Calculate the amount of heat for space heating. Calculation of the heating power of the cottage - how to do it right
Compared to electrical heating appliances, own heating system is more advantageous in terms of cost savings, and in maximum convenience when heating rooms.
Efficiency and profitability heating system at home depends on correct calculations compliance with precise rules and regulations.
Calculation of heating by the area of the house is a laborious and complex process. Don't skimp on materials. Quality equipment and its installation affects the financial budget, but then serves the house well and comfortably.
When equipping the house with a heating system, construction works and installation of heating must go strictly according to the project and taking into account all safety regulations for use.
The following points should be taken into account:
- house building material,
- footage of window openings;
- climatic features of the area where the house is located;
- location window frames by compass;
- what is the device of the "warm floor" system.
Subject to all the above rules and calculations for heating, some knowledge in the field of engineering is required. But there is also a simplified system - the calculation of heating by area, which can be done independently, again, adhering to the rules and complying with all norms.
Choosing a boiler requires an individual approach
If there is gas in the house, then the most the best option- This a gas boiler. In the absence of a centralized gas pipeline, we choose an electric boiler, a heat generator using solid or liquid fuel. Taking into account regional characteristics, access to the supply of materials, it is possible to install a combined boiler. Combined generator heat will always maintain a comfortable temperature, in any emergency and force majeure situations. Here you need to start from a simple type of operation, the heat transfer coefficient.
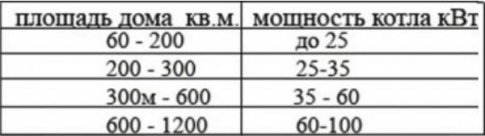
After determining the type of boiler, it is necessary to calculate the heating according to the area of \u200b\u200bthe room. The formula is simple, but it takes into account the temperature of the cold period, the heat loss coefficient for large windows and their location, the thickness of the walls and the height of the ceilings.
Each boiler has a certain power. With the wrong choice, the room will be either cold or excessively hot. Thus, if the specific power of the boiler per 10 cubic meters. taking into account the area of the heated room of 100 sq.m., you can choose the most optimal heat generator.
From the formula used by engineers, Wcat = (SxWsp)/10, kW. – it follows that the boiler with a capacity of 10 kW heats a room of 100 sq.m.
The required number of sections of the heating radiator.
To make it more clear, let's solve the problem using the example of specific numbers. If we assume that room area 14 sq.m. And ceiling height 3 meters, the volume is determined by multiplication.
14 x 3 = 42 cubic meters.

IN middle lane Russia, Ukraine, Belarus thermal power per cubic meter corresponds to 41 W. We determine: 41x 42 \u003d 1722 watts. Found out that for a room of 14 sq.m. need a 1700W heatsink. Each individual section (rib) has a power of 150 watts. By dividing the results obtained, we obtain the number of sections required for the acquisition. The calculation of heating by area is not the same everywhere. For premises over 100 sq.m. required circulation pump installation, which serves as a "forcer" of the movement of the coolant through the pipes. Its installation takes place in the opposite direction from the heating devices to the heat generator. The circulation pump increases the life of the heating system by reducing the contact of hot coolants with appliances.
When installing a heating system warm floor» the coefficient of heating of the house increases many times. You can connect the underfloor heating system to existing types of heating. A pipe is removed from the heating radiators and floor heating wiring is supplied. This is the most convenient and profitable option, taking into account the savings in time and money.
Before choosing a heater, you need to calculate the minimum heat output required for your particular room.
Usually for approximate calculation it is enough to divide the volume of the room in cubic meters by 30. Managers usually use this method when advising buyers by phone. Such a calculation allows you to quickly roughly estimate what total heat output may be needed to heat the room.
For example, to select a heat gun for a room (or office) with an area of 50 m² and a ceiling height of 3 m (150 m³), 5.0 kW of heating power will be required. Our calculation looks like this: 150 / 30 = 5.0
This calculation option is mainly used to calculate additional heating in those rooms where there is already some kind of heating and you just need to warm the air to a comfortable temperature.
However, this method of calculation is not suitable for unheated rooms, and if it is necessary to take into account the temperature difference between inside and outside, in addition to the volume of the room, and design features the building itself (walls, insulation, etc.)
Accurate calculation of the heat output of the heater:
To calculate the heat output, taking into account additional room conditions and temperature conditions, the following formula is used:
V × ΔT × K = kcal/h , or
V × ΔT × K / 860 = kW, Where
V- The volume of the heated room in cubic meters;
∆T— The difference between the air temperatures inside and outside. For example, if the outside air temperature is -5 °C and the required indoor temperature is +18 °C, then the temperature difference is 23 degrees;
K- Coefficient of thermal insulation of the room. It depends on the type of construction and insulation of the room.
K=3.0-4.0- Simplified wooden structure or corrugated metal sheet construction. Without thermal insulation.
K=2.0-2.9— Simplified building structure, single brickwork, simplified window and roof construction. Little thermal insulation.
K=1.0-1.9- Standard construction, double brickwork, few windows, standard roof. Average thermal insulation.
K=0.6-0.9– Improved building design, brick walls double insulated, few double-glazed windows, thick subfloor, high quality roof thermal insulation material. High thermal insulation.
When choosing the value of the thermal insulation coefficient, it is necessary to take into account the old building or the new one, since old buildings require more heat for heating (accordingly, the value of the coefficient should be higher).
For our example, if we take into account the temperature difference (for example, 23 °C) and specify the coefficient of thermal insulation (for example, we have an old building with double brickwork, take the value 1.9), then the calculation of the required heat output of the heater will look like this:
150 x 23 x 1.9 / 860 = 7.62
That is, as you can see, the refined calculation showed that in order to warm up this particular room, a greater thermal heating power will be needed than was calculated using the simplified formula.
A similar calculation method is applicable to any type of thermal equipment, with the possible exception of infrared heaters, since the principle of perceived heat is used there. For any other types of heaters - water, electric, gas and liquid fuel, it is suitable.
After calculating the required thermal power, you can begin to select the type and model of the heater.
How to determine the heating power
If you have built your own house and are ready to start building engineering networks, you need to familiarize yourself with some of the nuances that will affect the correct installation work. Let's talk about the heating system. And let's start with the room.
It would seem that here you can count - buy a boiler, pipes and radiators, install and connect all this. But not everything is so simple. After all, you have to invest your hard-earned money. A properly calculated system will save a lot of money.
Heating boiler calculation
This is the simplest of the calculations, because the power of the heating boiler depends on the area of \u200b\u200bthe premises that it will heat. To do this, take the ratio - 1 kilowatt of thermal energy heats 10 square meters area with a ceiling height of not more than 3 meters. Take the total area of the house, divide by 10 and get the power of the heating boiler.
This simplified formula can only be used for single-loop devices. For a two-circuit unit, the calculation will have to be carried out differently. For example, a house with an area of 240 square meters cannot be heated with a wall-mounted boiler with a capacity of 24 kilowatts. One heating circuit will work for space heating, and the second - for heating water for domestic needs. Therefore, the power will have to be divided by 2, and it turns out that such a boiler can heat a house with an area of no more than 120 square meters.
With a single-circuit device, everything is much simpler, but even here a small backlog is needed. For example, choosing a single-circuit boiler with a capacity of 24 kilowatts, you can guarantee that it will calmly heat a house of 200 square meters with a ceiling height of 2.5-2.6 meters. If the ceilings in the house are 3 meters, then the device will be able to heat the premises with total area 170 squares. Here are some manipulations.
The calculation of heating radiators in the apartment is also very important. And here it is necessary first of all to determine their number, and for each room separately. To do this, it is necessary to take as a basis not the area, but the cubic capacity. If there are few batteries, this will provide a lack of heat, which means that the rooms will always be cold. If there are too many radiators, then you will have to pay more for such heat, acquiring more fuel. So everything should be in moderation.
Alternative connection of heating radiators in an autonomous system
For example, let's take a room of 10 square meters with a ceiling height of 3 meters. There is a standard indicator that determines the amount of thermal energy that is enough to heat 1 cubic meter of space. It is equal to 39-41 watts. To calculate the volume of a room, you need to multiply the area by the height of the room - in our example, this is 30 cubic meters. Now we multiply this value by 41 watts. The result is 1230 watts. This is the power that will pull the volume of this room.
There is another standard indicator - this is the amount of thermal energy that 1 section of the radiator can generate. It is equal to 200 watts. Now we divide the received total power by the power of one section -1230/200=6.15. That's what it is required amount sections to be rounded up. The result is the number "7". This means that in this room you can install a radiator with seven sections. It's that simple.
For corner rooms calculation cast iron batteries carried out using an additional correction factor, which depends on the region. The coefficient is 1.1-1.3. In order not to be mistaken, take the maximum indicator as a basis. The formula will turn out like this - 1230x1.3 / 200 \u003d 7.995. Round up to 8.
Attention! In our case, the number of sections is not so large. Sometimes this number goes off scale for a couple of tens. For such cases, the advice is to break the number of sections into an equal number of batteries, installed evenly throughout the building and ideally under the window.
Calculation of other materials for heating
For those who have never encountered the installation of a heating system, it will be very difficult to calculate the necessary materials. The minimum that is needed is at least to have an idea of how the pipes will be laid out, how the heating boiler will be tied, and how the batteries will be connected. Therefore, before starting the calculation, it is necessary to study the scheme of the heating system. If you can't handle it, then it's best to contact the experts.

Radiator connection diagrams
What materials are needed for the heating system? Consider them using the example of a double-circuit boiler. To connect it to the heating system of the house, you will need at least four ball valves with detachable connections - one for each inlet and outlet of two circuits. Each faucet has one threaded adapter to connect it to pipelines. You will definitely need two filters for the mechanical purification of water entering the boiler.
Now let's move on to the piping of the radiators. Here you need two valves (regulating and shut-off), a Mayevsky valve (for air release), a plug, two threaded adapters and two tees for connecting pipes to the main line. This kit is for one radiator only. To calculate all the necessary products, you will have to multiply this by the number of batteries that are planned in your home.
As for the pipes, you will have to measure the distances from the radiators to the boiler and multiply the resulting footage by two. Because many systems work on the principle of supply and return of coolant. The only problem may arise with the diameters of the pipelines, but not everything is so complicated here. Many systems use mainly pipes from 20 to 32 millimeters in diameter. And if your house is not very large in size, then this figure will be sufficient.
Conclusion on the topic
As you can see, calculating the heating power of a cottage is a serious matter. Here it is necessary to take into account many parameters of the house itself. But in general, these mathematical calculations are not difficult if you understand them.



