Timing of ventilation checks in apartment buildings. We check the operation of ventilation. Backdraft due to kitchen umbrella
No one pays attention to ventilation if it functions properly. As a rule, exhaust vents are installed in the kitchen, bathroom and toilet. Air flows arise due to the difference in temperature inside the building and outside. At the same time, an influx of fresh air is necessary to ventilate the premises.
In the event of a malfunction, ventilation must be checked.
Kitchen
Cooking is carried out in this room and products of gas combustion and specific odors constantly appear. If a malfunction occurs in the hood, they spread to all rooms and remain there for a long time. In addition, the soot generated from the combustion of gas will be deposited on all surfaces. Most of it remains in the kitchen.
Bathroom
Violation of ventilation in the bathroom leads to an increase in humidity. At the same time, dark spots of mold appear in the corners, on the walls and ceiling, which is harmful to health.
High humidity is immediately felt by a person, and in this case, a ventilation check is necessary.
Toilet
If the hood in the toilet is clogged, being in it becomes unpleasant, and the smells from the bathrooms will spread throughout all the rooms of the apartment.
How to check for traction in a simple way
Ventilation is checked periodically as soon as dust appears on the grilles. To do this, they are removed and washed from dirt. After the lattice is installed back and the transom or window is opened slightly in the kitchen or in the room nearby. If the test is carried out in a bathroom or toilet, the doors are left open to create an air flow. To check the effectiveness of the hood, a sheet of paper is applied to it. He should "pull" to her, which is a signal of the presence of traction. Piece toilet paper must be held on the grate by itself. In another way, you can check for thrust by deflecting the flame of a lighter or candle. The procedure is repeated in all areas. Ventilation cleaning is required if the sheet is not attracted to the grate.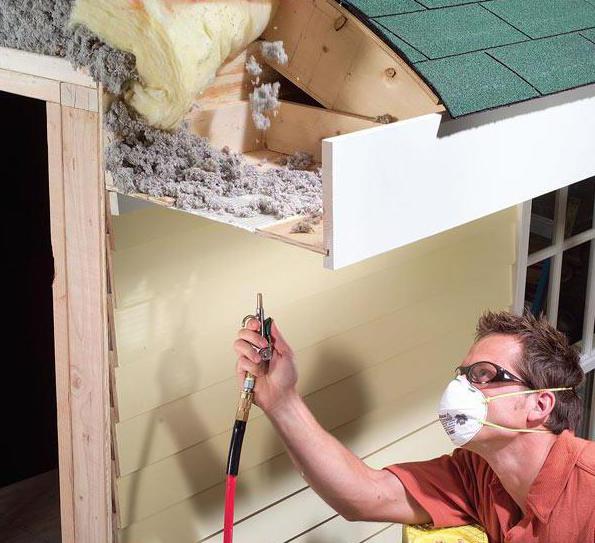 
You need to know that in hot weather the draft in the ventilation duct deteriorates and it is useless to check it. It depends on the temperature difference between the room and the outside. In this case, forced ventilation is activated.
How to properly organize ventilation in the apartment
The lack of fresh air in the apartment can also be the reason for its poor circulation. This became especially noticeable with the replacement of windows with plastic ones, which are distinguished by their tightness. In this case, residents need to resolve this issue on their own. Ventilation is improved as follows:
- frequent ventilation of the premises;
- micro-ventilation of plastic windows;
- Installation of air conditioner;
- the use of supply valves;
- application of supply and exhaust forced ventilation.
The reason for the lack of traction may be residents living upstairs, or when the system is overloaded from an enterprise built on the ground floor, such as a store or cafe. Here, even a ventilation check is required, since extraneous odors appear in the apartment. In both cases, you need to seek help from the housing office.
Rules for cleaning ventilation ducts
Do-it-yourself cleaning of ventilation is prohibited, since the mine is serviced by specialists from the management company on the roof or technical floors. She is usually approached with complaints about the lack of traction. When calling specialists, you should warn your neighbors about this, since when cleaning the mine, dust can fall into the apartments through the ventilation openings.
When an independent check of ventilation is made, it is only allowed to clean the channel leading from the apartment to the main shaft. To do this, perform the following operations.
- Move furniture, cover the floor and close the wall in the work area.
- Remove, clean and, if necessary, replace the grate.
- Wearing gloves on your hands, carefully remove the debris from the ventilation duct and remove the residue with a vacuum cleaner. It is better to remove debris with a tool such as a spatula so as not to get hurt by sharp fragments.
- Install the grille back and check for draft by opening the window.
Additional ventilation device
When the ventilation of the house is working properly, but there is not enough fresh air, the following measures are required to improve the microclimate.
- Plastic windows are airtight, but it is advisable to purchase window systems with a micro-ventilation function.
- The supply of fresh air can be ensured with the help of valves, gratings, filters, heaters and supply forced fans.
- Partially help out the air conditioner, refreshing and drying the air.
- Install
When choosing a way to ventilate rooms, you should determine its effectiveness and which devices are already working. Must be checked first exhaust ventilation and identified the need to install additional equipment that improves the quality of its work. 
No matter how efficiently the hood works, fresh air is needed. To do this, valves are installed behind the batteries. The diameter of the openings facing the street is 6-10 cm. A plug is installed in them, which can have manual or automatic control. The incoming air can be cleaned using filter elements installed in the valves.
Ventilation is classified according to the following criteria:
- forced or natural movement of air in the premises;
- exhaust or supply type of device;
- what kind of service is provided: local or general house;
- the presence of channels for air transmission;
- type-setting or monoblock design.
The choice depends on the area and purpose of the premises, the number of equipment and people in it, and the type of their activity. In all cases, natural exhaust is preferred as it is the most economical option.
How ventilation systems are checked
Ventilation systems are subject to inspection, which can be emergency or scheduled. Checking their work is done using an anemometer. It is introduced into the ventilation duct, while ensuring the flow of air into the room. 
In the branches of the mine, the air velocity must be at least 3 m/s.
The measurement results must be recorded.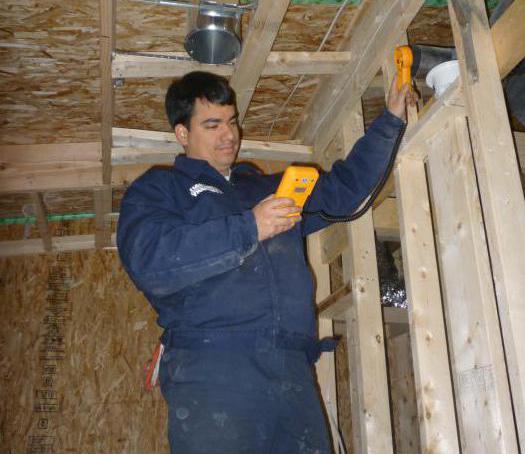 
They are recorded by devices, and then an act of checking ventilation is drawn up. It should provide data on how efficiently the system is performing and whether it meets design standards.
Conclusion
Checking the ventilation in an apartment is a simple operation that must be done in order to maintain optimal microclimate. ![]()
In case of violations in its work, you need to know what the owner of the home can do and in what cases he should contact the management company.
According to existing standards, each dwelling (apartment) must be equipped with ventilation, which serves to remove polluted air from the non-residential premises of the apartment (kitchen, bathroom, toilet). Ventilation is the movement of air, air exchange. Every person uses the stove during the day, does laundry or washes, goes to the toilet, many smoke. All these actions contribute to air pollution in the apartment and its excessive saturation with moisture. If the ventilation is working properly, then we do not notice all this, but if its performance is impaired, then this results in a big problem for those living in such an apartment - the windows on the windows begin to fog up and condensate flows onto the windowsill and wall; the corners are damp, and mold appears on the walls and ceiling; linen dries in the bathroom for 2-3 days, and when using the toilet, the smell spreads throughout the apartment. Plus, if there is a baby or a very small child in an apartment without ventilation, then sometimes one or two years of being in such conditions is enough for him to develop bronchial asthma or other respiratory diseases.
In order to find out whether ventilation works or not, you do not need to be a specialist. Take a small piece of toilet paper (10cm x 10cm). Open a window (window) in any room and bring a prepared piece of toilet paper to the ventilation grill in the bathroom, kitchen or toilet. If the leaf is attracted, the ventilation works. If the sheet does not rest on the grate and falls, the ventilation does not work. If the sheet is not attracted, but rather deviates from the ventilation grill, it means that you have a reverse draft and you breathe foreign odors, which means that the ventilation does not work.
Ventilation can be checked or measured. It is measured with a special device - an anemometer. This device shows how fast the air moves in the ventilation duct. Having a calculation table in hand, you can substitute the values of the anemometer and the cross section of your ventilation grill into it and you will get a figure that will tell you how many cubic meters of air per hour (m3 / h) passes through the ventilation grill. But that is not all. When checking, there are many conditions that cannot be ignored, otherwise the measurement data will be incorrect.
According to the “Methodology for testing the air exchange of residential buildings”, measurements are carried out at a temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air = 13 ° C (example: outside + 5 ° C; in the apartment + 18 ° C), and at the same time, the air temperature outside should not be higher than + 5 ° C.
The fact is that during the warm season, ventilation works worse and nothing can be done about it, because these are the laws of physics on this planet. If measuredventilation at a temperature warmer than +5°C, then the obtained measurement data will be incorrect. And the warmer the outside temperature is, the further the measurement data will be from the normative ones. In extreme heat, in some cases, even absolutely perfect ventilation may stop working or even work in the opposite direction (reverse draft).
To understand why this happens, we must remember what each of us heard at school in physics lessons. The lower the temperature, the greater the air density, i.e., the air is heavier. Therefore, the highest air density in winter is in frosty weather, and the lowest in summer.
Therefore, if in an apartment, for example, the temperature is + 18 ° C, and on the street -3 ° C, then warmer (lighter) internal air through the ventilation duct will tend from the apartment to the street. As the temperature rises outside, specific gravity outside and inside air will begin to equalize, which means that the draft in the channel will begin to weaken. And, if the temperature in the apartment is, for example, + 24 ° C, and the temperature outside is below + 30 ° C, then the cooler (heavier) internal air will simply not be able to rise up and exit through the ventilation duct into the atmosphere. It will be much easier for him to move not up, but down, that is, as if to “flow out” of the apartment.
That is why in hot weather there is a high probability that ventilation can give back draft, although in this case it cannot be considered faulty, because in these conditions, according to the laws of Nature, it could not work.
So, you can measure ventilation only if it works. But first you need to find out if it works.
As already mentioned, anyone can do this - it does not require much effort. To do this, you need a small piece of toilet paper. No need to take a sheet of newspaper, magazine or cardboard. Why?? According to existing standards, the kitchen (with an electric stove), bathroom and toilet are supposed to be: 60, 25 and 25 m3 / h, respectively. To achieve these values, a relatively low air velocity through the ventilation grill is required, and such movement can only be detected with a thin sheet of paper (it is better if it is toilet paper). In some apartments, a piece of thick, heavy paper can also attract, but this suggests that the ventilation in this apartment works so well that it exceeds the required rate. There is one more thing to consider here. necessary condition traction checks. According to the same “Method of testing the air exchange of residential buildings”, when checking ventilation, in one of the rooms, the window sash is slightly opened by 5–8 cm and the doors between this room and the kitchen or bathroom are opened.
We happened to be present at many commissions that met to assess the state of ventilation in various apartments and, sometimes, we had to observe how a representative of the inspecting organization checked the ventilation with the window closed. This is mistake!! In our country, ventilation in residential premises is forced-air and exhaust with a natural impulse, that is, not forced, not mechanical. And all air exchange rates were calculated specifically for natural ventilation. And in order for the air to go into the ventilation grill, it must come from somewhere, and, according to the norms, it must come (enter) the apartment through cracks in windows, doors and other structures. In the early 1990s, hitherto unseen plastic windows with sealed double-glazed windows and metal doors with seals. Undoubtedly, these products are not like our old wooden windows with their eternal drafts, but one problem has arisen here - new technologies have come, but the norms have remained old and, according to these norms, the air flow into the apartment is carried out through cracks and leaks, and new double-glazed windows completely eliminate these leaks . So it turns out that hermetic windows and doors create conditions in the apartment under which ventilation cannot work normally. And then, feeling the lack of fresh air in the apartment, people come up with another problem for themselves - they install fans.
Let's describe a situation that we often encountered. So, let's take an ordinary two-room apartment ("Khrushchev") with total area 53 m2. This apartment has a metal door with a seal and plastic windows. There are also two ventilation ducts - one for the bathroom, and the other for the kitchen and a “hood” above the stove is connected to the kitchen ventilation duct (one can say a classic situation). Now "hoods" (ie, an exhaust hood over the stove) are so powerful that at the maximum working position their capacity according to the passport is 1000 m3 / h and even more. Now imagine that in such a sealed room, the hostess decided to cook something and turned on the “hood” above the stove at full power. With a ceiling height of 2 m. 60 cm, the air volume in this apartment is only 138 m3. For the "exhaust", by definition, it will take quite a bit of time to "swallow", let through the cubic meters of air in this apartment. As a result, the “hood” begins to pump air out of the apartment and creates a vacuum, and since the windows and the door are very tight and there is no air to circulate through them, then there is only one place through which air can flow into the apartment - the vent from / node (!!!). In such a situation, even normally working ventilation from the / node (toilet and bathroom) will start to work in the opposite direction (reverse draft). And, since the ventilation within the attic is integrated into a common system, extraneous odors from other floors begin to enter the apartment, sometimes obscenely fetid.
In this case, the solution to the back draft problem is quite simple - open the windows while using the hood. Since you have decided to connect your life with sealed double-glazed windows and the same sealed door, you will have to come to terms with the fact that the air flow into your apartment will be carried out through open window- no other way. Supply devices are able to compensate for the air removed through standard ventilation ducts, but providing a powerful exhaust air with air is a difficult task for them.
It was not uncommon to see such a picture. There is a reverse draft in the ventilation duct, but during the examination it turns out that the duct is absolutely clean, in the attic the horizontal junction boxes (if any) are in perfect order and the shaft leading to the roof is also normal. It turns out that the reason for the "return" is that the ventilation grill is installed on the "passing" channel.
For normal operation ventilation, the ventilation duct of the apartment should begin with a “plug”, i.e., the air entering the duct through the ventilation grill should have only one way - up. In no case should there be a downward movement - either immediately at the bottom of the ventilation grill, or with a small recess, but the channel must be muffled (blocked) in its lower part. Otherwise, there is a high probability that such a channel will give a reverse thrust.
For the most part, this problem is faced by people living in houses of series I I-18 and I-209A. These are 14, 12-storey one-entrance "towers". However, a similar ventilation system is used in 9-storey panel houses and in some brick houses, if the ventilation is not lined with bricks, but mounted with whole concrete panels with channels cast inside.
This system looks like this. There is a collection channel (common shaft) with a diameter of about 240 mm, and satellite channels with a diameter of about 130 mm are located on the sides of the collection channel. Typically, apartments are connected to such a ventilation system "in a run" - for example, the 1st floor to the satellite channel to the left of the shaft, the 2nd floor to the right, the 3rd floor to the left, etc. The ventilation blocks are cast at the concrete goods plant in such a way that the satellite channels (they are also upper stages) communicate with the common mine through windows every 2.5 meters. That is, the air must enter the ventilation grille from the apartment, rise 2.5 meters up the satellite channel, rest against the “plug” and exit through the window into the common shaft (collection channel). But that's the whole trouble, that in these houses there are NO "stubs".
Most likely, the designer provided for the so-called "universal" ventilation unit. The fact is that if ventilation blocks are cast at the factory with a division into “right” and “left” or “for even floors” and “for odd”, then confusion is inevitable during their installation and problems are guaranteed. Therefore, the ventilation unit was made universal, so that during installation the worker would put it without thinking about its geometry. And after the installation, he chose which satellite channel would be used for the “even” floors of the house, and which one for the “odd” ones, and, based on this, the installer had to install plugs into the satellite channels on the spot.
The designer's faith in the conscientiousness of our builders while observing the technological process is truly naive. I myself have worked at a construction site for many years and I know how our apartments are built.
The result is the following. Instead of a ventilation system with a common (transit) shaft and two satellite channels, we have three transit channels in our homes. On the lower floors, this problem is not yet so noticeable, but on the upper floors, if the ventilation grill is installed on such a transit channel, then you should not be surprised by extraneous odors in the apartment. The air flow, rising through the channel and flying past the ventilation grille, will either give a reverse draft, or will greatly impede the removal of air from the apartment. And, if you install a plug, it will cut off the lower air flow and direct it to the collection channel through the provided window. Thus, the ventilation in the apartment begins, as it were, from scratch - without experiencing any obstacles and not burdened by the struggle with other air flows, that is, as it should be.
Sometimes, when people turned to us for help and when describing their problem, they said that they had the last floor in the house, then this was enough to establish the reason for the lack of normal ventilation without leaving the place. Then all that remained was to go out and confirm their assumptions. Believe me, a huge number of people, thousands, suffer from this problem. The fact is that for the normal operation of ventilation in an apartment, it is desirable for air to pass through the ventilation duct at least about 2 meters vertically. On any other floor, this is possible, but on the last one such a possibility is excluded - the attic space acts as an obstacle. There are three ways to bring ventilation from an apartment to the street. The first is that the ventilation ducts go directly to the roof in the form of a pipe head. Almost all houses were built this way until the beginning of the 20th century, and then they began to gradually move away from this method. The reason is the increase in the number of storeys of houses. This method does not interest us, because problems almost never arose with it. The second way - ventilation, reaching the attic, was covered with horizontal sealed boxes, which were connected to a shaft that went out over the roof. The third way (modern) - ventilation first enters the attic, which serves as a kind of intermediate ventilation chamber, and after that it goes outside through one common ventilation shaft.
We are interested in the second and third options. In the second case, the following happens - the air through the channels from all floors rises up to the level of the attic and breaks into a horizontal junction box mounted in the attic. In this case, the air flow hits the cover of the horizontal ventilation box. The air flow deviates slightly towards the ventilation shaft, but if the internal section of the horizontal attic box is insufficient, then an area of \u200b\u200bhigh pressure arises in the box and the air tends to find its way out into any nearest hole. There are usually two such outlets (holes) - a ventilation shaft designed for this and the channel of the upper floor, since it is the closest and is located almost in the box at a distance of only 40-60 cm and it is easier than ever to “push” it in the opposite direction . If the section of the box in the attic is sufficient, but the cover is mounted too low, then the same thing happens - reverse draft - the air flow, due to the small height of the cover, does not have time to deviate towards the ventilation shaft and an impact occurs. The reflected air flow “presses through” the ventilation of the upper floor and all the smells from the lower floors come into this apartment. There are two ways to deal with this - global and local. Global - to increase the cross section of the attic horizontal junction box by changing its height by 2 - 3 times, plus the device inside the box of "cunning" devices, which we call "cuts". But, firstly, this should be done by specialists, and secondly, it is not recommended to increase the section of the duct if the same ducts are attached to the ventilation shaft on the opposite side. The local method consists in the fact that the channels of the upper floor are separated from the general air flow and are separately brought into the shaft over the duct. These individual channels are insulated so as not to disturb the temperature and humidity regime (TVR) of the attic. And that's it - the ventilation in the apartment works.
Now, as for the third (modern) option for removing air. According to this principle, ventilation works in all high-rise buildings (series: P - 44, P3M, KOPE, etc.). The last floors in such houses suffer more often not from reverse thrust, but from weakened one. Instead of passing the norms of 2 meters vertically and then connecting with the general flow, the following happens on the upper floors - the air, entering the channel, passes only about 30 centimeters vertically and, without having time to gain strength and speed, dissipates. Ventilation thus does not disappear, but the air exchange in the upper apartment is greatly reduced. If the entrance and intersection doors of the attic are open (it often happens), then a strong draft arises that can “overturn” the draft in the apartments of the upper floor. To prevent this from happening, the individual channels of the upper floor must be increased. The diameter of these channels is 140 mm. It is necessary to put pipes of the same diameter on these holes, and carefully coat the joints with alabaster. Bring the pipes to a height of approximately 1 meter and tilt them slightly towards the common shaft so that the air flow rising from below, flying next to the removed pipes, picks up and draws air from the channels of the upper floor with the force of its flow.
Each of us has a kitchen in the apartment. Everyone has a stove (gas or electric) in the kitchen. And the vast majority have an exhaust "umbrella" above the stove (in the common people - "hood"). What is the delusion? That so many people consider a "hood" to be the equivalent of kitchen ventilation. Otherwise, how to explain the fact that, when installing the hood over the stove, the air duct from it is led into the kitchen vent, completely closing it?
They do this for several reasons - either they were advised by the builders who did the repairs, or from the full confidence that even so the air is perfectly removed from the kitchen. Plus, sellers of hoods claim that the power of the purchased hood should be selected taking into account the area of \u200b\u200bthe kitchen. Actually, this is all a delusion.
Let's try to figure out where it came from. If you carefully read the various regulatory documents for construction and operation, then a strange pattern can be traced: IN ANY document you will not find the word ... HOOD!
Note: 1) we are talking about normative documents, not reference; 2) hood - a kitchen hood (noun), and not a hood - as an action (verb).
So, if there is no such thing as an exhaust hood in the regulatory framework, then how can air exchange be normalized with its help ??? Nonsense.
Then the end users of hoods have a reasonable question: how is it that hoods exist, but words do not? And everything is very simple, there is a word and hoods, only they are, as it were, "outside the law." And this is due to the fact that ALL residential buildings (99.99%) in Russia (and former USSR) have natural ventilation, or, more correctly, ventilation with natural impulse.
Those. air enters our apartments through leaks in windows, doors and building structures, as well as through special supply valves or channels, but leaves through the ventilation channels located in the kitchen, bathroom, toilet.
How is this related? Let's try to explain. Any building structures or communications are calculated for certain loads. Ventilation is no exception to this list. Our channels have rather limited bandwidth capabilities. IN best conditions their performance is 150 - 180 m3 / h (for comparison: modern hoods have a capacity of 600-1100 m3 / h)
Sorry if we took a lot of your time. Here we come to the confusion. The fact is that there are still norms for mechanical ventilation, which differ significantly from the norms for natural ventilation. For example, air exchange for a kitchen with natural ventilation should be 3-fold, and with mechanical ventilation - 10-12-fold. So, the sellers of hoods apply the norm (10-12 times), without thinking that the hood above the stove and the norms of mechanical ventilation are in no way connected with each other and the hood above the stove has NO RELATIONSHIP TO THE VENTILATION of the premises.
The exhaust hood is not designed to ventilate the kitchen. It is only to remove polluted air located in a small space above the stove. The hood is not able to cope with the air that has risen to the ceiling better than a conventional ventilation duct in the upper part of the room. For the hood, “reaching out” to this air is an almost impossible task. The fact is that the behavior of the air flow during suction and ejection is different. During suction, air is taken from a distance of not more than one diameter of the suction hole, and an air jet is ejected at a distance of fifteen hole diameters. That is why we vacuum the carpet not from a height of a meter, but by pressing the brush. That is why in the heat we direct the fan towards ourselves with the front side, and not the back. That is why the hood cannot "take" the polluted air (odors) that has risen to the ceiling.
The hood during operation removes air above the stove and nearby. This creates air movement in the room, and additional air flows are involved in the mixing process. How much is pumped out of the room, the same amount is supplied for replacement. If the hood has pumped 1000 cubic meters of air, this does not mean at all that the air in the room has been completely renewed several times. The resulting void, which Nature does not like, will be filled with air that came from anywhere - from the window, from other rooms, from cracks. But cooking odors that have risen to the ceiling are hardly involved in mixing and are difficult to remove. It is not for nothing that the instructions for the hoods say that ... "... for the purpose of maximum efficiency, the exhaust hood should be located 60 cm from the electric stove and 75 cm from the gas stove ...". "... During operation of the hood, avoid air currents - this can cause odors to spread throughout the room." If the hood were designed to ventilate the kitchen, then there would be no such recommendations in the instructions, and the exhaust “umbrella” itself would be advised to be installed at the top, instead of a chandelier.
By the way, in the instructions for the hoods there is no mention of how much room it is designed for. This has already come up with the sellers of this product. The area of the room does NOT affect performance. And vice versa, the power of the purchased hood does not follow from the size of the room.
The main factor affecting the performance of the hood is the cross section of the ventilation ducts in our homes.
The vast majority of channels in our country have a cross section of 130 x 130 mm, or a diameter of 140 mm. By attaching mechanical (forced) ventilation to such a small channel, we get a meager effect. More air than such a channel can still not let through, no matter how hard you try. In almost every manual for a fan or hood, a diagram is drawn that shows a curve of performance versus pressure, from which it is clear that the higher the pressure, the lower the performance of the hood or fan. The main factors due to which there is an increase in pressure in the channel and, as a result, a drop in productivity are: irregularities inside the channel; displacement of floor blocks; protruding solution; narrowed section; material and shape connecting ducts; every turn in the airflow path.
As a result, due to the influence of these factors, in the channel and on the approach to it, high blood pressure, and, as you know, the higher the pressure, the lower the performance of the hood. This means that a POWERFUL hood “suffocates” itself. And the more powerful the hood, the more it "locks" itself.
You can connect an exhaust hood with a capacity of 1000 m3 / h, you can 1500 m3 / h, you can 5000 m3 / h (if any), but in all cases the result will be the same - you can push a little more air into the channel and that's it !!! The rest is loss!
Once, on one of the connections of the hood to the ventilation duct with a diameter of 140 mm, in the P-44 series, we specially took with us a cup anemometer for measurements. When almost everything was mounted, they asked the client for permission to experiment a little. The air duct was disconnected and a pre-prepared insert with an anemometer was installed. Extractor hood four-speed "SATA". The fan is centrifugal. The length of the duct is 3.5 meters with two turns. The air duct is plastic, with a diameter of 125 mm. The maximum productivity of the exhaust dome is 1020 m3/h. The anemometer was installed before the last turn (at the very entrance to the ventilation unit). The first speed - the anemometer showed 250 cubic meters / hour. The second speed - indications of 340 cubes/hour. The third speed - indications of 400 cubes/hour. Fourth speed - 400 cubic meters / hour. Bottom line: 1) the difference in performance between the first and fourth speeds is minimal; 2) the channel missed EVERYTHING THAT COULD, which means that the losses are simply huge; 3) the noise at the third and fourth speeds has grown, but there is no sense. And this despite the fact that the walls of the connecting air ducts and the ventilation duct are very smooth!!! Imagine what the performance loss will be if you connect the hood to a ventilation duct, which is made, say, in brickwork!!!
Of course, you can use the hood as a simple fan, but in this case, you should not hope that it will provide you with full air exchange. We do not discourage the purchase of a hood in general and do not claim that this is not a necessary and useless thing. Of course it is not. The only goal that we pursue is the desire to warn the consumer against general delusion. Namely: 1) you should not take the exhaust hood in the kitchen as an equivalent of room ventilation - it has nothing to do with this; 2) when buying a hood, you can not build on the size of the room - these are unrelated things.
It happens. It seemed to work, worked for many years and "suddenly" stopped. Many residents tend to believe that the reason for this is the neighbors who climbed into the ventilation riser and blocked something there. Of course, there are such “craftsmen”. These "specialists" are well aware that current flows through the electrical network, poop flows through sewers, water flows through pipes, but when it comes to ventilation, logic fails them - they cannot understand that there is not a void at all that needs to be filled, there - air is moving.
But it's not about them. If you immediately cut off all the cases when the neighbors really violated the ventilation and try to figure out the rest of the reasons that affected its performance, it turns out that the residents themselves create a huge number of problems with ventilation.
Let's see how it goes. For example, let's take the most common modern scheme of natural ventilation: a) a multi-storey building, b) the ventilation of the house goes to a warm attic and consists of a collection channel (common shaft) and a satellite channel. Houses of the following series are suitable for this scheme: P-44, P-3M, KOPE, P-46, P-55, P-30, P-42, P-43, some monolithic houses and many less common series.
The ventilation in these houses consists of a prefabricated channel (common shaft), which goes in transit from the ground floor to the attic. In addition, for each apartment there is an individual channel (satellite channel), which starts from the ventilation grill in the apartment, then rises one floor and, not reaching the same individual channel of the apartment above, exits through the hole into the common shaft, where the air continues to their movement to the attic and further into the street.
To make it easier to understand this scheme, imagine a full-flowing river with small streams flowing into it. This is the ventilation in question. The river is a prefabricated mine; streams flowing into it are satellite channels.
As tributaries feed a full-flowing river, so satellite channels fill the prefabricated mine with air. If you start blocking the tributaries, the river will become shallow and dry up. If air does not escape from the satellite channels, then the speed and volume of air in the collection shaft will decrease significantly. Since the ventilation system of a house is a chain of interrelated and interdependent links, a violation of one of the links leads to changes in the entire chain, which ultimately turns into problems for the entire ventilation system of the riser, entrance, and sometimes the house.
You can trace all the stages of violation of the ventilation system.
Imagine the most ordinary 17-storey panel house, which is full of them all the time. The ventilation scheme used in these houses is perhaps the best that a person has come up with for residential high-rise buildings. This ventilation system is able to work even in extreme heat. Although by definition it should not work in the summer. In hot weather, according to all conditions and rules, ventilation must stop or tip over (reverse draft). But this does not happen in these houses, because the ventilation duct, which is the prefabricated shaft, has a height of about 50 meters. And due to such a difference in height, and hence the difference in pressure difference between the first and last floor, traction arises. And this drop is not able to "win" even a strong heat. BUT ... only if the conditions necessary for it to work are created for this ventilation system.
Let's try to explain.
One entrance of any multi-entrance building with a warm attic can be represented as a system. Closed and isolated system. Ventilation of any apartment of this entrance is an integral part of this system. That is, the ventilation of each apartment depends on the other apartments in the entrance and, conversely, each apartment affects all other apartments.
The influence of one apartment on its riser or the entire entrance is insignificant and is not able to change the “balance of power”. But this is if one apartment. What if there are several? If there are five, or ten, or twenty, or half. What if more than half? That is, if there are apartments that do not participate in the system (fall out of it), then this system loses its strength, weakens. There is a certain critical point after which it fails. That is, the sum of all air flows entering the attic is not enough to push this air out of the attic into the atmosphere. Because the common exhaust shaft going from the attic to the roof (to the street) is quite impressive in size. And this abyss "wants to eat", i.e. its dimensions are designed for the passage of a certain volume of air, which it does not receive. There is a saying: “You can’t warm the sea with an awl.” This is just our case. As a result, the speed and density of the air flow in such a mine is reduced and the thrust overturns. In winter, the “heavier” cold air sinks, and the outgoing warm air stream (“awl”) is too small for the large size of the mine (“sea”).
A reasonable question arises: “Why does the volume of air emitted through the ventilation shaft into the atmosphere decrease? What is the reason?".
Let's explain on the example of the smallest link common system ventilation - on the example of ventilation of a single apartment.
The apartment has two ventilation ducts. One works for the kitchen, the other for the bathroom (bathroom + toilet). Two channels 24 hours a day pump air out of the apartment into the ventilation. The remote dirty, humid, exhaust air must be replaced by another air - outside, fresh, enriched with oxygen. i.e. INFLOW. Thanks to this circulation, this constant replacement (inflow), normal living conditions are maintained in the apartment.
Only the influx of outside air can be considered normal, full-fledged inflow. The air that comes from landing through the cracks in front door or, who came from the next room (apartment), in terms of quality, nothing better than that air that is already in the apartment. It is just as dirty, damp, it has already been smoked, puffed with toilet freshener and saturated with the “aromas” of the kitchen. It's like in the old joke about the concentration camp: “Today there will be a change of linen. The first barrack changes with the second.”
Previously, the flow into the apartment was mainly carried out through cracks and leaks in our old, terrible, crooked, leaky windows. When replacing these shameful windows with new sealed double-glazed windows, the previous order of air circulation is violated. New windows are very tight, there are practically no gaps in them, which means that the inflow of outside air through them is almost zero. Temporary opening of vents and sashes is self-deception. Ventilation works constantly, which means that the need for inflow is also constant.
Has anyone tried to suck the air out of plastic bottle?? Right. This is impossible. What if you make a hole in the bottle? Then you can pump air out of the bottle indefinitely. The hole is the inflow. A bottle is an apartment with sealed double-glazed windows. When the windows are closed, ventilation cannot work normally. Under these conditions, only two things can happen to her:
a) one of the ventilation ducts of the apartment (a stronger duct) will start pulling the other duct. That is, the second, weaker channel will begin to function as an inflow, which was ruined by the installation of new windows;
b) both ventilation ducts will work as before, and the missing inflow will be compensated through the gaps between other apartments. That is, they will suck into the apartment exactly the same exhaust air that is removed, only with other people's smells.
And so it turns out that: in one case, instead of two normally working apartment channels, we have only one working channel. This means that the volume of air removed from one apartment has decreased by at least half (!!!). In the second case, the channels seem to fill the prefabricated shaft with air, but this is air inside the house, not outside. This means that the channels do not work for the apartment in which they are located and the air circulation in this apartment is disturbed.
Now go outside, look at any house, select any riser of apartments and count how many old windows are left along the entire vertical, and how much plastic ones cost. Those with plastic can be excluded from the general ventilation system of the entrance. This is ballast. Without an inflow, these apartments hang like weights on the legs of the ventilation system. And if in summer or winter (less often in winter) a reverse draft “suddenly” comes out of your ventilation ducts, then you can safely tell them “thank you very much” for this. They tried very hard.
Main conclusion.
You can not thoughtlessly install sealed double-glazed windows. These windows are not on their own. They are part of the ventilation system. It is up to you whether the ventilation will work or not. Decided to install sealed double-glazed windows?? Arrange an INFLOW.
www.ventkanal.ru Vershinin A. A. and Vershinin S. A.
Apartment renovation
In accordance with accepted standards, any living space, including an apartment, must be equipped with a ventilation system, which is necessary to release polluted air and remove unwanted odors from non-residential rooms of the apartment - such as a toilet, bathroom, kitchen.
What is ventilation? In simple words This is air exchange, that is, the movement of air. Any person during the day uses the stove, visits the toilet, some smoke. All of these processes pollute the air and contribute to its oversaturation with moisture.
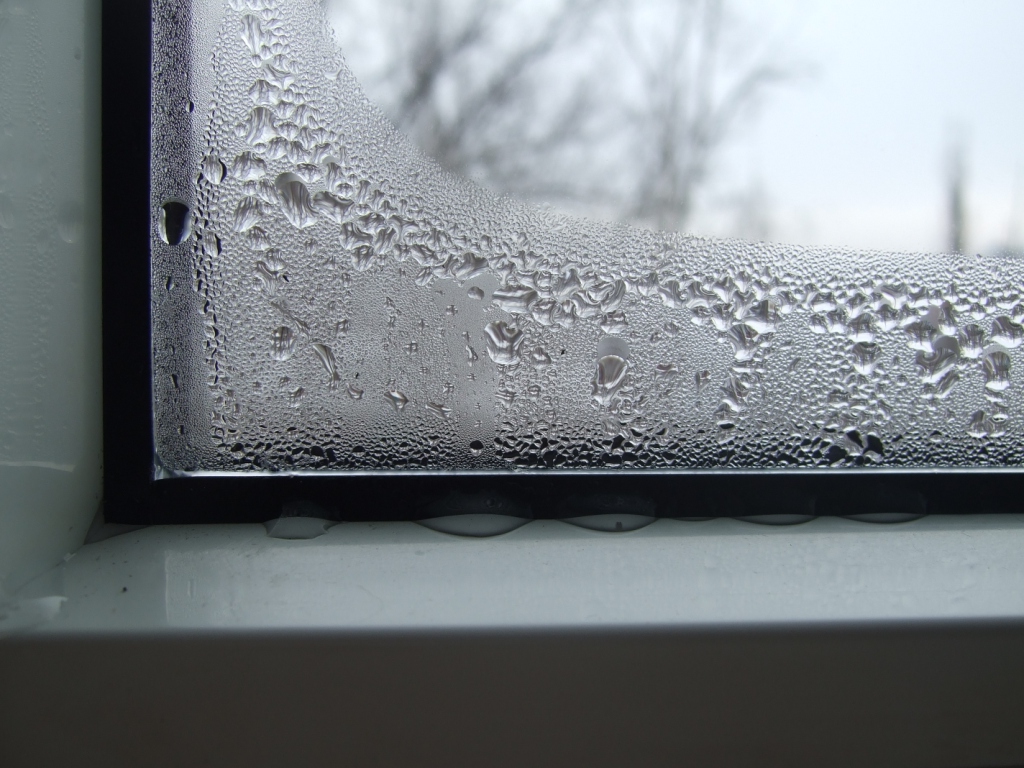
In the event that the ventilation system is functioning properly, then most likely you will not notice all this, otherwise it causes a number of unpleasant problems for those living in such an apartment - the windows begin to sweat on the windows and the condensate dripping onto the wall and window sill, the corners become damp, and There is mold on the ceiling and walls.

How to check if the ventilation in your apartment is working?
To check the operation of ventilation, it is not necessary to be a specialist. You need to take a small piece of toilet paper. Then open a window in any room and bring the prepared piece of toilet paper to the ventilation grate in the toilet, kitchen or bathroom. If your leaf is easily pulled, this means that the ventilation is functioning normally.
If the leaf cannot stay on the grate and disappears, then the ventilation is not working. If the sheet is not only not attracted to the vent, but also, on the contrary, deviates from it, it means that you have a “reverse draft” in your apartment and extraneous odors are drawn to you, that is, ventilation does not function. The same effect can be obtained by bringing a burning lighter to the ventilation grill.
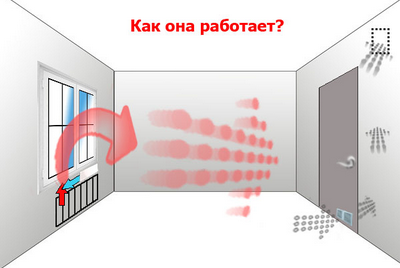
How to measure the ventilation performance in your apartment?
The performance of ventilation, in addition to checking, can also be measured. It is measured using a special device - an anemometer. This device can show the speed at which air passes through the ventilation duct. Using the calculation table, and the anemometer readings, as well as the section of your vent, you get a figure that will show how much air (in cubic meters) in 1 hour (m3 / h) passes through the vent.
In accordance with existing standards, the kitchen (having an electric stove), bathroom and toilet need: 60, 25 and 25 m3 / h, respectively. To achieve such figures, a rather small speed of movement of the air flow through the vent is needed, and such movement can only be determined by a thin piece of paper (preferably toilet paper).
There are apartments in which a sheet of thick, rather heavy paper can also be attracted, which means that in this dwelling the ventilation system works very well, which even exceeds standard norms.
Common causes of ventilation failure
In Russia, in residential apartments, supply and exhaust ventilation is adopted, which has a natural impulse, in other words, not mechanical, not forced. Naturally, all norms for air exchange were calculated just for such ventilation. And in order for the air to go into the vent, it must come from somewhere, and in accordance with the norms, it must enter the living room through non-densities (slots) in doors, windows and other structures.
At the end of the last century, new designs appeared in our state - metal doors with seals and plastic windows with sealed double-glazed windows. Of course, such products easily outperform old wooden windows with their endless drafts, but here another problem has arisen - despite the fact that new technologies have already arrived, but the standards remain the same and, according to them, air should enter the room through cracks, and new constructions completely exclude such non-densities.
As a result, with the help of hermetic doors and windows in the dwelling, conditions are created that do not allow ventilation to work normally. What causes the lack of fresh air in the apartment. In order to somehow cope with such problems, people began to use forced kitchen hoods.
In addition, people living in houses on the top floor often complain about poor ventilation, usually this information is enough to immediately determine the reason for the lack of good ventilation. The thing is that for optimal operation of the ventilation system in the apartment, the air flow must pass vertically in the ventilation duct for at least about two meters. On all floors, this is possible, except for the last one - here the attic space will act as an obstacle.
In order for the air in the room to be fresh, we ventilate the apartment every day, and sometimes several times. And if the internal ventilation system works, this is quite enough to avoid the appearance of a musty smell and other unpleasant phenomena. But if simple ventilation does not help, it is urgent to examine the air outlet channels for blockages and draft. Therefore, we will consider in more detail how to check the ventilation in the apartment and independently troubleshoot its operation.
Why is poor ventilation dangerous?
If the air circulation system in the house is broken, this can lead to a number of unpleasant consequences, which will be much more difficult to eliminate than to clean the ventilation.
Lack of ventilation causes:
Increased humidity levels.
Condensation on windows.
Development of fungi.
Occurrence of unpleasant odors.
Reducing the service life of finishing materials, furniture, household appliances.
Deterioration of health - the appearance of allergies, frequent infectious diseases of the respiratory system, especially in children.
But all this can be avoided if you periodically check and clean in time. ventilation system Houses.
The problem with air ducts is the scourge of all old houses. The main problem of such apartments is the narrow channels leading to the only air riser for the entire entrance. Such a system is designed for the natural flow of air through wooden windows, doors and other gaps that we so carefully eliminate during the repair process.

Therefore, the causes of improper ventilation can be:
1. Sealed double-glazed windows - block the possibility for air circulation, which was well provided by old wooden windows. The first signs of a problem are the accumulation of condensate on the glass, the appearance of wet spots and mold stains on frames and slopes.
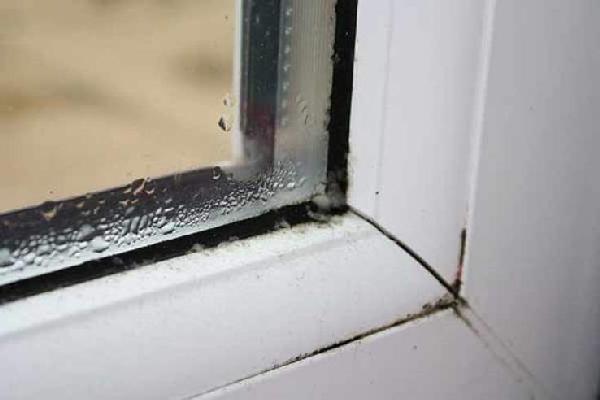

Solution: monitor the humidity level in the room. To do this, you can purchase a hygrometer and, if necessary, turn on an air conditioner or a moisture absorber (the normal humidity level for residential premises is within 40-50%). Regular cross-ventilation and the installation of a special valve on the double-glazed windows for air microcirculation will also help.

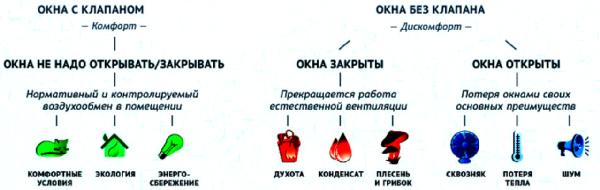
By the way, you also need to ventilate properly. It is much more effective to open all the windows than to keep the window wide open in one of the rooms for a long time, interior doors and balconies for 5-10 minutes and arrange through ventilation. This method is especially relevant in winter - the air in the apartment is quickly and completely renewed, and the room does not have time to cool down.
2. Temperature difference - according to the laws of physics, natural ventilation It works most effectively when the air outside is cooler than indoors. In winter, warm air easily enters through cracks and vents, but in summer there can be problems with circulation. That is why mold in the bathroom most often appears when it is warm and humid outside.
The solution to the problem: install a fan on the grate in the toilet, in the kitchen and in the bathroom and, again, ventilate more often. The ideal option is to install a complex supply and exhaust ventilation, but such a project requires a large-scale reconstruction in an apartment located in an old house (in most new buildings such a system is already provided).
![]()
3. Low air duct capacity - this can be not only a banal blockage due to accumulations of debris, but also blocking the channel during redevelopment or connecting powerful systems for forced air removal in other apartments. The natural ventilation system is designed for an air volume of no more than 90 m3 / h, which is 10 times less than what comes in when one hood is working. That is, while forced ventilation is turned on in one apartment, air will not be removed through the ventilation duct in other rooms connected to the same riser.
Solution to the problem: independent intervention in the ventilation system of the house is not allowed for any redevelopment, therefore, the neighbor who started the repair should eliminate the violation. You can "join" the flow of other people's forced ventilation systems only by installing your own hood or fans.
How to check the ventilation
Checking ventilation is a simple matter, it can be completely carried out with the help of simple improvised means, for example, a lighter or a sheet of paper. You need to open a window or window in any room of the house and bring a lit fire or leaf to the ventilation duct. With well-functioning ventilation, the flame will noticeably deviate towards the ventilation grill, and the sheet will stick.
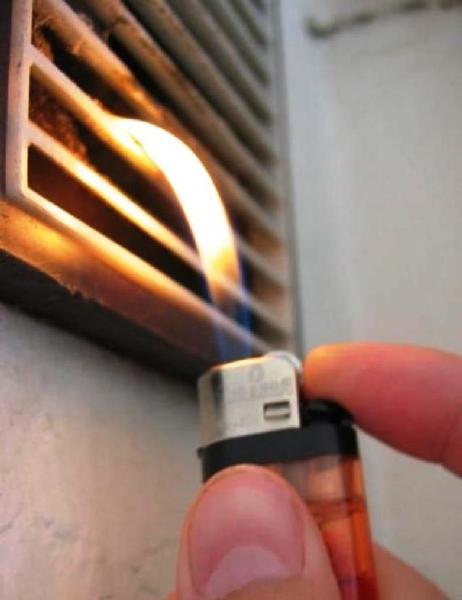
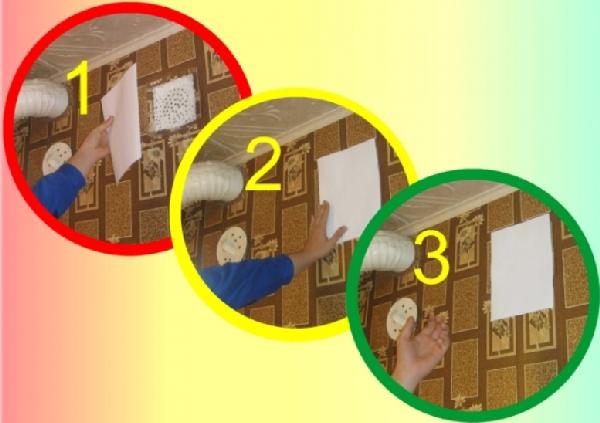


Nothing happened? So the system is not working. It is much worse when the flame deviates in your direction - this is a sign that there is a reverse draft in the ventilation, that is, the exhaust air from other apartments is not brought out, but enters your apartment. In this case, the problem cannot be solved by itself - most likely, its cause lies not in the channel, but in the air riser itself, so it is better to contact the housing office or a service with the appropriate license. But a small blockage can be completely eliminated on your own.
We clean the ventilation ducts with our own hands
Garbage also accumulates in the ventilation shafts. Dust, body fat, small motes over time block the width of the channel and prevent air circulation in the apartment.
The algorithm for removing blockages is simple:
Remove the grates from the ventilation holes and clean them. You can use dishwashing liquid to remove grease.
Dirt accumulated on the walls of the channel, scrape off with a stiff brush.
Vacuum the hole and the accessible area of the ventilation duct.
After dry cleaning, the surfaces can be wiped with a damp (but not wet) cloth and covered again with a grate.
 A hygienic shower is an excellent alternative to a freestanding bidet: it allows you to comply with hygiene requirements, but at the same time takes up an order of magnitude less space (which, you see,...
A hygienic shower is an excellent alternative to a freestanding bidet: it allows you to comply with hygiene requirements, but at the same time takes up an order of magnitude less space (which, you see,...
To check the operability of ventilation, there is no need to call specialists at all. All work can be done independently, without any special training.
What do we need to check ventilation?
All that is needed for this is a piece of newsprint or toilet paper, which you just need to bring to the ventilation duct. If you have a leaf stuck, then there is traction. From how strongly the sheet sticks to the grate, one can judge the traction force. In the event that the traction is weak or not at all, it is necessary to take action. There are times when the sheet, on the contrary, blows away from the grate, this is also not correct.
Measures to be taken into account when checking ventilation.
- Do not test the thrust force with fire, this may cause a fire or other harmful consequences.
- Ventilation must be checked only with the window ajar, an exception may be if you have valves for supply air.
- In hot weather, ventilation may not work due to objective reasons, so you should not make hasty conclusions, but rather wait for cool weather.
What are the ventilation problems?
If the apartment has too much humidity and stuffiness:
- There is no air supply;
- Clogged ventilation shaft;
- You live on the top floor;
- Poor installation of the ventilation shaft;

The air in the apartment is full of smells: smoking, cooking:
- There is no normal air flow, as a result of which air is drawn in through cracks in the ceilings and from the ventilation duct passing next to yours;
- The ventilation duct is clogged;
- Do you live on the top floor?
- There was a violation of the tightness and isolation of the ventilation shaft;
- Your ventilation duct immediately crashes into a common ventilation riser;
- Poor installation of the ventilation shaft;
A little theory on which conclusions are drawn on possible ventilation malfunctions
- The main reason (for which ventilation does not work, or works, but poorly) is the lack or insufficient air flow. The thing is that the laws of physics work here. The apartment must be air exchanged. How much air is removed, the same amount should come in. If you installed plastic windows and thereby completely blocked the air flow, do not expect that ventilation will work for you. In this case, you can set .
- For proper operation of ventilation, a minimum of two meters of vertical ventilation duct is required.
- The temperature regime for the proper operation of the ventilation system should be as follows: the temperature difference between the internal and external air must be at least 13 degrees, which is why ventilation deteriorates in hot weather, up to the appearance of reverse draft.



