Basement waterproofing - groundwater protection: all methods of insulation from the outside and from the inside. The price of roofing works per unit, rubles. Rigid sheet waterproofing.
So! A solid design organization issued a complete set of drawings to the future owner of a private house. The customer, following the advice of friends, found an organization capable of performing an examination of this project. Inaccuracies, errors, missing parts, assemblies were identified, elements of foundations, walls, ceilings, roof structures were corrected ... That's it, the project can be transferred to builders and start building your dreams.
Construction services were offered by firms with a name, and not very noticeable, but with good advice, there were proposals from the "wild" brigades. After much deliberation, preference was given to the handsome head of the construction organization, who showed several photographs of objects built by unknown persons, recommendations of reputable customers. A respectable office, a pleasant manager, an agreement that provides for all sorts of options ... They hit on the hands!
The situation is quite typical.
At the construction site, however, things are not so optimistic. It turned out that the builders, striving for maximum profit, use "specialists" of very dubious qualifications, the materials are far from the best, the foreman began to appear less and less on the site and all this began to lead to marriage, defects, often difficult to fix.
We will try to dwell briefly on typical construction defects.
Excavation. Foundation
The cost of building a "zero cycle" device can be more than a quarter of the cost of the entire house. Defects made during the production of these works can be impossible to eliminate in the future or become an extremely expensive undertaking. A pit was dug, trenches for the future foundations of the house. Excess soil has not been removed from the construction site, its layout has not been completed. Trenches and pits are filled with water. The base under the foundations is broken. Additional costs required.
We prepared and installed reinforcing cages in the formwork for future foundations, but forgot to put clamps to create a protective layer. Unprotected reinforcement quickly rusts, very soon reinforced concrete foundations will turn into concrete - with all further possible deformations.
The foundations were concreted, and waterproofing began. The surfaces of the walls of the basement or basement in the shells are not cleaned, they are coated with bituminous mastic or rolled waterproofing is glued on the same unprepared surface. If this work is not done according to the rules - to be in the basement of the water, do not avoid deformation of the house.
Basement walls are usually insulated. Laid in one layer of 100 mm. Joints are not closed. The protection effect is weak. Correctly 2 layers of 50 mm each and with overlapping joints - then everything is as it should. A trifle, but important for the house.
Another variant. "Forgotten" to perform thermal insulation of the basement walls. The need for insulation is due to the fact. that heat loss through underground part building accounts for up to 20% of total heat loss. Without thermal insulation of the walls of the basement, condensation, dampness, and mold are inevitable.
The pressure wall protects the thermal insulation from wet soil, water. It must be plastered or the seams are rubbed and smeared with 2 layers of bituminous mastic. Often this is done carelessly. So the design is useless and the cost of it is not justified.
Let's start backfilling the trenches. Where are our “frogs” for layer-by-layer soil compaction, why did clay soil go into the backfill, capable of squeezing out foundations in winter due to its heaving properties?
Backfilling should be carried out only with sandy or sandy-gravelly soil with its obligatory layer-by-layer compaction.
After backfilling the trenches, it is necessary to complete the entire floor pie for the floors of the 1st floor. If this monolithic slab, sand preparation, waterproofing in concrete preparation, thermal insulation and the slab itself should be provided. Here you need an eye for an eye.
Often something is missed. Poorly laid thermal insulation, not designed or of the wrong thickness - and the floors in the house will never be comfortable. To protect the insulation from moisture, it must be insulated with a layer of vapor barrier material, which must be laid above the insulation, and not under it, because. water vapor comes from warm rooms in the cold. If the film is not placed on top of the insulation, but on the bottom - it will be trouble, the floors will turn out to be cold, as if there were no thermal insulation at all.
And further. Air ducts are required to ensure ventilation of the underground and cellars. If they are not fulfilled, the floor insulation will be wet and dampness, fungus, mold are inevitable.
The plate has been laid. It is necessary to prepare for the blind area around the building, complete the vertical planning, remove all excess soil, and plan the remaining soil in such a way that water cannot get under the foundations of the building. This work is often not carried out during the entire construction. As a result - water in the basement, expensive additional work.
For all works of the "zero" cycle, acts must be drawn up hidden works, keep logs of earthwork, concrete, reinforcement work.
And this is just the beginning!
Walls of the future building, ceilings, installation of windows and doors. Preparation for future floors. Masonry partitions made of bricks with a thickness of 120 and 250 mm. Jumper device. Roof framing work. The device of the roof itself with all the elements and fixtures necessary for it. The implementation of a very important constructive “pie” of the roof itself with its mandatory ventilation system, without which the roof is not a roof, and life under it will never be full-fledged.
And this is not a complete list of works that require an eye and an eye of a qualified graduate specialist with extensive experience working on construction sites of the for various purposes. Control over compliance with the project and Building Regulations, the quality of materials, the necessary sequence of work, timely examination of hidden work, the prevention of marriage - this is an incomplete list of what the experts of ASK "Quality Advocate" LLC carry out at the objects entrusted to them.
The utility model relates to construction and can be used to prevent the penetration of moisture in the basements of buildings, basements and other underground structures type of underground passages, tunnels, cellars. Technical result: an effective solution is provided to prevent the penetration of moisture through the walls of buildings and other underground structures without the use of energy-consuming equipment and the need for waterproofing; the acceleration and reduction in the cost of the construction of waterproofing protection is ensured. The claimed technical result is achieved due to the fact that the device for waterproofing the walls of basements, basements and other underground structures, consisting of a pressure brick wall, characterized in that as a pressure brick wall, masonry is used from raw brick (unbaked brick) of plastic molding, protected from drying to installation.
Application area
The utility model relates to construction and can be used to prevent the penetration of moisture in the basements of buildings, basements and other underground structures such as underpasses, tunnels, cellars.
State of the art
Currently, in buildings there is a need to ensure a stable microclimate in the basements, basements of buildings and other underground structures so that moisture does not concentrate in them, which contributes to the reproduction of mosquitoes and molding of the walls.
At the present stage, with a large accumulation of liquid in the basements, it is pumped out with pumps.
However, with small insignificant accumulations of liquid in basements, as a rule, nothing is done to eliminate it.
Water in the basement penetrates through the pores in the walls during floods and rains, with close groundwater standing.
To ensure the exclusion of the accumulation of even small amounts of moisture in the basement, it is necessary to ventilate (dry) the basements.
According to SNiP 31-02-2001, during the construction of houses in areas where, according to engineering and environmental surveys, there are emissions of soil gases (radon, methane, etc.), measures must be taken to isolate floors and basement walls in contact with the ground in order to prevent penetration of soil gas from the ground into the house, and other measures to reduce its concentration in accordance with the requirements sanitary norms. To prevent the entry of soil gases, the concrete slab of the basement floor must be hermetically sealed to the wall around the perimeter of the basement, and the junction area must be covered with sealant, that is, the concrete slab acts as an "air barrier" that prevents the penetration of soil gases. However, attempts to solve this problem by hermetically sealing cracks and other openings in the basement are not always effective, therefore, in the basement, the installation of systems for removing such gases is provided - a ventilation duct is arranged through which the basement communicates with the atmosphere. To prevent the entry of soil gases, a drainage layer of gravel under concrete slab the basement floor must also communicate with the atmosphere. Thus, the arrangement of ventilation of basements in apartment buildings sometimes it becomes a necessity not only because of plans to use the basement area, but also purely because of considerations of compliance with sanitary standards in the operation of buildings.
However, the ventilation device is expensive, not always possible, and in addition, with constant moisture penetration, it requires continuous operation, and in the event of a breakdown, the basement quickly becomes damp.
Moisture from other underground structures such as tunnels, passages and cellars is not pumped out at all, except occasionally by mobile pumping units, with large volumes of accumulated moisture.
Underground structures are rapidly destroyed.
To eliminate these problems in buildings and underground structures, waterproofing is used, with a pressure brick wall.
A typical architectural detail of an external waterproofing device with a pressure brick wall, usually made in half a brick, serves to protect the waterproofing from mechanical damage.
The disadvantage of this type of technology is that it is expensive and inefficient, since the pressure wall acts as a drain, passing moisture into the internal cavity in the area between the wall and the waterproofing layer. A hydrostatic backwater is formed in the cavity, which finds holes in the waterproofing and damages it.
Moisture penetrates through the pressure wall, no matter what layers of bitumen are coated on the outside of the pressure wall. This is due to annual temperature fluctuations, which form cracks in the pressure wall coating layer, through which moisture penetrates.
Technical result: an effective solution is provided to prevent the penetration of moisture through the walls of buildings and other underground structures without the use of energy-consuming equipment and the need for waterproofing; the acceleration and reduction in the cost of the construction of waterproofing protection is ensured.
Implementation of the utility model
The claimed technical result is achieved due to the fact that the device for waterproofing the walls of basements, basements and other underground structures, consisting of a pressure brick wall, characterized in that as a pressure brick wall, masonry is used from raw brick (unbaked brick) of plastic molding, protected from drying to installation. The masonry is made in half-brick (120 mm thick).
Brief description of the drawings
Figure 1 shows the constructive device of the utility model, where 1 - the interior of a building or underground structure, 2 - foundation slab or floor of a building or structure, 3 - protective masonry made of raw bricks, 4 - internal walls of a building or underground structure, 5 - accumulated soil moisture - 6.
Implementation of the utility model
During the construction of the basement or basement of the building (see Fig.1) or underground structures after installation on the foundation slab-base (2) of the outer walls (4) of the building, the outer walls along the perimeter of all the walls of the building adjacent to the ground and the walls of the underground structure are laid out with masonry from raw brick (3) - unbaked brick from pure raw clay.
Raw brick is obtained at a brick factory without the use of burnt additives and is stored until delivery to the construction site (before the wall is laid) in the form in which it is obtained during manufacture. Protecting the raw brick from drying out is necessary with the goal that after drying, the raw brick cracks, becomes swollen, loses its shape and is not suitable for laying.
Laying is done like this. The raw brick is quickly dipped into a bucket of water and just as quickly planted on the mortar. The brick almost instantly absorbs moisture, and if you delay, it will go inside and adhesion between the raw material and the clay mortar may not occur.
Compact and trim the masonry with a wooden or rubber mallet.
Masonry is preferably done in half a brick (120 mm). It is not advisable to do more in order to save internal space, and it is impossible to do less masonry, since the laid out wall can fall off (unstable).
When the bricks are completely laid in the masonry, and the mortar has dried up, they carefully examine the relief and remove all kinds of bumps and sagging with a greasy scraper, knife or chisel. Separate roughness is removed with sandpaper of various grain sizes. Flat masonry surfaces are rubbed without water with a burnt red brick grater. All kinds of cracks and dents found after grinding are immediately sealed with clay mortar. Pre-cracks are cut with the tip of a knife so that grooves about 4-5 mm wide are formed in their place. The grooves are abundantly moistened with water using a sponge or a washbrush and covered with clay mortar so that small tubercles rise in place of the former cracks. After drying, the clay "sits down" and the tubercles disappear.
The principle of operation of the utility model is as follows.
When moisture penetrates to the masonry (3) of raw brick, it is absorbed by it until the masonry clay is completely saturated with water. At the moment of complete saturation with water, the masonry (3) of raw brick ceases to pass moisture through itself to the inner walls (4) and ceases to absorb moisture.
Liquefied, the masonry (3) begins to expand and self-removes all the pores and cracks of its walls, as well as cracks and pores internal walls(4) premises.
Thus, even with a continuous supply of moisture, raw brick masonry will serve as an excellent barrier for its further penetration into the interior (1) of basements and basement floors of buildings and underground structures and does not require any energy consumption and the use of waterproofing.
In addition, since raw brick is much cheaper to manufacture and faster to manufacture than fired brick, the process of building a waterproofing structure is cheaper and faster. Speeding up and reducing the cost of building a waterproofing structure is also ensured by eliminating the need to use cement during the construction of masonry.
Sources of information:
1. http://www.rubliovka.ru/isk/iskpir.htm
2. http://novostrojka.ru/content/view/1557/28/
3. http://www.kamenschik.com/kinds-waterproofing-appointment.html
1. A device for waterproofing the walls of basements, basements and other underground structures, consisting of a pressure brick wall, characterized in that as a pressure brick wall, laying of raw brick (unfired brick) of plastic molding is used, protected from drying out until the moment of laying.
2. The waterproofing device according to claim 1, characterized in that the masonry is made in half a brick (120 mm thick).
General requirements for waterproofing
Foundation waterproofing
When to waterproof a foundation
Slab foundation waterproofing
Waterproofing strip foundation
Waterproofing of column and pile foundations
Plinth waterproofing
Basement waterproofing
What materials should not waterproof the foundation and basement
General requirements for waterproofing.
We often do not attach due importance to waterproofing, and after a while we observe the results of the destructive effect of water on house structures.
Non waterproofed basement
It is much easier to prevent these consequences. To do this, it is important to protect the following structures from moisture:
house walls
floors on the ground
junctions of door and window openings.
foundation
basement floor and walls
If you pay attention, then almost all the structures of the house are listed here, except, probably, for internal partitions.
So, how to make the correct waterproofing of the foundation, basement and other structures? The waterproofing layer of any design must be continuous and without breaks over the entire insulated surface. A waterproofing layer is arranged on the side of the structure that is affected by hydrostatic pressure, or there is a threat of capillary rise and water seepage.
Foundation waterproofing.
When should foundation waterproofing be done?
Any foundation should be protected from two types of water: surface (precipitation) and underground (groundwater).
The blind area protects from the penetration and negative impact on the foundation of surface water. And this is its main function. You can read more about the blind area in the article: Blind area. The device blind area at home. And if there is surface water in any area and a blind area, thus, it should always be done by everyone without exception, then groundwater and, accordingly, waterproofing from them is not always needed. Say that in any area there is no groundwater and there you can not waterproof the foundation will not be true. Indeed, in our area, groundwater is almost everywhere. The question is the depth of their occurrence relative to the level of the foundation, as well as the level of seasonal groundwater rise during the spring flood.
1. Waterproofing of the foundation must be done if the groundwater level (GWL) is located at a depth of less than 1 meter from the bottom of the foundation. This value is indicated taking into account the spring rise of the GWL, since it often happens that the GWL, located at the same depth in summer, rises 1-2 meters higher in spring due to snowmelt. With this arrangement of the GWL, the waterproofing will protect the foundation from the capillary rise of groundwater, and coating waterproofing will be sufficient for these purposes.
2. If the GWL lies at a depth of more than 1 m from the bottom of the foundation, then waterproofing, in principle, can be omitted. But I would like to draw your attention to the fact that GWL tends to increase not only seasonally - in spring, but also over time (over the years) due to an increase in building density, due to drainage in neighboring areas, asphalting of adjacent territories, as well as when creating non-waterproof artificial reservoirs at a distance of even 1 km. Such changes are commonly referred to as long-term GWL fluctuations. Considering them, even with a low groundwater level, it is advisable to make at least the most inexpensive waterproofing of the foundation - coating, especially if there is a basement.
3. If the GWL is high - above the bottom of the foundation, then in addition to waterproofing, drainage must also be done to drain water from the foundation.
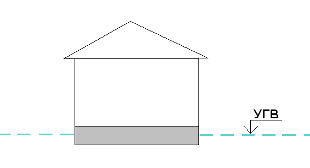 GWL above the level of the bottom of the foundation
GWL above the level of the bottom of the foundation
Why not just waterproofing? When water is above the level of the base of the foundation, it creates hydrostatic pressure on the foundation, which reduces the pressure force of the foundation on the foundation. Those. in simple words, the foundation support force decreases, as a result of which foundation shifts and even its overturning can occur if left unloaded on such soils, for example, for the winter. Therefore, the foundation must not only be protected from excess moisture, but also lower the GWL. And drainage just allows you to lower the GWL and thereby reduce the hydrostatic pressure on the foundation, which waterproofing does not provide.
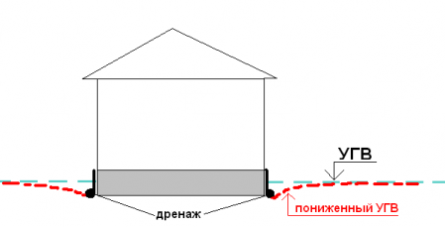 GWL decrease
GWL decrease
4. Sometimes a serious waterproofing of the foundation should be done regardless of the groundwater level. There is a need for this if the construction of a house is planned on waterproof or so-called water-resistant soils (clay, loam) with layers of permeable soil. Because such soils do not allow surface water to easily leave permeable areas into the underlying soil layers, and water moves along the path of least resistance, namely, to the foundation. Therefore, it must be waterproofed.
 Construction on waterproof ground
Construction on waterproof ground
Soils with filtration coefficient k<10 -6 cm/s. Filtration coefficient, k, cm/s (accepted soil permeability characteristic) has the following values for different soils:
sands10 -2 -10 -4
sandy loam and loam10 -3 -10 -8
clay10 -7 -10 -10 .
5. Regardless of the groundwater level and the type of foundation, it is very important to pay attention to the composition of groundwater (GW), which is shown by engineering and geological surveys. In some areas there are aggressive GW. They negatively affect the bearing capacity of concrete, simply destroying it, which is commonly called concrete corrosion.
 Concrete corrosion
Concrete corrosion
Therefore, to protect such foundations, it is recommended to build them from moisture-resistant concrete of grade W4 and higher (according to clause 2.9. SNiP 2.03.11-85). And all waterproofing materials used for such foundations must be resistant to aggressive environments. The most dangerous for concretes and solutions are pressure aggressive groundwater.
Next, we will analyze the types of waterproofing for different foundations. You can choose the right waterproofing by knowing the type of foundation, and how "pressure" groundwater is, so a few words about this. All groundwater is conditionally divided into suspended, non-pressure, low-pressure, and pressure.
Non-pressure groundwater- are in direct contact with the atmosphere through the open pores of the permeable medium.
Pressure water separated from the atmosphere by relatively impermeable rocks, they have sufficient pressure to self-spill to the surface of the earth.
low pressure water are in transitional conditions, characteristic of both pressure and non-pressure waters.
suspended waters- the first non-pressure waters from the earth's surface are located above the main zone of non-pressure waters and are more or less isolated accumulations of water.
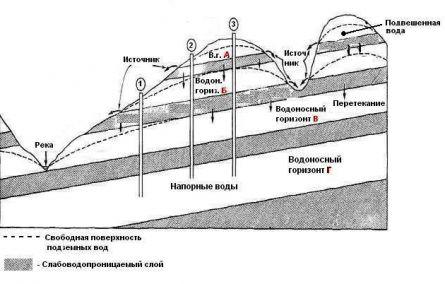 An example of the occurrence of aquifers
An example of the occurrence of aquifers
The figure shows a typical occurrence of aquifers represented by sedimentary rocks. (Fig. Pressure, non-pressure aggressive water). In the position when well 1 is laid, the water of horizon B is considered suspended, and the water of horizon C is free-flowing. Well 2 passes through suspended water of horizon A, free water of horizon B and pressure water of horizons C and D. Well 3 reveals pressure water in all horizons, except for horizon A.
Thus, in a small area with a simple geological structure within the same aquifer, water can be suspended, free-flowing and pressured.
Wherever the GWL is located, the foundation of any foundation must be laid with a layer of permeable material, for example sand + crushed stone.
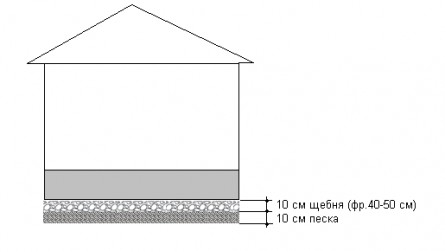 Sand-gravel pillow from the capillary rise of GW
Sand-gravel pillow from the capillary rise of GW
Such a cushion breaks the capillary rise of groundwater.
 Capillary elevation of HS
Capillary elevation of HS
Below we will consider how to make waterproofing of the foundation of various types and the features inherent in each type.
Waterproofing of the slab foundation.
 slab foundation
slab foundation
The slab foundation is recommended to be waterproofed with a rolled roofing felt. Waterproofing is placed on the foundation slab. If its surface is uneven, then a leveling screed is first made. A heater is laid on top of the waterproofing, a screed is made over it, and a floor covering is already placed on the screed.
Waterproofing strip foundation.
The strip foundation can be waterproofed in various ways.
1. Coating with bituminous mastic.
 Coating with bituminous mastic
Coating with bituminous mastic
The most economical option. Suitable in such cases: protection of the foundation from a possible capillary rise of the GWL, protection of the foundation from the possible penetration of surface water. Coating waterproofing does not protect against pressure water, as it does not withstand a set of more than 2 meters. This waterproofing is most often and most easily damaged, and therefore most often leaks, as it cannot withstand shear and tensile loads. Therefore, such waterproofing must be applied to a flat surface, always pre-dried, round the corners of the house, and also protect the waterproofing from mechanical damage. Such waterproofing is usually damaged already when the excavation is backfilled with backfill soil, which often contains construction debris (stones, fragments of reinforcement, glass, etc. debris).
You can protect:
EPPS insulation (given that the foundation should be insulated to the level of soil freezing);
 EPS waterproofing protection
EPS waterproofing protection
rolled geotextile, can be needle-punched, it is cheaper than thermally bonded, the required density is at least 180 g / sq. m;
a pressure wall made of bricks, this is sometimes done, but the option is rather laborious and expensive, therefore it is inferior to the two options for waterproofing protection described above;
if the foundation pit is backfilled with soft soil without debris, such as sand, then it is enough to protect the waterproofing only at the corners of the house, with geotextile strips 20 cm wide.
2. Waterproofing with roll material.
 Waterproofing with roll material
Waterproofing with roll material
Most often, roofing material is used from rolled materials. This is a slightly more expensive option than coated waterproofing, but more durable and strong. If the backfill soil does not contain debris, then such waterproofing can not be protected. The foundation surface must be flat. The foundation is treated with hot bituminous mastic, on which at least 2 layers of roofing material are glued with an overlap of 10-20 cm.
3. Sprayed waterproofing.
 Spray waterproofing
Spray waterproofing
Very easy and quick to apply with a special sprayer. Easily repeats all the irregularities of the foundation, does not need special surface preparation, except for cleaning from dust. More expensive material than conventional bituminous mastic. Requires obligatory reinforcement with thermally bonded geotextile material with a density of at least 130 g/sq. m, which simultaneously performs a protective function for this waterproofing. The material is quite expensive and it is cost-effective to use it for foundations of complex shape (which are difficult to glue with rolled material) or for a foundation laid very close to another building (that is, if it is very inconvenient to waterproof such a foundation due to the lack of free access to it).
In addition to the methods described above, it is possible to perform waterproofing by applying 25-30 mm of cement mortar with a water pressure of up to 20 m.
 Waterproofing with cement mortar
Waterproofing with cement mortar
It is also possible to waterproof the foundation with various penetrating waterproofing materials (a mixture of cement, quartz sand and active additives), which protects the foundation from excess moisture and some chemical compounds (depending on the brand of waterproofing), but this material is quite expensive.
 Penetrating waterproofing
Penetrating waterproofing
Waterproofing of the foundation in a pit with walls of 90 °.
 Pit with a wall slope angle of 90 degrees.
Pit with a wall slope angle of 90 degrees.
Sometimes the foundation is built close to the walls of the pit, this is the only possible option under cramped construction conditions. In this case, the pit is erected with walls at an angle of 90 °, pressure walls are erected close to the walls of the pit, waterproofing material is nailed to them (or first drainage, and then waterproofing, depending on the groundwater level). The formwork is installed at a distance from the pressure wall equal to the width of the future foundation. And in the resulting formwork (on the one hand, a pressure wall with waterproofing, on the other, just a formwork, pre-bonded reinforcement is laid and the foundation is poured. In this case, the pressure wall with waterproofing is called “lost formwork”, since it is not removed, but remains in the ground If in cramped conditions to build a foundation of blocks, then the blocks are laid at a short distance from the pressure wall and the resulting distance between the block foundation and the waterproofed pressure wall is filled with mortar.
Protection of walls from capillary rise of moisture.
 capillary rise in moisture
capillary rise in moisture
Anti-capillary waterproofing in the walls is laid on a plinth, which usually ends at a level of 15-50 cm above ground level. The surface of the plinth is pre-leveled, dried and covered with a layer of bituminous mastic. Then 2 layers of roofing material are laid. This type of waterproofing is known as continuous screed and must completely traverse the full thickness of the wall and interior plaster.
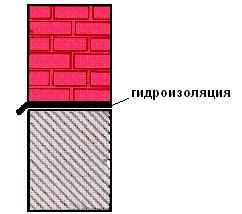 Protection of walls from capillary rise of moisture
Protection of walls from capillary rise of moisture
Waterproofing of columnar and pile foundations.
Waterproofing of pile foundations is done according to the grillage.
It is extremely difficult to waterproof piles and poles, it will take a lot of time and effort in the case of poles and almost impossible in the case of piles. Therefore, such pillars or piles are recommended to be made of moisture-resistant concrete of grade W4 and higher for non-aggressive hot water and from grade W6 and higher for aggressive ones.
The foundation of wooden piles must be treated with an anti-corrosion solution.
 Foundation made of wooden piles
Foundation made of wooden piles
At the same time, it is important to remember that it is not desirable to carry out measures to lower the GWL, i.e. do any drainage, as wooden piles do not rot just being completely in the water. Otherwise, there is a high risk of reducing their service life.
Basement waterproofing.
 Plinth waterproofing
Plinth waterproofing
The plinth from the outside to the level of a continuous gasket (10 -50 cm from the ground level) must be waterproofed in order to protect the wall of the house from surface water. The fact is that the average height of the snow cover is usually 10-50 cm, and also raindrops, fighting off the blind area, most wet 10-50 cm from the ground level. That is why the plinth must be lined with a waterproof material, such as water-repellent tiles.
Basement waterproofing.
For a house with a basement, a waterproof blind area is required, which will reduce the influx of surface water to the basement walls.
The basement floor is waterproofed by concrete preparation. For these purposes, waterproofing from 2 layers of rolled bitumen material is very well suited.
The walls of the basement are waterproofed according to the same principle as the strip foundation, which was described above. Also for basement waterproofing, waterproofing made of bentonite mats is very effective.
 Bentonite mats
Bentonite mats
This is a modern compact analogue of the classic clay castle. The material is a bentonite enclosed on both sides in a textile material. It is easy to mount, while replacing 1 meter of clay (classic clay castle).
If the groundwater in the area is pressurized and drainage needs to be done around the perimeter of the basement, it is very important to remember that the drainage begins to work only from the moment the water from the drainage material (falling further into the drainage pipes at the base of the foundation) begins to be discharged, for example, into the storm sewer . Up to this point, there may even be water in the pit, despite the fact that all drainage materials have already been laid.
I want to draw your attention - do not regret the waterproofing of the basement and do it very carefully. And if you hire builders for this work, then carefully control this stage. Because this is the kind of work that is quite difficult to fix when leaks already appear. After all, to repair the waterproofing of the basement, you have to break the foundation pit again. And by this time, the blind area is often already standing and the surrounding territories are partially inhabited. Therefore, basement waterproofing should be taken seriously.
If it so happened that for some reason the basement began to leak, then the best option would be to re-dig the foundation pit and replace the completely or partially damaged waterproofing. If it is not possible to dig a pit, for example, due to building density, then waterproofing can be done from the inside of the basement. But in this case, the walls will unfortunately continue to get wet, despite the fact that from the inside of the basement they will look dry.
What materials should not waterproof the foundation and basement.
The foundation and basement cannot be waterproofed with roofing films (waterproofing, vapor barrier) and membranes, including windproof ones. These materials are too thin and are designed for loose laying with sagging (they can't even be stretched). In addition, films and membranes will not withstand friction against the foundation surface due to constant seasonal ground movements, not to mention the fact that they are not designed to be protected from pressure groundwater. Therefore, their use for waterproofing foundations and basements is impractical.
It is not economically feasible to use materials with UV stabilization for these purposes, for example, a UV-stabilized PVC membrane. Since UV-resistant materials are more expensive, and this function will simply not be used underground.
Melt water and groundwater are the reasons why the life of the foundation and the residential building as a whole is reduced several times. From time immemorial, this has been fought by any means. Great experience has been accumulated. But until now, the owners of private houses are concerned about such an issue as basement waterproofing.
Waterproofing methods
First of all, it is necessary to decide from which side the waterproofing process will be carried out: from the inside or from the outside. The best option is outside.
Outdoor
Even at the stage of foundation construction, it is worthwhile to ensure its protection from moisture. There are several options here:
- Coating.
- Plaster.
- Okleyechnaya.
One of the best options: apply a plaster mortar to the walls of the foundation, treat it with hot bitumen, and then raise the wall next to half a brick. In addition, blind areas 1.5 m wide are poured, storm sewers are installed.
If the groundwater level is high enough, then drainage must be arranged.
Internal
Internal waterproofing of basements is carried out if the external waterproofing was performed poorly or the groundwater level is so high that it creates a lot of pressure on the foundation walls. They, in turn, cannot withstand the pressure of water. Although atmospheric precipitation creates conditions for the penetration of moisture into the basement. There are three main types of basement insulation from the inside: 
- Anti-pressure.
- Non-pressure.
- Anticapillary.
The first is used if the groundwater level is above the basement floor. The second, if the amount of precipitation in the region is large enough.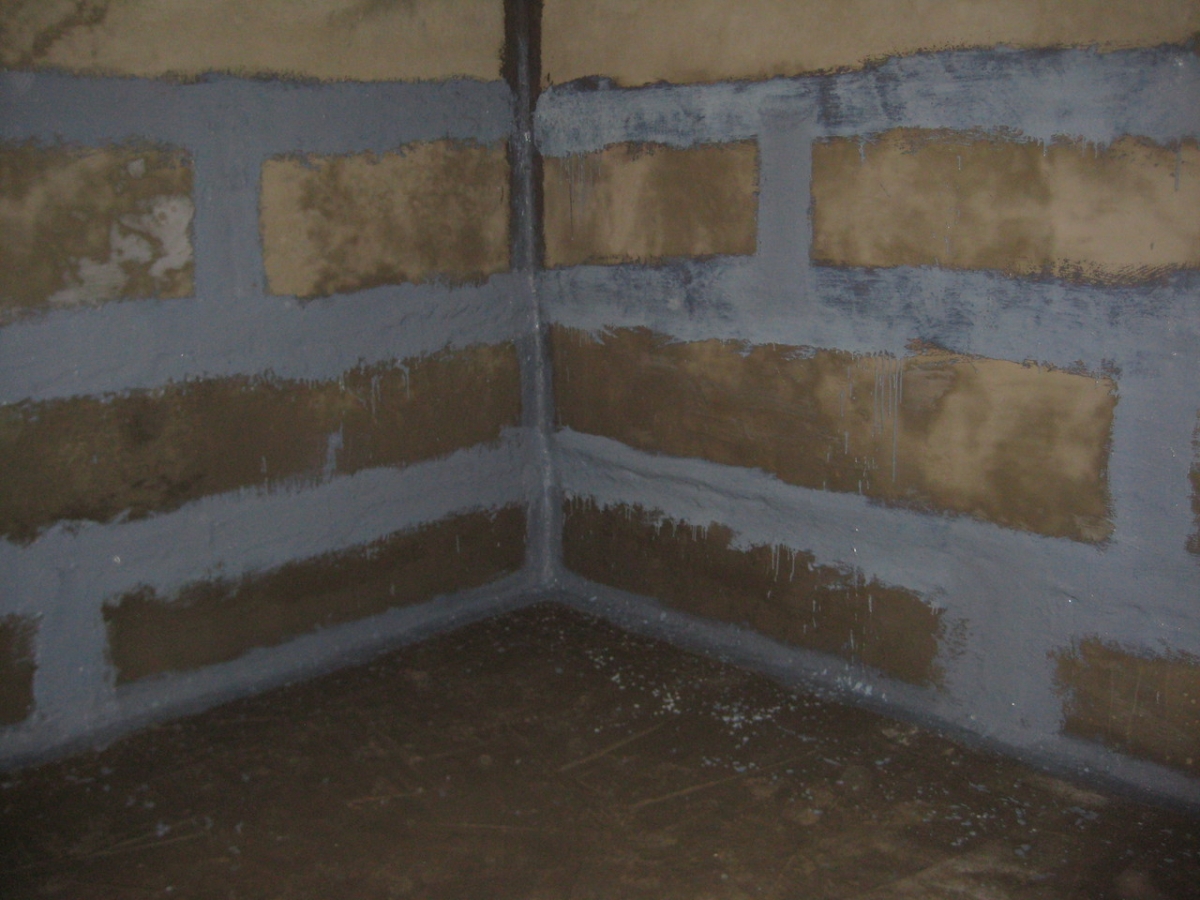  The third option is the so-called. It (the most modern) is today used more often than anyone else under any building operating conditions.
The third option is the so-called. It (the most modern) is today used more often than anyone else under any building operating conditions.
Waterproofing materials
Waterproofing materials on the market are represented by a large assortment. All of them can be divided into several categories. It all depends on the method of application and on the principle of action: coating, hydrophobic (injection), pasting (roll), penetrating.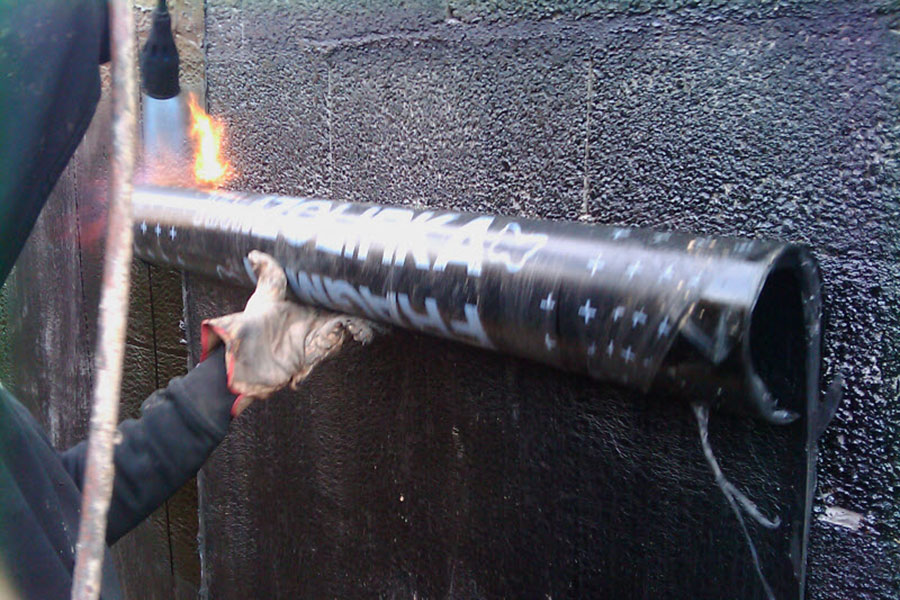  Next, we will consider how and how to waterproof the basement in a private house. We will pay special attention to the choice of materials, their exact purpose and the method of applying house structures to the nodes.
Next, we will consider how and how to waterproof the basement in a private house. We will pay special attention to the choice of materials, their exact purpose and the method of applying house structures to the nodes.
Coating
This category mainly includes various kinds of mastics based on bitumen, cement or polymers. Some are applied cold, others hot.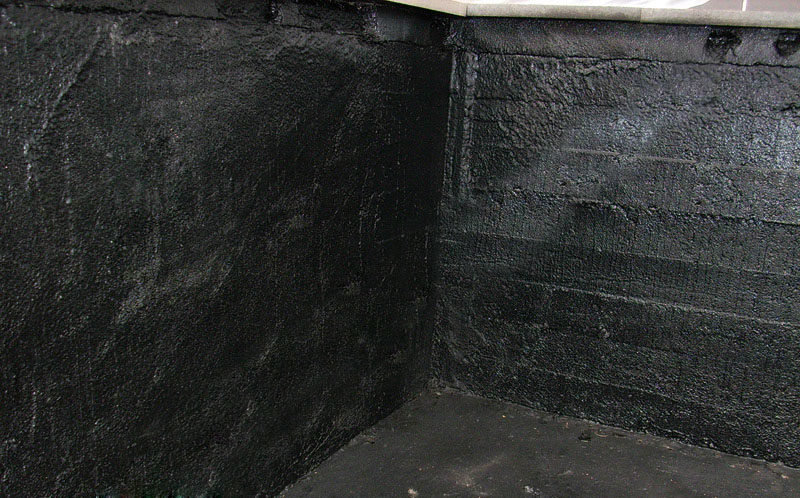  Bituminous mastic and cement mixtures are applied in a thick layer, polymer emulsions in a thin layer.
Bituminous mastic and cement mixtures are applied in a thick layer, polymer emulsions in a thin layer.
Mechanism of action
Many professionals prefer to work with cold-applied mastics. They create a thick protective layer on the walls of the basement in a private house, which penetrates into all cracks in concrete or brickwork. A seamless film with a high elasticity index is formed on the surface.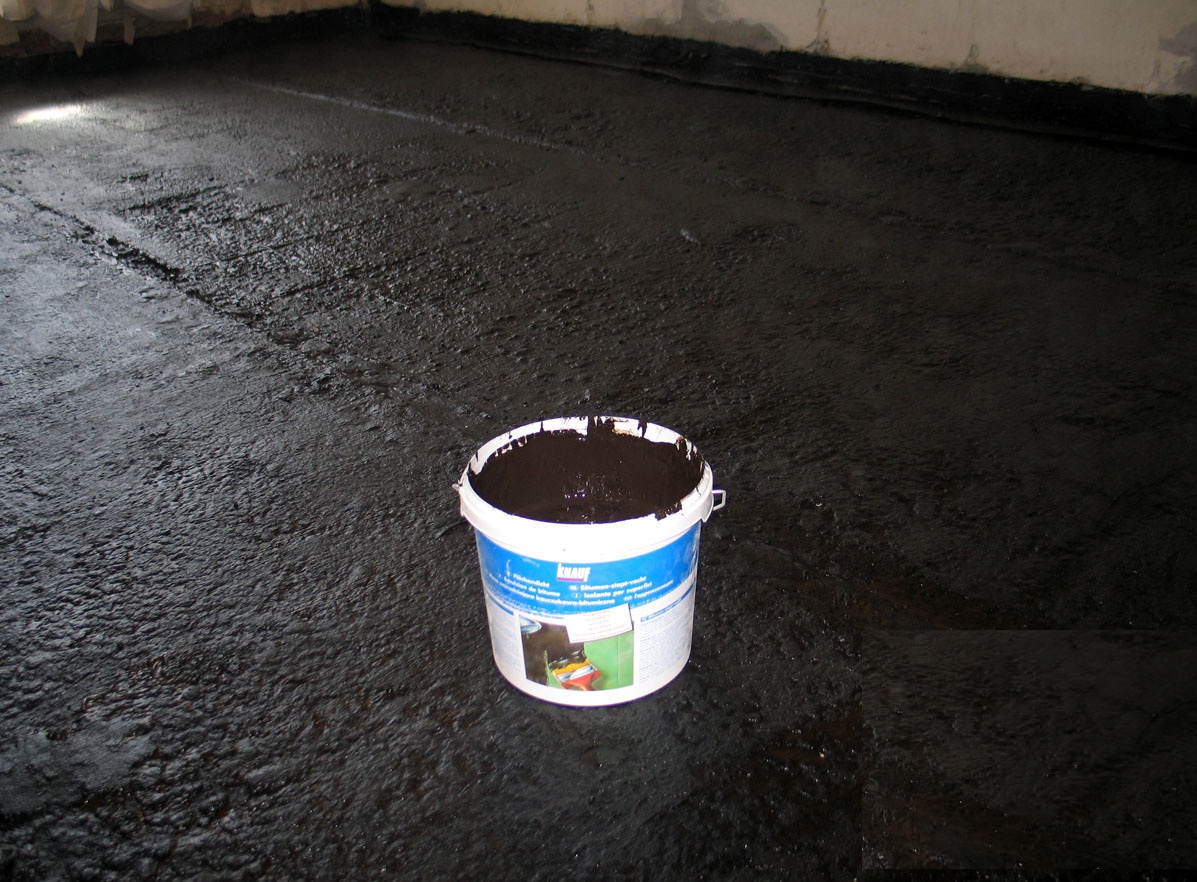  Please note that special bituminous mastic is used for seams (knots). The contact node is first embroidered, then filled with cement mortar, and after it has dried, it is treated with mastic.
Please note that special bituminous mastic is used for seams (knots). The contact node is first embroidered, then filled with cement mortar, and after it has dried, it is treated with mastic.
Application method
The technology for applying mastic is quite simple. This will require either a brush or a roller. The material is applied according to the type of paint. The main thing is to evenly distribute the mastic over the entire surface to be treated. The strips are overlapped relative to each other.  Some mastics are called liquid rubber. These include the brand "Elastomiks" or "Elastopaz".
Some mastics are called liquid rubber. These include the brand "Elastomiks" or "Elastopaz".
Note that this is a good way to waterproof a basement, but it can only be used if the foundation has been externally insulated. Liquid rubber itself cannot withstand the pressure of water even with a slight pressure.
In the category of waterproofing materials, liquid glass occupies a certain place. Someone treats him with distrust, someone considers him an excellent waterproofing agent.  In any case, the technology of its use has been known for a long time.
In any case, the technology of its use has been known for a long time.
Application technique
Liquid glass is most often applied outside the foundation. At the same time, it is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:2. The seams and knots of the structure are treated with special attention. The main requirement is a solid and even surface without grease and oil stains. Therefore, before applying liquid glass to the treated plane, the latter will have to be prepared.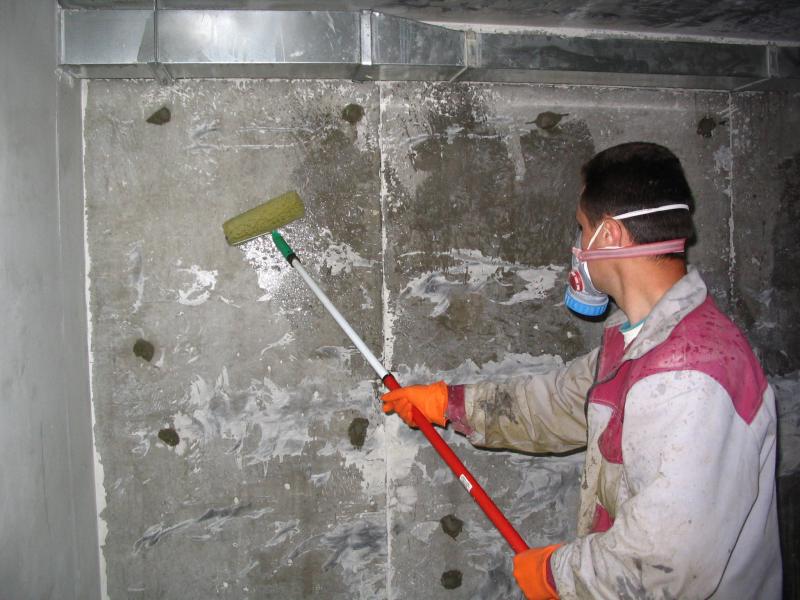  The material is applied with a brush, brush or roller. In fact, this is still the same basement in terms of coloring. There is another option for using liquid glass. It is introduced into the cement plaster mortar, which is used to treat the walls of the basement inside. Such mixtures create an excellent waterproof layer.
The material is applied with a brush, brush or roller. In fact, this is still the same basement in terms of coloring. There is another option for using liquid glass. It is introduced into the cement plaster mortar, which is used to treat the walls of the basement inside. Such mixtures create an excellent waterproof layer.
Pasting
Can be used both outside and inside. Most often it is used outside. For this, the walls of the foundation are prepared: they are leveled to a difference of 2 mm, treated with a bitumen emulsion, then the rolls (roofing felt, roofing felts and others) are laid in overlapping strips. Seam processing is carried out continuously, that is, two strips cannot be joined at the junction of two planes.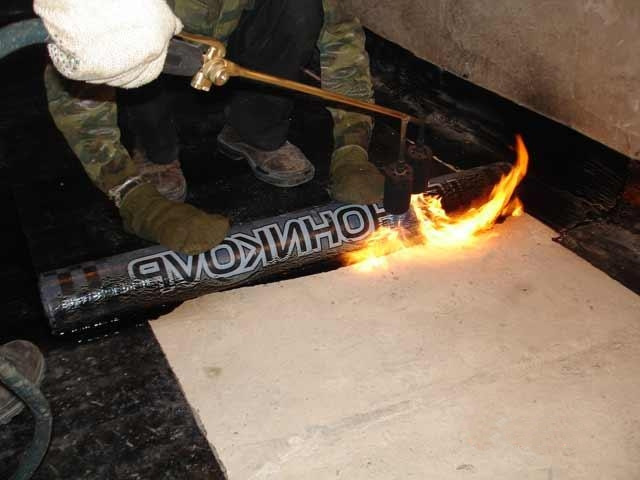  Roll waterproofing is very sensitive to mechanical stress, so experts advise installing a brick pressure wall to the foundation. This is done with roofing material, and with hydroisol, and with other materials.
Roll waterproofing is very sensitive to mechanical stress, so experts advise installing a brick pressure wall to the foundation. This is done with roofing material, and with hydroisol, and with other materials.
Penetrating
Penetrating waterproofing is a modern technology that is mainly used for interior treatment. Its main purpose is to make concrete waterproof.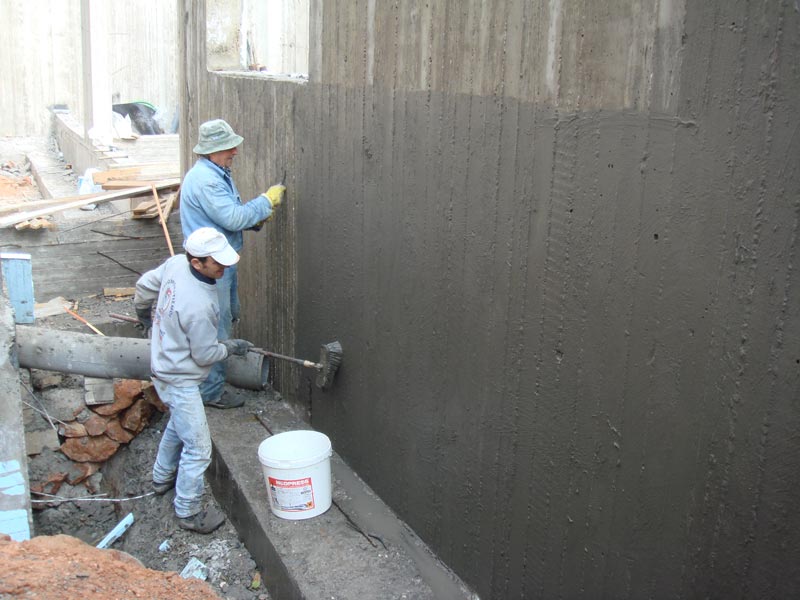  To date, this is the best waterproofing for basements that you can do yourself.
To date, this is the best waterproofing for basements that you can do yourself.
Composition and properties
In fact, this is a mixture that includes cement, quartz sand and active chemical additives. It is the latter that penetrate deep into the concrete structure, clogging the capillaries through which water penetrates into the room. Penetration depth up to 25 cm.
Mode of application
In order for penetrating waterproofing to last for a long time after application, it is necessary to clean the concrete wall from efflorescence. This can be done with an iron brush by hand. But it is better to use a drill with an iron brush on it or rinse the surface with water under pressure. In any case, the surface to be treated must be moistened. And the deeper the moisture penetrates into the concrete, the deeper the chemically active additives will penetrate, clogging the capillaries.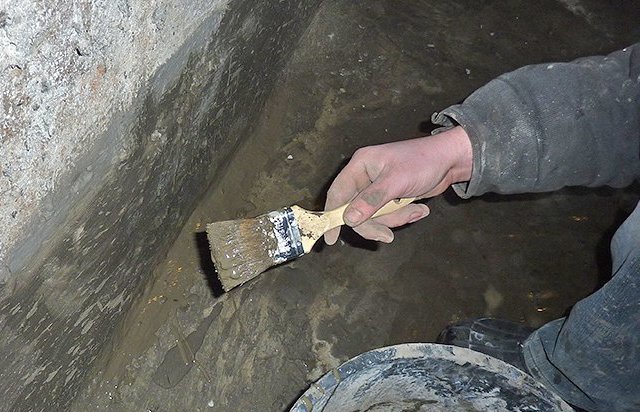  Experts recommend applying 5 liters of water per 1 m² of surface. The best option is to apply water in several layers with the absorption of the previous one. The solution itself is applied to the walls in two layers with a brush, spatula or roller. The second layer is applied perpendicular to the first after the latter has dried. Next, another moistening of the treated surfaces with a small amount of water is carried out.
Experts recommend applying 5 liters of water per 1 m² of surface. The best option is to apply water in several layers with the absorption of the previous one. The solution itself is applied to the walls in two layers with a brush, spatula or roller. The second layer is applied perpendicular to the first after the latter has dried. Next, another moistening of the treated surfaces with a small amount of water is carried out.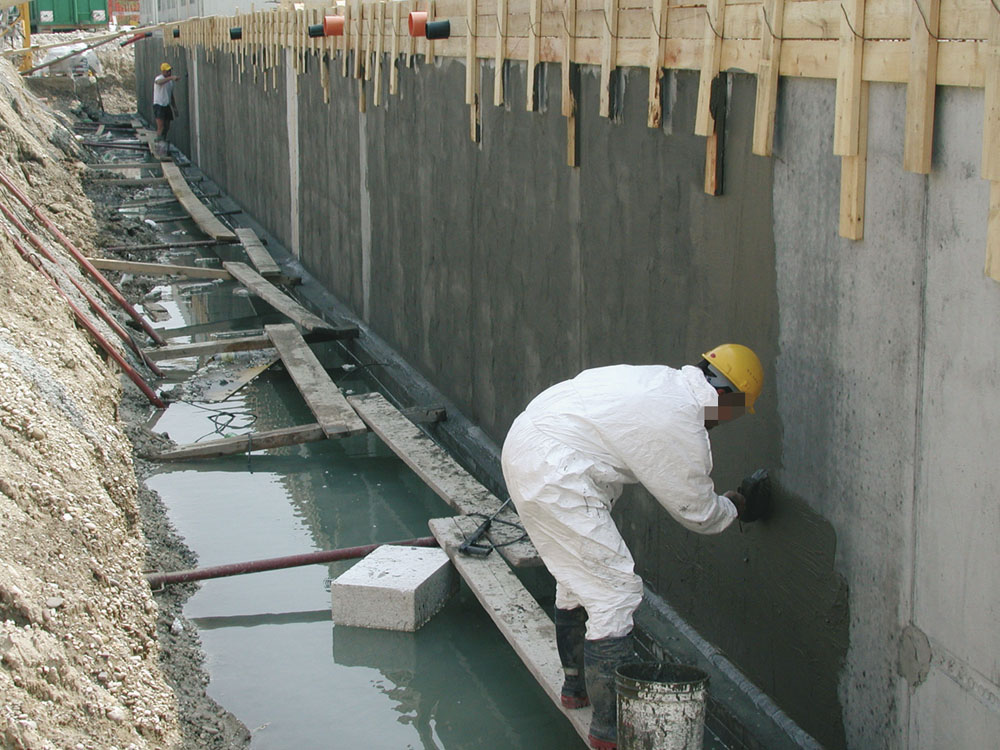  But this option also has one drawback - it can only be used for processing concrete structures. At the same time, the quality of concrete should be high with cracks no more than 0.4 mm deep.
But this option also has one drawback - it can only be used for processing concrete structures. At the same time, the quality of concrete should be high with cracks no more than 0.4 mm deep.
hydrophobic
Hydrophobic injection basement waterproofing is one of the best, but very complex technologies for protecting basements from water. For this, various gels based on polymers or acrylates are used.  The essence of the principle of operation of this type of insulation is that the gels, in contact with water, begin to harden. Therefore, they are pumped into places where groundwater penetrates from special containers or cans. To do this, holes with a diameter of 12-20 mm are drilled in the concrete walls and floor. Some holes are through, others are blind. They are distributed alternately every 30-50 cm. It is difficult to carry out this type of waterproofing on your own. It is especially difficult to determine the place of penetration of moisture. Therefore, this work cannot be done without specialists.
The essence of the principle of operation of this type of insulation is that the gels, in contact with water, begin to harden. Therefore, they are pumped into places where groundwater penetrates from special containers or cans. To do this, holes with a diameter of 12-20 mm are drilled in the concrete walls and floor. Some holes are through, others are blind. They are distributed alternately every 30-50 cm. It is difficult to carry out this type of waterproofing on your own. It is especially difficult to determine the place of penetration of moisture. Therefore, this work cannot be done without specialists.
Waterproofing scheme
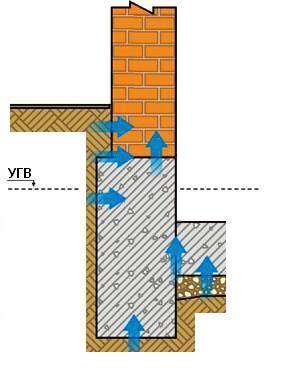
Do-it-yourself basement waterproofing usually includes several types of work being done. Everything will depend on the UGV.
If the level is high, then first of all it is necessary to build a drainage system, coat the outer walls of the foundation with bituminous mastic or stick a rolled waterproofing, raise the pressure wall.  Then go inside the basement and treat all surfaces (floor and walls) with anti-capillary protection and liquid rubber.
Then go inside the basement and treat all surfaces (floor and walls) with anti-capillary protection and liquid rubber.
Low groundwater level
If the GWL is low, then good blind areas and storm water must be built. External coating insulation or gluing (for example, roofing material) is produced.  From the inside, it is best to use an integrated approach using several materials.
From the inside, it is best to use an integrated approach using several materials.
Progress of internal work
A multi-layer insulation device is a guarantee of protecting the room from moisture. You can find out how to properly complete the whole range of work below.
Surface preparation
You have to start with preparation. To do this, the floors and walls are aligned. You can pour a screed on the floor, plaster the walls. Then capillary waterproofing is applied to all surfaces with a brush or roller.  Insulation layer 1-2 mm. We are waiting for everything to dry. Then another layer of the same type.
Insulation layer 1-2 mm. We are waiting for everything to dry. Then another layer of the same type.
Material laying
Now you can use the roll material. Its strips are laid in the form of a trough, that is, from the upper edge of the wall along the floor to the upper edge of the opposite wall.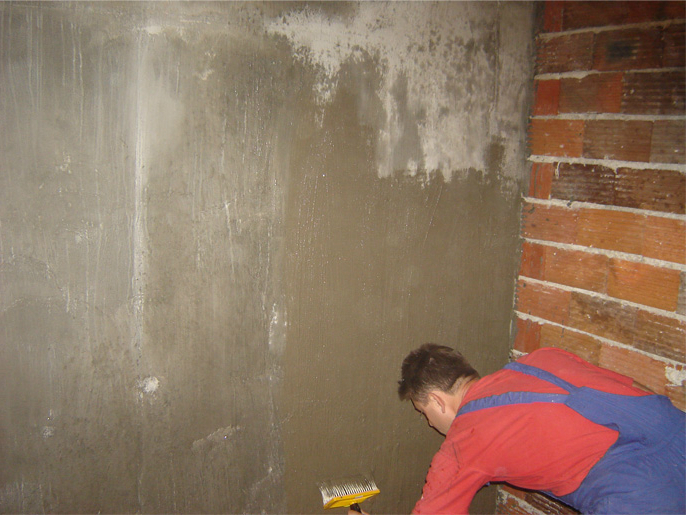  The best option is to lay in two layers, perpendicular to each other with an overlap. Rolled material can be replaced with coating material.
The best option is to lay in two layers, perpendicular to each other with an overlap. Rolled material can be replaced with coating material.



