is significant energy savings. You can get tangible and desired results using the products of the Svetovoy online store.
Energy-saving fluorescent lamps, which have already become familiar to many, are gradually becoming a thing of the past. It is being replaced by lighting equipment of a fundamentally new type, with different light and quality characteristics. Modern LED light sources have a whole range of advantages over their predecessors. This applies to light output, energy consumption, service life, environmental friendliness, fire and mechanical safety. The "minuses" that make their implementation difficult include the higher cost and the conservatism of a certain part of the population.
To overcome doubts, it is enough to turn to table of correspondence of power of LED lamps characteristics of light sources of the previous generation.
Table comparing characteristics of lamps: incandescent, halogen, energy-saving and LED lamps
|
Name |
incandescent lamp |
Halogen lamp |
Fluorescent Lamp |
Light emitting diode (LED) lamp |
|
Virtually no heat |
||||
|
vandalism |
Very fragile |
Virtually unbreakable |
||
|
Power, W) |
||||
|
Luminous flux (Lm) |
||||
|
Service life (hour) |
||||
|
Electricity fee per year (rub) with 20 lamps in an apartment (at the rate of 4 rubles / kW, 5 hours a day) |
The table of correspondence between the luminous efficiency of energy-saving (fluorescent) lamps and incandescent lamps corresponds to
LED and Incandescent
It should be noted that the table figures are averages and may differ for specific products. However, the conclusions are clear. Traditional, but obsolete, uneconomical light bulbs lose significantly. The given table of correspondence of the power of LED lamps, even taking into account the inevitable error, convincingly proves the advantages of the new generation systems. To this must be added a long service life, due to their design features and providing a quick and repeated payback. Analysis of tabular data, simple calculations show: the present and the future are behind the LEDs!



