Underground electricity input. Underground cable entry to the house
Underground cable gland to the house is a reliable option for supplying electricity to a private house, but at the same time the most expensive undertaking. The counterbalance to reliability can be considered the inconvenience associated with repairing the cable in case of damage. After all, for this it will be necessary to dig a hole, look for a problem, then bury this hole again, and if all this happens in winter period, then frozen ground will add problems.
Scheme of underground cable entry into the house
Of course, it would be possible not to mess with this method, but to conduct electricity to the house by air, but in practice there are various situations when this is not possible. For example, interfere tall trees, which are not possible to cut down or the support from where it is supposed to pull the cable is too far.
The depth depends on the power load on power cable laid from a power line support (power line): for 20 kW, this depth should be 70 cm, and for 50 kW, one meter. For laying the cable, plastic pipes and, in some cases, metal pipes are used, laid on bricks laid out tightly to each other in a row.

Armored cable VBBSHV with copper conductors
On the support, the cable is protected by pipes up to a height of two meters, and armored cable VBbShv is used in this section. The cable rises along the wall to a height of 2.75 m and at the same time about two meters of its length must be protected by a pipe. And in this case also its armored variant.
For reference
Armored power cable VBBSHV has copper conductors with PVC insulation, which are reliably protected by two metal tapes. The upper tape is positioned so that its turns overlap the gaps of the lower tape.
In principle, it is possible to make a completely underground cable entry into the house from an armored cable, however, its price per linear meter is twice as much as the VVG cable. Although manufacturers do not recommend using it for underground electricity supply, therefore the last word remains with the owner of the house.
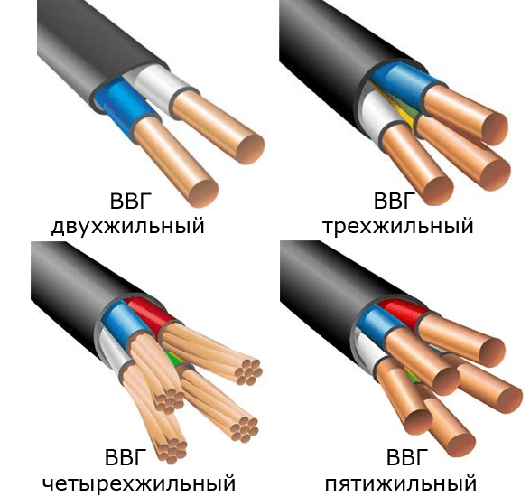
VVG cable
It is possible to carry out the supply of electricity through the foundation or directly above it, but in no case under the foundation. To do this, first, during the arrangement, a thick-walled metal pipe is laid into it, through which the input is made. If the cable is laid over the foundation, then asbestos-cement or PVC pipes can be used. Many at the input site on the wall of the house insert a two-pole circuit breaker (AZ) into the cable break.
Theoretically, an underground spur appears to be a more stable and safe type of spur that is not subject to wind loads, icing breaks, touching long objects, or the passage of an oversized vehicle. But all this is true only if the entire underground branch passes through your site. Imagine that some part of your underground branch runs along the street or, God forbid, along a neighboring site, and your neighbor decided to connect to the water supply and hired guest workers to dig a ditch just through the place where your underground branch line passes ...
The beginning and end of the underground branch from the overhead line must be laid in a protective metal pipe that emerges from the ground to the support and to the steppe of the building to a height of at least 1.8 m. Part of the underground branch between the initial and final pipe is entirely in the ground and may not be protected by the pipe. Ideally, if on a support or on a wall of a building, the pipe will reach the VU cabinet. In the ground, the initial and final pipes should reach a line laying depth of 0.6 ... 0.8 m and have a horizontal section, the length of which is not negotiated . That is, both pipes must have L-shape. It is very useful to protect with pipes and a section of the underground line between the initial and final pipe. Pipes should not be butted. Between them it is better to leave a gap of several centimeters or make it so that the pipe sections fit one into the other.
Underground lines are never made of separate conductors, this requires a cable. After laying the underground branch, the trench is covered with sand, and then with seeded pounds without solid inclusions and foreign objects. Of decisive importance for the underground branch cable is the strength of the outer insulation. Copper is recommended as the conductor material for the cable. There are no restrictions on the minimum size of the cross section of the conductors, based on strength considerations, like overhead cables, for underground cables. The most commonly used sections are 6 and 10 m / t. IN this case the margin does not hurt, therefore it is recommended to use a copper cable with a core cross section of at least 10 mm 2. The industry produces a special armored cable of the VBbShv type (wrapped with a steel tape with a PVC insulation sublayer), which comes with three, four and five conductive cores. Steel protective pipes are selected with such a diameter that the cable occupies no more than 50% of their internal section.
We are waiting for you in the office for a free consultation on engineering networks!
Foreword
Correct input electricity to the house guarantees an uninterrupted supply of energy for the operation of all household appliances.
Content
 Proper input of electricity into the house guarantees an uninterrupted supply of energy for the operation of all household appliances. The introduction of electricity to the site begins with the approval of the project and the receipt of technical specifications from the energy supply organization. Then the introduction of electricity into a private house provides for the organization of all components of the internal network. Installed meters and distribution devices. Direct input to the house of electricity is carried out by specialized contractors. But in terms of primary preparation, the input of electricity can be carried out partially on its own.
Proper input of electricity into the house guarantees an uninterrupted supply of energy for the operation of all household appliances. The introduction of electricity to the site begins with the approval of the project and the receipt of technical specifications from the energy supply organization. Then the introduction of electricity into a private house provides for the organization of all components of the internal network. Installed meters and distribution devices. Direct input to the house of electricity is carried out by specialized contractors. But in terms of primary preparation, the input of electricity can be carried out partially on its own.
Scheme of entering electricity into the house
The scheme for introducing electricity into a house is strikingly different from the electrification of a home in apartment building. Living in an apartment, you may not know anything and not even guess about the existence of all kinds of input devices, gas grounding buses, electrical panels and other equipment, and entrust all issues related to electricity to the Housing Office, Homeowners' association, etc. Being engaged, you will have to decide everything yourself, including delving into the many subtleties of the operation of electrical equipment. It is also important to consider that the apartment is a relatively small room with almost the same microclimate.
A private house is literally given over to all the elements - heat, frost, wind and precipitation, which, in turn, has a lot to do with a stable supply of electricity. In addition, on suburban area Electricity is connected not only to residential buildings, but also to various outbuildings.
As a rule, electrical work begins simultaneously with construction. Before building a house, you should think carefully about how to bring electricity to the site.
Two electrical inputs
There are two inputs of electricity to the house: air and underground. The most common is the laying of an overhead line from a power transmission line (TL) to the house.
First, you should determine the distance between the support and the wall of the house through which the input will be made.
All work on connecting a private house to a power line can only be performed by a specialist of the organization that owns this line.
Pipe stand for input of electricity
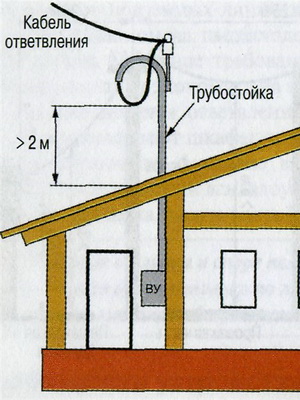 If it is more than 20 m, then you will have to put an additional support in the middle - between the house and the support pole, since the cable can break under its own weight or under the influence of wind and precipitation. A cable is pulled from the support to the wall of the house to support the cable and prevent it from sagging. This structure is called a pipe rack for introducing electricity into the house by air.
If it is more than 20 m, then you will have to put an additional support in the middle - between the house and the support pole, since the cable can break under its own weight or under the influence of wind and precipitation. A cable is pulled from the support to the wall of the house to support the cable and prevent it from sagging. This structure is called a pipe rack for introducing electricity into the house by air.
The conductor is attached to the cable with clamps. If the cable runs over the carriageway, then it must be at a height of at least 6 m from the ground, if above pedestrian roads - at a height of at least 3.5 m. It is not allowed to pass the cable through thickets of bushes and tree crowns. The point of attachment of the line to the wall is located at a height of at least 2.75 m.
The input of energy into the house must be organized as carefully as possible, the reliability of the power supply of the house and its safety depend on this. The cable can be laid in several ways.
Air power input
 The air input of electricity is carried out as follows: the cable is attached to special insulators, which are attached to the wall with a hook (if the wall is wooden) or special fasteners (if the wall is made of stone). Then the cable is passed through the wall through a metal pipe; for its free passage, it is advisable to choose a larger pipe diameter.
The air input of electricity is carried out as follows: the cable is attached to special insulators, which are attached to the wall with a hook (if the wall is wooden) or special fasteners (if the wall is made of stone). Then the cable is passed through the wall through a metal pipe; for its free passage, it is advisable to choose a larger pipe diameter.
To prevent rain from entering the pipe through which the cable enters the house, its end can be slightly pushed out of the wall and bent down.
If a cable is used, you can limit yourself to one metal pipe. When using a special SIP wire, a plastic one is inserted inside the metal pipe, since this conductor does not have an outer sheath, but only core insulation. To close the opening of both pipes, special sleeves are put on them. Gap between cable and inner surface pipes are filled with mineral wool - it serves as an additional insulation and insulator.
Inside the house, the cable is inserted into the house shield and connected to the control and protection circuit breakers.
Air cable laying
In order to carry out the air laying of the cable, a special metal pipe-riser is used, which serves both as a channel for the cable and as a support for fastening the insulators. Mounting insulators to such a rack is much easier than to the wall of the house. You can use fasteners for metal - self-tapping screws or bolt clamps. The pipe rack for the input of electricity is connected to the ground wire. The cable itself must be located at least 2 m from the roof surface. For laying an overhead line, almost any type of cable or wire is used, the main thing is that its characteristics satisfy the conditions of outdoor wiring.
The choice of SIP wire for electrical wiring
Until 1991, AC wires without insulation were used for laying the overhead line. Now the choice of SIP wire has been replenished with another sample designed specifically for overhead lines. Its insulation is designed for large temperature differences and resists sunlight well. In addition, such a cable is not stretchable, it can be laid without a supporting cable. The choice of wire for electrical wiring is quite simple: there are two types of SIP - two-core and four-core. The most common varieties are SIP 4 x 16/25 and SIP 2 x 16/25. The numbers indicate the number of cores and their cross section. There are many additional accessories for this cable. They are used to connect the wire to the mount, they are very convenient and do not require much effort during installation.
Underground electricity input to the house underground
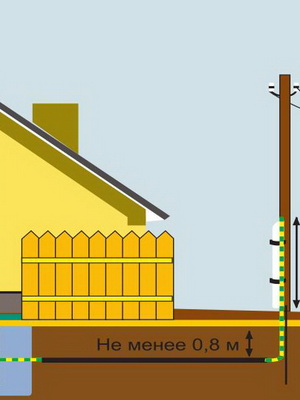 Underground input to the house of electricity is considered safer, since the cable is in the ground and is not affected by weather and climatic conditions. However, the input of electricity underground is the most laborious: to lay the cable, it is necessary to dig a trench at least 0.7 m deep.
Underground input to the house of electricity is considered safer, since the cable is in the ground and is not affected by weather and climatic conditions. However, the input of electricity underground is the most laborious: to lay the cable, it is necessary to dig a trench at least 0.7 m deep.
To begin with, the L-shaped bent pipes that protect the cable are attached to the support and the wall of the house - for this, one end of the pipe rises to a height of at least 1.8 m. The other end goes into the ground to the depth of the cable (usually this distance is 80 cm). It is best when the cable is protected by a pipe along the entire installation path. However, if there is no pipe of sufficient size, you can limit yourself to protecting the cable entry into the ground and in the open air. This is the easiest and cheapest way to run a cable underground.
Selection of the section of high-voltage wires according to the load
The selection of the wire cross-section according to the load is preliminarily made, taking into account the requirements of safety engineering. For laying in the ground without protection, the armored VBBSHv is best suited. If you decide to use VVG, AVVG or their modifications, it is better to protect the cable all the way with steel or plastic pipes. Select the diameters of the pipes so that they fit into each other, the border of the joints can be wrapped with a cloth and impregnated with resin or bitumen. Then you do not have to weld the pipes together, which is not only long, but also expensive.
The choice of high-voltage wires should be carried out taking into account the fact that the cable can be introduced into the building without lifting it to the wall, but hidden in it above the foundation. In this case, a hole is drilled in the wall slightly below ground level, where asbestos-cement pipes are embedded, through which the cable enters the house.
If there are several conductors, then there should also be several such pipes. The depth of the trench depends on the power of the supplied energy. If it does not exceed 20 kW, you can limit yourself to a depth of 70 cm, at 35 - 45 kW the depth should be at least 1 m. A depth of 1 m is also required if the cable passes through the road. When laying cables in plastic pipes enough depth of 50 cm.