The speed of air movement in the workplace is measured
The creation of favorable working conditions and the correct aesthetic design of workplaces in production has great importance both to facilitate labor and to increase its attractiveness, which positively affects labor productivity. The coloring of rooms and furniture should contribute to the creation of favorable conditions for visual perception, Have a good mood. In offices where monotonous mental work is performed, requiring considerable nervous tension and great concentration, the color should be calm tones - low-saturated shades of cold green or blue.
The environment is further divided into school environment and residential environment. The decree divides the year into so-called hot and cold periods, which is rather problematic because it no longer specifies when the period starts and ends. Otherwise, the air supply is determined in conditions where the production technology acts as a source of pollutant emissions into the atmosphere of the workplace. This government decree natural ventilation is not differentiated, but ventilation is forced, and therefore air exchange can be allowed in any way.
When developing optimal conditions the work of a programmer, it is necessary to take into account the illumination, noise and microclimate.
Illumination of the workplace
Rational workplace lighting is one of the critical factors affecting efficiency labor activity person, preventing injuries and occupational diseases. Properly organized lighting creates favorable working conditions, increases efficiency and productivity. The lighting at the programmer's workplace should be such that the employee can perform his work without straining his eyesight. Fatigue of the organs of vision depends on a number of reasons:
Clean zones Special chapter - special industrial or medical zone - clean rooms. These are areas in which the concentration of particles in the flow is controlled. Therefore, these spaces are designed and used in such a way as to minimize clogging, formation and retention of particles in the controlled area.
Currently, special spaces are used for electronic manufacturing, precision mechanics and optics manufacturing, food manufacturing, pharmaceutical manufacturing and finally hospitals. Measurement of microclimate parameters. This temperature is measured with a thermometer with a probe inserted into a polyurethane ball with a diameter of 100 or 150 mm. The temperature measured by the thermometer inside the flask after precipitation is the received temperature. This temperature reflects the simultaneous effect of air temperature, ambient temperature and airflow rate.
lack of illumination;
excessive illumination;
wrong light direction.
Insufficient lighting leads to eye strain, weakens attention, leads to premature fatigue. Excessively bright lighting causes blinding, irritation and pain in the eyes. The wrong direction of light in the workplace can create harsh shadows, glare, and disorientate the worker. All these reasons can lead to an accident or occupational diseases, so the correct calculation of illumination is so important.
From the obtained temperatures, which are measured at the level of the head, abdomen and ankle, the average value is determined. Measuring the airflow rate in the environment The thermal comfort is of course also dependent on the airflow rate. At higher flow rates, comfort is achieved even with more high temperatures environment. However, if the speed is too high, it can lead to medical problems. In order to measure the air flow rate in the environment, it is necessary to use instruments capable of measuring low flow rates.
The calculation of the illumination of the workplace is reduced to the choice of the lighting system, the determination of the required number of lamps, their type and placement. The process of a programmer working in conditions where there is insufficient or no natural light. Based on this, we calculate the parameters of artificial lighting.
Artificial lighting is provided by electrical sources two types of light: incandescent lamps and fluorescent lamps. We will use fluorescent lamps, which, compared with incandescent lamps, have significant advantages:
Blade anemometers or thermal anemometers are suitable for measuring flow velocity due to the cooling of the electric heating element. Measurement of air humidity. Relative humidity measurement is used to estimate the ambient humidity in a room. This is the ratio between the instantaneous amount of water vapor in the air and the volume of vapor that must have the same pressure and temperature at full saturation. Relative Humidity indicated as a percentage. In practice, it is most often used to measure capacitive hygrometers, where the fluctuation of the electrical capacitance of the sensor is converted into a humidity value.
in terms of the spectral composition of light, they are close to daylight, natural lighting;
have a higher efficiency (1.5-2 times higher than the efficiency of incandescent lamps);
have increased light output (3-4 times higher than that of incandescent lamps);
longer service life.
Parameters of the microclimate at the workplace
Microclimate parameters can vary widely, while necessary condition human life is to maintain a constant body temperature due to the property of thermoregulation, i.e. the body's ability to regulate heat transfer to the environment.
Cleanrooms When measuring air purity in cleanrooms, it is necessary to classify measurements from operational monitoring. For classification purposes, a portable particle counter with a short tube length should be used. This classification dimension determines if a cleanroom meets the cleanliness requirements of its class. Cleanrooms must also be monitored regularly during operation.
Conclusion It is not easy to navigate the rules and regulations regarding the parameters of the internal environment. They have several definitions, and in addition, the required parameters of the internal environment are missing for some types of space. This poses significant challenges for designers, builders and users. However, for a production environment, these parameters are handled quite clearly. Compliance with the parameters in the working environment is not only important from the point of view of legislation, but mainly because of the health and productivity of employees.
The basic principle of microclimate regulation is the creation of optimal conditions for the heat exchange of the human body with environment. IN sanitary standards SN-245/71 microclimate parameters are set to create comfortable conditions. These norms are established depending on the time of year, the nature of the labor process and the nature of the production premises (significant or insignificant heat generation). For working premises with excess heat release up to 20 kcal / m3, permissible and optimal values microclimate parameters are given in the table:
The only way to know and verify these parameters is to measure them. The article was published in the journal. In ten years of independent existence, the cave administration of the Czech Republic has lagged behind. He manages fourteen caves open to the public and one abandoned mining work with pseudo-classics.
The main task of the administration is their consistent protection and care, which will ensure the maintenance and further optimal development of this extraordinary and non-renewable phenomenon. During this time, the caves, their premises and care for them have undergone significant changes.
Table 1.
|
Season |
Air temperature, C |
Relative humidity, % |
Air speed, m/s |
|
|
cold period |
Optimal Both the title and the founding statute are its "statutory mission" to ensure the protection, care and exploitation of the accessible caves of the Czech Republic and their directly connected underground spaces, as well as the accessibility, protection and care of the premises, provided that the activities are carried out on the basis of local and material environmental authority or will be used for purposes subject to state mining supervision. The cave administration provides security for the accessible caves, guide services and a number of related visitor services such as information, souvenirs and drinks, car parks, etc. The basis of cave care is the implementation of measures of care plans, systematic monitoring and intervention as a result of its results. | |||
|
Transition period |
Permissible | |||
|
Warm period of the year (t > 100 C) |
Optimal | |||
|
Permissible |
< 28 в 13 часов самого жаркого мес. Research, exploration and documentation of caves, collection of information about karst and caves and their archiving, as well as the completion of the National Unified Abstract of Speleological Objects are being carried out. The administration publishes advertising and professional press releases, organizes various professional and cultural events. The impact of cave management is unthinkable without close cooperation with the Nature Conservation Agency of the Czech Republic, especially with its regional jobs. The Caves Administration of the Czech Republic is located in Pruhonice and has ten regional jobs - caves. Center of Specialization and Documentation - Cave Care Department. The technical background is in Blansko. Thus, the separate management of the caves continues to meet the goals that they set twenty-five years ago, when the administration and operation of the accessible caves became part of the state nature conservation in the newly created resort. The independence of cave management in the form of a donating organization was a positive contribution to its management and a relief to its founder's budget. |
At present, to ensure comfortable conditions both organizational methods and technical means are used. Among the organizational ones are the rational organization of work depending on the time of year and day, as well as the organization of the correct alternation of work and rest. In this regard, it is recommended to organize a green area with benches for recreation and a pond (pools, fountains) on the territory of the enterprise. Technical means include ventilation, air conditioning, heating system.
This allows you to economically process your income and rationally return it to the cave. The independence of the administration of the caves also contributed to its visibility and recognition of the results of its work. There was a great deal of interest in the satisfaction of the visitors, which contrasted sharply with the protection of the caves. Technical condition underground and surface facilities reflected a significant lack of funds and some lack of interest on the part of the operators.
In the new organization, along with the newly formulated human trafficking rules, the first force of real care for caves also became the first principles for cleaning and revitalizing underground areas adversely affected by old exploration and access works and long-term visitor traffic. After all, some of the caves have been used for tourists since the turn of the century, released at the turn of the century, and the last major wave of access to the cave was in the 1950s. The relationship with the caves and the mining methods used in some of the caves were very negative.
Noise regulation
It has been established that noise worsens working conditions, having a harmful effect on the human body. With prolonged exposure to noise, undesirable effects occur on a person: visual acuity and hearing decrease, blood pressure rises, attention decreases. Strong prolonged noise can cause functional changes in the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Many excavations were carried out ruthlessly, numerous natural spaces were covered with rubble or construction waste. Lekde's walls were decorated with soot, mold and a pink light bulb. Favorable economic conditions in the environmental sector have allowed relatively early adaptations and reconstructions of routes and their technical equipment. It was an opportunity to implement new ways of working to a greater extent. It was not only about replacing an existing device. The technology and capabilities of the supplier companies are used to remove old deposits, deposits and backfills.
According to GOST 12.1.003-88 ("Noise. General requirements safety") characteristic constant noise at workplaces are RMS pressure levels in octave frequency bands with geometric mean standard frequencies: 63, 125, 250, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000 and 8000 Hz. This GOST indicates the values of the maximum permissible noise levels at the workplaces of enterprises. For indoor design bureaus, calculators and programmers, noise levels should not exceed respectively: 71, 61, 54, 49, 45, 42, 40, 38 dB. This set of eight standard sound pressure levels is called the limiting spectrum.
New approaches were also reflected in the construction and technical equipment of walking routes. redundant concrete surfaces and unused stairs were removed, new walkways were kept to a minimum to allow for the number of visitors. The connecting tunnels and passages were equipped with a wind door to maintain a microclimate. Each year, painted railings replaced stainless steel, which was also used on walkways and suspended stairs where concrete had damaged the agglomerates. Hidden water distribution allows sidewalks to be washed and walls to be rinsed.
Noise protection methods
Construction-acoustic methods of noise protection are provided for by building codes and regulations (SNiP-II-12-77). This:
soundproofing of enclosing structures, sealing around the perimeter of the porches of windows and doors;
sound-absorbing structures and screens;
noise silencers, sound-absorbing facings.
At the programmer's workplace, as a rule, noise sources are technical means, such as a computer, printer, ventilation equipment, as well as external noise. They make quite a bit of noise, so it is enough to use sound absorption in the room. Reducing the noise penetrating into the room from the outside is achieved by sealing around the perimeter of the porches of windows and doors. Sound absorption is understood as the property of acoustically treated surfaces to reduce the intensity of the waves reflected by them due to the conversion of sound energy into heat. Sound absorption is a fairly effective measure to reduce noise. Fibrous-porous materials have the most pronounced sound-absorbing properties: fiberboard, fiberglass, mineral wool, polyurethane foam, porous polyvinyl chloride, etc. Sound-absorbing materials include only those whose sound absorption coefficient is not lower than 0.2.
If necessary, the wash water is collected again and discharged separately from the cave. Cabling is concealed as far as possible and non-corrosive materials are used for installation. Lighting is divided into shorter sections, scenic lighting is separated from pavement lighting. The result is a minimal light and thermal effect of stalactites. Electronics help to protect open blocks, traffic safety increases telephones, mainly with a call to the public network.
Within 25 years after the unification of the cave caves, eight caves were completely reconstructed, and the remaining six were partially restored. An all new operational facility was built in nine caves. As part of the systematic maintenance of the cave, the monitoring and implementation of measures arising from it was observed. First of all, we are talking about maintaining optimal microclimate conditions, protecting against the growth of light bulbs and protecting the visitor from mechanical damage. The seasonal opening hours of the caves are determined by the hibernation period on the planes.
The microclimate of domestic and industrial premises is determined by the combinations of temperature, humidity and air velocity acting on the human body.
The main requirement that ensures normal living conditions for a person during a long stay in the room is the optimal combination of microclimate parameters. First of all, they must eliminate the tension of the body's thermoregulation mechanisms or maintain health and performance. Deviations of individual microclimate parameters from biomedical reasonable values can lead to various diseases, especially in people with weakened immune systems.
The number of visitors in groups is determined by the need to check their leadership. He proved sufficient stability of all parameters of the cave environment. One of its results is also a certified methodology for monitoring the microclimate in caves.
In addition, the urgent need to get rid of unwanted green light, called lampenflora, has been the subject of lengthy research experiments. Their result is a methodology that has made it possible to abandon the previous mechanical cleaning and maintain the optimal condition of the stalactite forms without damaging them or negatively affecting the cave fauna. The Czech methodology is also of interest abroad.
It is known that lowering the temperature causes increased heat transfer to the environment, which causes cooling of the body, lowers its protective functions and contributes to the occurrence of colds. On the contrary, an increase in temperature leads to an increased release of salts from the body, and a violation of the salt balance of the body also leads to a decrease in immunity, a significant loss of attention, and, consequently, to a significant increase in the likelihood of an accident.
An increase in air humidity disrupts the balance of moisture evaporation from the human body, which leads to a violation of thermoregulation with the above-mentioned consequences. On the other hand, a decrease in relative humidity (up to 20% and below) disrupts the normal functioning of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. The speed of air movement is also a factor influencing the mechanism of thermoregulation of the body.
It has been established that the action of the air flow depends on the room temperature and affects the human condition at a speed of 0.15 m/s. Such a flow at a temperature of less than 36 ° C has a refreshing effect and promotes thermoregulation, and at a temperature of more than 40 ° C it has the opposite effect.
Medical and biological optimal norms of microclimate parameters are set taking into account the period of the year, while it is considered that in the warm period of the year (spring, summer) the average daily temperature of the outside air is +10 ° C, in the cold period (autumn, winter) the average daily temperature of the outside air is -10 °C. In both cases, the optimal relative humidity is taken within 40 - 60%.
If we talk about the microclimate of industrial premises, then it is determined by the category of work that is performed in them. GOST 12.1 005-76 provides for three categories of work:
Light physical.
Physical moderate.
Severe physical.
In this case, the job of a software engineer is light physical work. Energy costs of the body during the performance of work - 120 - 170 kcal / h. The work is done while sitting, standing, or associated with walking and is accompanied by minor physical stress (mostly people of mental labor).
In table. 5.1 shows the optimal allowable values of the microclimate parameters of industrial premises in the cold and warm periods of the year for light physical work.
As can be seen from the table below, all microclimate parameters are related to air, so the level of its pollution is of great importance. It is known that during the production process, harmful substances can be released into the air, which enter the human body through the respiratory tract.
To ensure the necessary parameters of the microclimate and purify the air environment in industrial premises use different ventilation systems. Types and designs of ventilation systems is a separate topic, which is not considered in this section. The main requirement for any ventilation system is to ensure the necessary air exchange rate, which ensures the removal of all harmful components from the production room, that is, excess heat, moisture, vapors of various substances.
Table 5.1
Optimal allowable values of microclimate parameters
The room in which the workplace of a software engineer is located has the following characteristics:
room length: 5 m;
room width: 6 m;
room height: 2.7 m;
number of windows: 1;
number of jobs: 1;
lighting: artificial;
number of computers: 1.
Under the frequency rate of air exchange is understood:
where L B - the amount of air entering (or removed) into the room, m 3 / h;
V P - the volume of the room, m 3.
In the presence of excess heat, the amount of air that needs to be removed from the room,
 (5.4)
(5.4)
Where Q izb – excess heat, kcal/h;
C B is the heat capacity of air (0.24 kcal/kg K);
 t- the temperature difference between the incoming and incoming air;
t- the temperature difference between the incoming and incoming air;
 \u003d 1.206 kg / m 3 - specific gravity of the supply air.
\u003d 1.206 kg / m 3 - specific gravity of the supply air.
Excess heat:
Where Q about, Q osv, Q l - heat generated by production equipment, artificial lighting system and working personnel, respectively;
Q p – heat introduced by solar radiation;
Q otd - Heat dissipation in a natural way.
Heat generated by production equipment:

Where 860 – thermal equivalent 1 kW/h;
R o6 – power consumed by the equipment, kW;
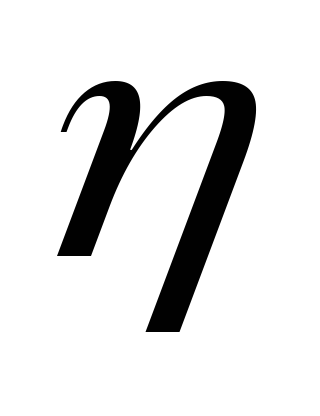 -coefficient of heat transfer to the room;
-coefficient of heat transfer to the room;
Initial data R about = 1;  = 0.5; calculate
= 0.5; calculate  :
:
Heat generated by lighting installations:
Where R osv - power of lighting installations, kW;
 –Efficiency of conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy;
–Efficiency of conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy;
 – Efficiency of simultaneous operation of equipment in the room;
– Efficiency of simultaneous operation of equipment in the room;
cos 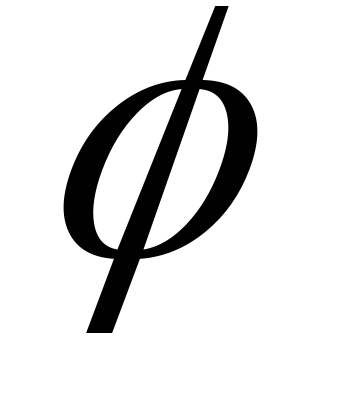 – electrical coefficient;
– electrical coefficient;
 – phase shift angle between current and voltage;
– phase shift angle between current and voltage;
Initial data R osv = 0,2; = 0,2;
= 0,2; = 0.8; cos
= 0.8; cos  = 0.8, calculate
= 0.8, calculate  :
:
Heat generated by people:

Where TO l - the number of workers;
(q-q Spanish ) - sensible heat, determined by special graphs, kcal / h,
Where q– heat dissipation of one person for the corresponding category of work;
q Spanish is the heat expended for evaporation by the body;
Initial data TO l = 1;(q-q Spanish )
=
120 , let's calculate 
 kcal/h
kcal/h
Heat generated by solar radiation:
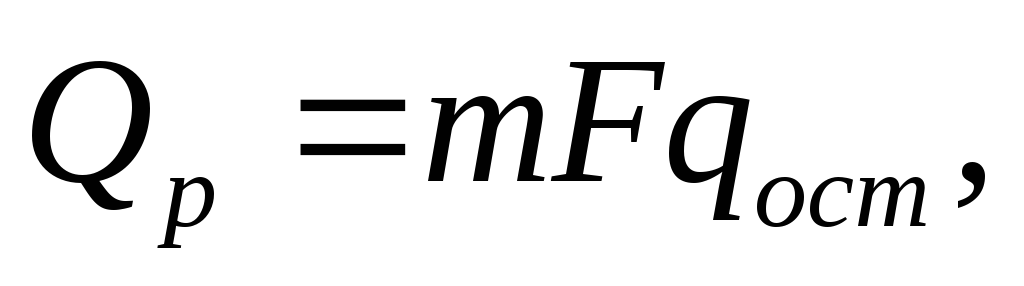 (5.6)
(5.6)
Where T- the number of windows in the room;
F– the area of one window, m 2;
q ost - the amount of heat introduced in one hour through a glazed surface with an area of \u200b\u200b1m 2 (table value) kcal / h * m 2.
In rooms with large excess heat Q otd = Q R. For the warm season Q otd = 0.
From the calculated parameters Q about , Q osv , Q l , Q R , Q otd we can calculate the excess heat, the amount of air to be removed from the room and the air exchange rate.
Initial data for calculating excess heat Q about = 430;Q osv = 22,02;Q l = 120;Q R -Q otd= 0, calculate the excess heat using formula 5.5:
 Initial data for calculation Q hut =
572,02;C V = 0,24;
Initial data for calculation Q hut =
572,02;C V = 0,24; = 1,2;
= 1,2; \u003d 6, we calculate the amount of air that needs to be removed from the room, according to formula 5.4:
\u003d 6, we calculate the amount of air that needs to be removed from the room, according to formula 5.4:
 Knowing these parameters, it is easy to calculate the air exchange rate according to formula 5.3, which will be equal to:
Knowing these parameters, it is easy to calculate the air exchange rate according to formula 5.3, which will be equal to:
Air purification from dust and the creation of optimal microclimate parameters at the workplace of a software engineer is provided by a ventilation (air conditioning) system.



