Calculation of composite tree-reinforced concrete beams for bending. Calculation of floor beams. Properties of wood materials
Wooden floor beams
Timber beams are often the most economical option. Wooden beams are easy to manufacture and install, have low thermal conductivity compared to steel or reinforced concrete beams. Flaws wooden beams- lower mechanical strength, requiring large sections, low fire resistance and resistance to damage by microorganisms and termites (if they are found in your area). Therefore, wooden floor beams must be carefully treated with antiseptics and flame retardants, for example, XM-11 or HMBB manufactured by Antiseptic (St. Petersburg).
Floor Padding: Is More Wood Better? Without any other factors, this may be true. But when other factors come into play - mainly cost and size - you need to calculate gaps that match your actual situation. Pay special attention to how the change in beam size changes when you change one of the factors, such as the distance between the bars or the length of the span.
Calculation of reinforced concrete beams
Exist different types live and dead loads. Live loads on the first floor have higher requirements than those on the second floor. These joist floors are based on hardwood. Hem-fir is a common type of lumber and is. These are the type of species you'll find at your local Lowe, Home Depot, or Menard.
How to calculate the required cross-section of a wooden floor beam?
The optimal span for wooden beams is 2.5-4 meters. The best section for a wooden beam is rectangular with a height to width ratio of 1.4:1. The beams are led into the wall by at least 12 cm and waterproofed in a circle, except for the end. It is advisable to fix the beam with an anchor embedded in the wall.
Floors and panels spaced apart
However, Austrian spruce, an imported species, can accommodate an additional half foot of span under the same conditions. You need to travel 5 feet for a live load. You need to fly the same distance, 5 feet, for a live load. But circumstances dictate that you can only run beams every 24 inches.
Installation Interval: 24. You are building a one-room addition to your home that is 16 feet long. This means you need to cover a distance of 5 feet for a live load. Installation spacing: 16. Your floor beams should be spaced 8 feet apart for live load.
When choosing a section of a floor beam, the load of its own weight is taken into account, which for beams of interfloor floors, as a rule, is 190-220 kg / m2, and the temporary (operational) load, its value is taken equal to 200 kg / m2. Floor beams are laid along a short section of the span. It is recommended to choose the installation step of wooden beams equal to the installation step of the frame racks.
Calculation by the formula of maximum stress when bending a profile pipe
While 8 feet is a short span, remember that this is a workshop. Or will it just be used for a light hobby? These are factors to consider when laying a floor slab. A nuanced look at floor openings can be found in range calculators or tables, some of which are listed below. True floor slab calculations can only be performed by a civil engineer or contractor.
Calculating the material cost of adding a room is essential to the building process. An accurate material cost estimate allows you to create a budget that will guide the entire job. It also allows you to deal confidently and confidently with contractors and, if you borrow money to finance additional space, lenders. Calculating the cost of a material before you start adding requires simple math and minimal design knowledge, but will save you time, money, and headaches later.
To calculate the minimum and optimal cross-section of a wooden floor beam, you can use the Romanov online calculator for wooden floor beams
Below are several tables, with the values of the minimum sections of wooden beams for various loads and span lengths:
Maximum Load Level Calculations
Sketch to enlarge the room you want to add. Get a draftsman or architect to draw the plans if you want a more accurate estimate. Measure the perimeter of the three new walls to determine the number of linear feet needed for the bottom and top slabs of your wall sections, as well as the number of wall studs required. multiply total number by 2 and divide by 8 to determine the number of boards you will need. Figure 3 studs for every 4 feet of length.
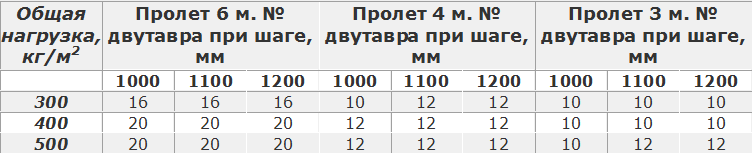
Table of sections of wooden floor beams depending on the span and installation step, with a load of 400 kg / m2. - it is recommended to rely on this load
If you do not use insulation or do not plan to load floors (for example, an uninhabited attic floor), then you can use the table for lower load values of wooden floor beams:
Drawing up a design diagram of a beam
For example, a 12 by 12 room requires 36 feet of bottom plates and 36 feet of top plates for a total of 72 feet. Dividing 72 feet by 8 feet per board gives 9 boards. Three studs for every 4 feet makes 27 wall studs. Twenty-seven boards plus 9 boards gives 36 boards.
Calculate the number of ceiling and floor beams and rafter slings. The ceiling beams are spaced two feet apart, so a 12 by 12 room needs six ceiling beams. Floor space is 16 inches apart. Build ceiling beams 2 by 8, and multiply the price per piece by 6 to find the total cost.
Table of minimum sections of wooden floor beams depending on the span and load, with loads from 150 to 350 kg / m2.

If you use round logs instead of rectangular beams, you can use the following table:
The minimum allowable diameter of round logs used as floor beams depending on the span at a load of 400 kg per 1 m2
Measure the length and width of your walls, ceilings, and floors and multiply the length by the width to find the area of each. Divide the area of the wall and ceiling by 32 to determine the number of wall panels. Divide the floor area by 24 to determine the number of sheets for the floor. Multiply the number of drywall and floor boards by their unit price to determine the total cost.
Determine the number of squares of siding and roof tiles. Area - an area of 100 square feet. Multiply the price per square by the number of squares to find the total cost. Determine the amount of wire and the number of electrical outlets, switches and boxes. Multiply the price per foot by the number of feet of wire and the price per piece by the number of outlets, switches, and boxes to get the total. Perform the same calculation for each pipe for any desired pipeline.
![]()
If you want to block large runs, we recommend using the experience from the Okolotok website.
Steel (metal) I-beams
An I-beam metal floor beam has a number of undeniable advantages, with only one drawback - high cost. metal I-beam it is possible to block large spans with a significant load, the metal steel beam is non-combustible and resistant to biological influences. However, a metal beam can corrode in the absence of a protective coating and the presence of aggressive environments in the room.
Find prices for lighting and plumbing fixtures. Estimate your preferred paint and flooring. Price doors, windows and finishing materials. Add total prices for individual components to find an approximate total add-on cost.
What load acts on the profile pipe
Since determining the load-bearing capacity of a floor beam requires a deep understanding of the structural properties of wood as well as building code requirements, it is best to consult a building specialist when it comes to determining the specifics of a building structure. However, understanding the basics of the calculations can help you understand the load limits of your existing floor.
To calculate the parameters of an I-beam metal beam you can use good
In most cases, in amateur construction, when calculating in the above program or others similar to it, it should be assumed that the metal beam has articulated supports(that is, the ends are not rigidly fixed - for example, since in the frame steel structure). The load on the floor with steel I-beams, taking into account their own weight, should be calculated as 350 (without screed) -500 (with screed) kg / m2
The step between the I-beams is recommended to be equal to 1 meter. In case of economy, it is possible to increase the step between metal beams up to 1200 mm.
Floors must be able to support two different types weight loads. Dead load on a floor is the weight of the floor structure itself and everything else that is permanently attached to the floor. A live load is a mass of furniture, people, and anything else that needs to be supported on the floor, but that isn't permanently tied down.
Beam deflection on two supports at a distance z from the left support at a ≤ z ≤l
The dead load on the floor is determined by the materials used in the construction of the floor. A typical wood frame covered with carpet or vinyl flooring has a dead load of about 8 pounds per square foot, if a wall has a covered ceiling suspended from the underside of that floor, the dead load increases to about 10 pounds per square foot. Heavier floor materials increase the dead load even more.
Table for selecting the number of an I-beam metal beam with different pitches and lengths of runs
Reinforced concrete floor beams
On device reinforced concrete beams you need to use the following rules (according to Vladimir Romanov):
Local building codes specify the minimum live load that floors must support. The International Housing Code, upon which most local building codes are based, requires floors in non-stained rooms to support a minimum 40 pounds per square foot live load, and floors in bedrooms must be capable of handling a 30 pounds per square foot live load.
What determines the strength of the coating?
The codes also determine how many floors are allowed to flex under load, a measurement called the deflection limit. Architects and engineers use these tables to determine the required size and distance from beams when designing buildings, but you can use them for reverse work and calculation of the load capacity of the existing floor. First, determine the size, spacing and span, as well as the type and level of lumber of your floor beams. Look for the mark on the beam, which indicates the type and grade of lumber.
- The height of the reinforced concrete beam must be at least 1/20 of the length of the opening. Divide the length of the opening by 20 and get the minimum height of the beam. For example, with an opening of 4 m, the height of the beam should be at least 0.2 m.
- The width of the beam is calculated based on the ratio of 5 to 7 (5 - width, 7 - height).
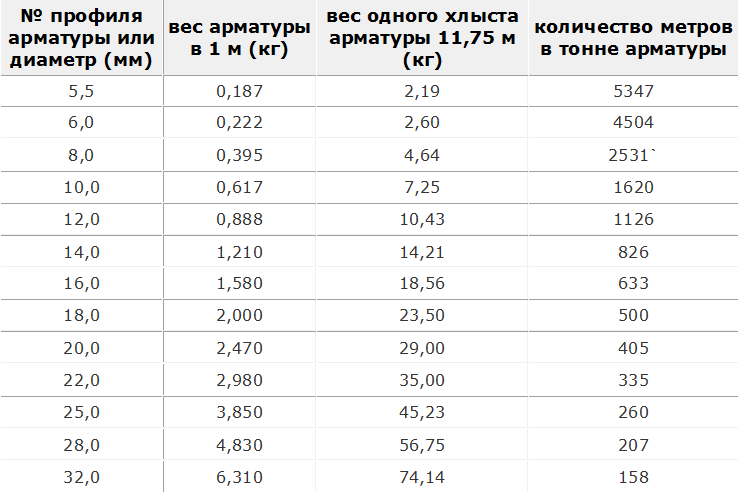
- The beam should be reinforced with at least 4 bars of reinforcement d12-14 (it can be thicker from below) - two at the top and bottom. Tables of the ratio of the length and mass of reinforcement of various sections.
- Concrete at one time, without interruptions, so that the previously laid portion of the mortar does not have time to grab before laying a new portion. Concreting beams with a concrete mixer is more convenient than ordering a mixer. The mixer is good for quickly pouring large volumes.
The weight of building reinforcement or how many meters of reinforcement in a ton. Weight of rebar 11.75 m long. Weight of rebar with a diameter of 5.5 to 32 mm.
As an example, consider a room with a floor area of 10 feet by 11 feet, 2 inches, made with four sheets of 4 liters of Douglas spaced 16 inches from the center. Use intermediate tables for heavier loads until you find the floor boundary.
Calculation of a wooden beam for overlapping: what to look for
Once you have determined the load limit for your beams, you can use this figure to determine the total permissible load for the room or building in question. In this example, the space is about 112 square feet.
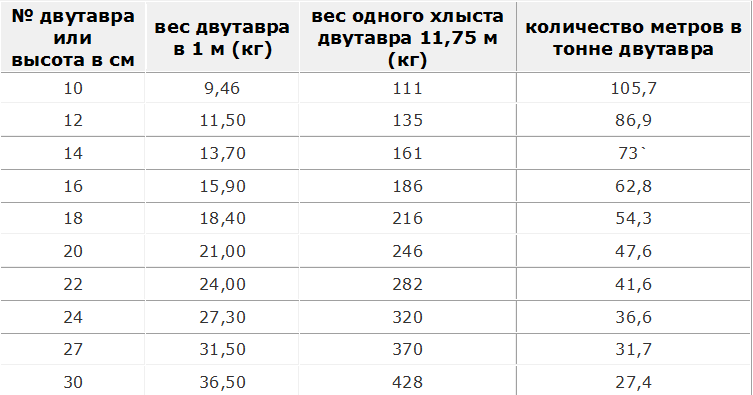
I-beam weight and number of meters per ton of I-beam
During the construction of private residential buildings, outbuildings and other buildings, it is important to correctly calculate the parameters of each structural element. One of the key elements of any wood structure is the floor.
For long lasting and flawless floor covering The choice of flooring is not only decisive. Substructure also plays an important role. If there were defects before, such as cracks or settlements, this is also negatively affected. The lack of sound and thermal protection also reduces functionality. The substructure of the floor is placed on the raw ceiling, today screeds are often used. Other designs are also possible for wooden ceilings. If the floor is to be repaired, great care must be taken.
As the base of the floor between the quilt and the top cover, screeds in different finishes are a top priority. A lubricant consists of a mixture of a binder, sand or gravel in the form of an aggregate, and water. If necessary, additives for certain properties can be added. Screeds are classified according to the type of binder.
About floor materials
Properly selected material, choice of length, section and installation scheme determines its durability and the loads that it can withstand. The selection and calculation of wooden beams for floors between floors is one of the most important decisions in private construction. Since wood is an environmentally friendly material and quite durable.
Cement screed calcium sulfate screed mastic asphalt magnesiastrich synthetic resin screed. The classic cement screed is mainly used in residential construction. Another distinguishing criterion for conventional types of screeds is the method of production. A distinction is made here between on-site construction sites, self-levelling floor screeds, and prefabricated floor sections.
Finally, there are also various designs, with which the screed is built on a damp floor. Between the blanket and the screed there is an insulating layer with an intermediate separating layer. The screed tile is free to move and does not have any substructures or ascending components. As a special form of floating screeds, one is installed in heating screeds directly or below the screed layer. Possibility of water or electrical systems floor heating. The sliding screed is built on a separating layer and is used wherever sound or thermal insulation is not required, such as in the basement. The separating layer, on the one hand, serves as "freedom from movement", on the other hand, sealing against moisture from below. For better strength of the release layer, it is basically two-layer. Edge strip connections on ascending components must be secured against repositioning when moisture or flow tie is inserted and can be compressed up to 5 mm. In case of high load-bearing capacity requirements and on adjacent bases, a composite screed can be installed. This type of tie is also supplied without additional outlets and is directly connected to the blanket. To ensure that no cracks or deformations are found on the finished screed, it is very important to match the properties with the substrate. Installation on a wet surface is recommended. If the layer is installed directly on the installation lines of the raw ceiling, it is necessary to install a compensation layer between the ceiling and the screed.
- In hostels, the screed is installed in most cases in a floating way.
- Failure to do so will result in unwanted noise and noise.
The only supposed minus of wood when compared with concrete is its combustibility, the indicator of which, if necessary, can be reduced if the wood is treated with special compounds.
It is generally accepted that concrete is refractory, although this is not entirely true: it cracks at temperatures above 250 and crumbles at a temperature of 550 degrees, that is, it is completely destroyed in a fire. Therefore, wood is a good alternative to concrete.
But, in order to calculate how much wood is needed for construction, so that there is no excess of it, so that the maximum load bearing capacity this wooden beam, often use a calculator for automatic calculation of floor parameters. The calculator for calculating wood floor beams will help you quickly and fairly accurately determine the safety margin indicators when using different materials and, accordingly, choose one of them. The best materials, section parameters, design features, high-quality floor beams allow you to optimally distribute the load without exceeding the permissible one, as well as walls made of brick or made of other material.
What determines the strength of the coating?
The main parameters that affect the quality of the overlap depend on the properties of the material, technical parameters and operating conditions.
Properties of wood materials:
- Type of tree. Pine, spruce, larch are considered popular species for use in residential construction. Sometimes oak, birch, aspen, as well as combined materials are used.
- Sort. Three types of wood are determined, which are numbered 1 (the best), 2 and 3. The grade is determined by the maximum number of knots on the wood, the bending of the beams, including healthy and rotten ones, the number, depth and length of cracks, and other wood defects. Detailed requirements for wood are determined by standards, norms, rules (SNiP II-25-80, SP 64.13330.2011 and others).
Each material has its own strength and deflection characteristics, which depend on the technical parameters described below. Some breeds are lighter, others more resistant to moisture.
For example, softwoods have better resistance to moisture. The first grade of wood is of the best quality, lack of flaws, but it is correspondingly more expensive.
Technical indicators:
- Beam type. Defines types such as rectangular beams, round logs, beams,. glued from boards or LVL veneer.
- Span length. Typically, a beam span for private residential buildings is no more than 6 meters. It is important to remember that this indicator is different from the length of the beam itself, which must also capture the supporting sections on the walls or other supports.
- Beam height and width. For a beam, another rectangular beam, these indicators may be the same or different. The greater their height, the greater the rigidity and the less they flex. In the case of logs, the diameter or average diameter of the log is taken into account. When choosing these parameters, the features and ease of manufacture, transportation, and installation of beams are also taken into account.
- Beam step. This is the distance between two adjacent beams in the floor. The closer the beams, the higher their consumption of beams, the strength of the overlap, but the deflection and maximum load decrease. and concentrated load, which are defined by standards and depend on the type of premises, the number of residents or employees, the type and amount of furniture or equipment in them, and other features of their use.
- Cover type. This refers to interfloor floors with increased requirements for relative deflection, which is 1/250; attic floors, the requirements for which are lower - 1/200; coatings and floorings, the relative deflection of which is 1/150.
The last 3 items are also defined as operating conditions hardwood floor, which depend directly on the features of the construction.
Result and calculation example

How the wooden beam calculator works and how the load is calculated are the main questions to be answered here.
The 2 main indicators that determine the quality of the floor are the distributed load on the floor itself, as well as the concentrated load on the crossbars, if they are used. The quality of the crossbar also depends on the method of fixing it.
The online calculator automatically shows how big the stock will be distributed load and deflection at the overlap. Or vice versa, it will indicate an overload.
Calculation example
For example, the following input parameters are used: pine timber, single-span for interfloor overlapping, 6 meters long, has a square section of 120 by 120 millimeters. They will be located in increments of 40 centimeters with a load on the beam, which is 60 kilograms per square meter.
The moment of inertia of the section will be 1728 cm⁴, and such beams weigh 43 kilograms each.
As a result, the calculated deflection of such an overlap will be 23 millimeters (or 1/261 of the relative deflection). It will have a deflection margin of 1.04 times and collapse under a load of 845 kilograms.
For the corresponding crossbar with a concentrated load of 90 kg, the calculated deflection will be 23 millimeters, and the deflection margin will be 1.04 times. The design will not withstand loads over 422 kilograms.
Consequently, building experts will recommend not to use a floor between floors with such indicators, since the deflection margin is too small.
The optimal deflection index is from 1.5 to 3, respectively. The higher this indicator, the higher the wood consumption, but the lower the deflection margin, the less stable the building as a whole and its elements in particular will turn out.
Benefits of a calculator
Using the calculator, the builder can independently select the necessary parameters, selecting each of the available or desirable options and calculating more profitable materials and type of beams.



