Types of fluorescent lamps. LED lighting lamps
Incandescent lamps
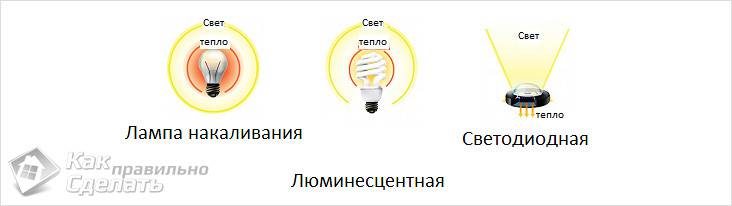
Ordinary light bulbs that are familiar to all of us, and their main advantage is the pleasant color of the light they emit. Object colors tend to look more accurate under this type of lamp. Incandescent light bulbs use a lot of electricity as they produce a lot of heat.
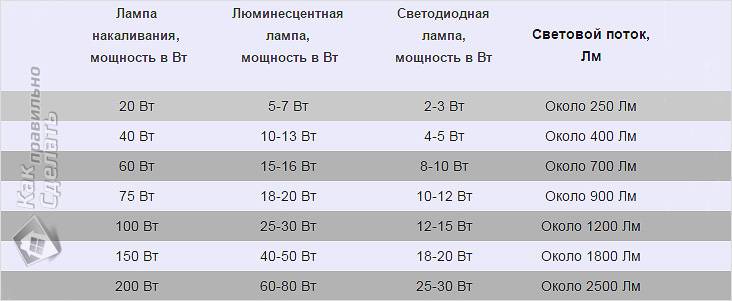
Incandescent lamps produce 8-12 lumens of light per 1 watt of energy consumed. The more powerful the incandescent lamp, the more lumens of light it produces per unit of power consumed. For example, one 100W lamp produces almost exactly the same amount of light (1360 Lumens) as two 60W lamps (1420 Lumens).
The disadvantage of these lamps is that these bulbs are inefficient by today's standards and have a relatively short lifespan (about 1000 hours). Incandescent lamps are available in a variety of shapes and sizes and have a range of different bases.
Matte or transparent?

- The basic principle of choosing between frosted and transparent lamps is as follows:
- If the lamp has transparent shades, use transparent bulbs
- If the lamp has frosted shades, use frosted light bulbs
- In the children's room, use frosted light bulbs. Toddlers love to look at the lamp, and these lamps give a light that is more comfortable for the child's eye.
- In crystal lamps, lamps with a lot of pendants, crystals and other light-refracting details, use transparent bulbs, as the bright open spiral of a transparent incandescent lamp gives necessary game Sveta
Reflector lamps
Reflector incandescent lamps have a silver-plated surface - this is their only difference from conventional incandescent lamps. A reflective surface directs light in a certain direction. Such lamps are usually designed for directional light fixtures - spots. The most common types of these lamps are R50, R63, PAR38.
Halogen bulbs
Halogen light bulbs are light bulbs with an incandescent filament containing halogen gas. They give, like incandescent lamps, a very attractive light that resembles sunlight. But they are somewhat more efficient than incandescent bulbs, as they produce 20% more light per wattage and last longer, around 2,000 hours.
The main advantage of a halogen lamp is its small size. The appearance of this lamp allowed designers to create new designs of lamps and shades. The GU10 halogen lamp with built-in reflector is the most common recessed lamp. And it is used in many directional light fixtures (spots).
The emergence of powerful linear halogen lamps of the R7S type, with a power of 300W, made it possible to create a class of floor lamps that give soft, pleasant lighting reflected from the ceiling and illuminate the entire room. The main types of halogen lamps: G9, G4, R7S, GU10. Each type is available in several capacities.
Fluorescent lamps
They are - energy saving light bulbs. They contain gas in the tube and do not have a filament. They have been used everywhere for many years and are better known as the long white pipes commonly found on the ceilings of public buildings.
The latest technology has reduced the size and improved the efficiency of light bulbs. Compact fluorescent lamps appeared, which are now commonly called Energy-saving lamps. There are many different shapes and wattages of light bulbs available now.
The term "Energy Saving" should also apply to other types of low energy lamps, such as LED.
The advantages of compact fluorescent lamps - low energy consumption due to the release of a small amount of heat - consume 20% of the energy of a conventional light bulb, with the same radiated luminous flux. Long service life, up to 8000 hours.
Compact fluorescent lamps produce 50-60 lumens per watt, five times more light per unit of wattage than incandescent lamps. They are ideal for use where the light must be on for a long time. "Warm white" lamps with improved light color are available from many leading lamp manufacturers. The color, color impression that a fluorescent lamp creates during operation is characterized by the Color temperature parameter. The unit of measurement is Kelvin.
- For fluorescent lamps, the color temperature is divided into these main categories:
- Below 3300 K - white, warm light
- 3300-5000K neutral light
- Over 5000 K "cold" light
Information about the color temperature of fluorescent lamps is placed on their packaging.
The disadvantages of this type of lamps include their high cost and light that is not as pleasant as that of incandescent lamps. Also, with almost all energy-saving fluorescent lamps, you cannot use a dimmer (power rheostat). Only a few of the world's leading lamp manufacturers, notably Philips, have a range of fluorescent lamps that can be dimmed.
Due to the low heat generation, energy-saving lamps can be used (if they fit the ceiling) to increase the amount of light from the fixtures. For example, a chandelier rated for 5 x 40W incandescent bulbs = 200W. We want more light from her. We cannot use more powerful incandescent lamps, as we have a limitation on the power of the lamp in the cartridge. (From a more powerful lamp, the cartridge may melt). But if five energy-saving lamps are used in this chandelier, each power is 20W, then due to the fact that a 20W energy-saving lamp gives light like a 100W incandescent lamp, such a chandelier will give light like a 5 * 100W incandescent chandelier.
On the popular wave of movement to reduce energy consumption, modern manufacturers are now paying great attention to the development and production of series of luminaires designed specifically to work with energy-saving lamps and sold immediately with such lamps.
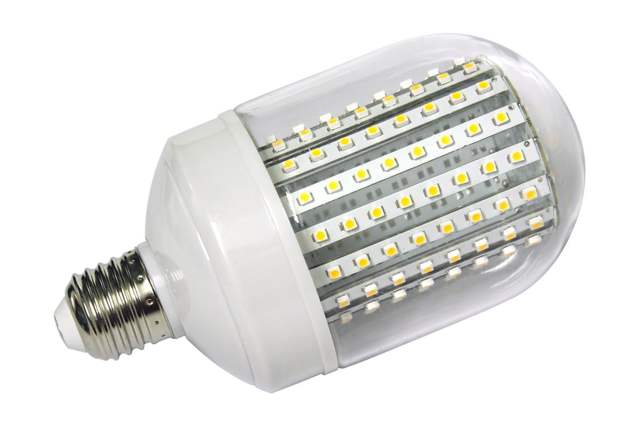
LED light bulbs
LED lamp made on the basis of the LED.
An LED is a semiconductor that converts electrical current into light. The basis of the LED is a semiconductor crystal. When passing electric current light is emitted through this crystal. The color of the radiation can be different, depending on the composition of the crystal. In LEDs for household lighting a semiconductor crystal of gallium nitride is used, this crystal gives a blue color. To obtain white light, a phosphor is applied to the crystal. Phosphor is a complex chemical substance that is excited by the light of a crystal and produces its own yellow light emission. In this case, the phosphor absorbs only part of the light from the semiconductor crystal, and transmits part of it. As a result of mixing blue light from gallium nitride, which has passed through the phosphor, and yellow light from the phosphor, white light is obtained.
LED light sources have huge advantages over all other lamps:
- Profitability. LEDs convert up to 80% of the electricity received into light radiation. The luminous efficiency of the best modern LEDs has reached 160 lumens per watt of power. This is almost twice as much as energy-saving fluorescent lamps and almost twenty times more than incandescent bulbs.
- Long service life - 50 thousand hours and more. This will ensure the operation of the LED lamp for about 20 years without replacement, when used 8 hours a day.
- High mechanical strength - unlike all lamps made of glass, the LED is resistant to external influences.
- The number of on/off switches has no effect on the life of the LED.
- Small size, compactness - unlike conventional lamps, which structurally require a bulb - the LED is just a small plate. The small size of the LED opens up opportunities for creating new types of lamps. It is possible that the increasing use of LEDs in residential lighting may change the approach to all forms and types of lamps. Now, most of the LEDs for household lighting are placed inside lamps with familiar shapes and with a standard base.
The spread of LED lamps is constrained only, for the time being, by a high price. But LED prices are dropping every year and in the near future, as many predict, all household lighting will be created using LEDs.
There are many types of lamps, and they all differ in principle of operation, operating conditions and, of course, design. To make the right choice of a light source, you need to understand the types of lighting equipment and the conditions for its connection.
The main characteristics of the lamps
You can find lamps of various shapes, but all models have a base - a part with which the lamp is connected to the electrical wiring. Plinths are found with threads and pins.
Threaded plinths come in three sizes: E14, E27 and E40. In everyday life, E14, E27 are used, and E40 is used in street lamps. Installing or changing such options is not difficult - the light bulb is screwed into the cartridge until it stops, and it is ready to go. Both incandescent lamps and LED or energy-saving lamps are equipped with such a cartridge.

Pin bases are mainly used in compact halogen and fluorescent lamps. With the help of pins, they are attached to the socket of the lamp. There are 2 or 4 pins in designs. Such socles are most often designated by the letter G and a number indicating the size: G5, G9 or 2G10, 2G11.

Consumers are primarily interested in such characteristics of light sources as power and light output. The manufacturer indicates the power on the base or cylinder of the product.
Lamps different types have different light output. The lowest light output in incandescent lamps, and the highest - in fluorescent. For example, energy saving types 10 watts will give a stream of light no worse than a 100 watt incandescent lamp. So, when purchasing lighting fixtures, be sure to consult the sellers.
The most common lamps
To determine which light source is best, you need to know what lamps are. Not so long ago, the most common sources of electric light were incandescent lamps (JIOH), which appeared in the 19th century. All JIOHs had a vacuum bottle made of glass, a plinth with contacts and fuses, and a filament in the form of a spiral made of tungsten. In modern versions, the cylinder is filled with some kind of inert gas. When current passes through the coil, it becomes hot and glows brightly.
The light output of such sources is not very high - 4-9 times lower than energy-saving fluorescent ones. JIOH differ in power, size, color of the cylinder and its design. Models shaped like a burning candle are popular, which favorably emphasize the exquisite forms of many modern fixtures and add flair.
Modern incandescent lamps
It differs from the usual shape of the bulb and a special coating on the inside of the bulb, which allows you to collect the entire luminous flux into a single beam, which is sent to the right place. They are used:
- in industry for drying, heating and firing;
- for photo and video filming;
- in farms and veterinary medicine;
- for bathroom ceiling lighting and .

They differ from ordinary ones only in the contents of the cylinder. Bromine and iodine are added to the inert gas to protect the filament and extend its life. In such sources, the flasks are small, which makes it possible to use expensive inert gases as fillers. Such light sources have a number of advantages:
- the brightness of the glow is maintained throughout the entire period of operation;
- natural color reproduction of illuminated objects is ensured;
- the service life is at least doubled compared to conventional JIOH;
- significantly higher light output at smaller sizes.

The only disadvantage of such light bulbs is their sensitivity to significant voltage drops in the network, so lighting fixtures are often supplemented with special transformers.
Fluorescent lamps
Luminescent models are fundamentally different from LON - they do not glow with incandescent filaments, but with mercury vapor and a phosphor covering the walls of the tube. They are often fastened inside the luminaire not with a threaded cartridge, but with pins located on both sides of the glass tube. The main advantages of such lamps include:
- high light output;
- more natural color reproduction of illuminated objects;
- creation of soft diffused light due to the low brightness of a relatively large surface;
- low cost;
- low surface temperature.

Their direct connection to the network is almost impossible, so special ballasts and starters are used to turn on at the moment of ignition. AT recent times compact versions of energy-saving fluorescent lamps appeared on the market, in which all the shortcomings of their predecessors were eliminated.
LED models
LED lamps began to conquer the market since 1962. They are high-tech, have excellent light output and have three main advantages:

- energy consumption is up to 10 times lower than in LON, and 3 times lower than in fluorescent ones.
- long service life (the manufacturer promises at least 10 years);
- they are relatively harmless - do not contain mercury.
LED mirror lamps are also manufactured based on LED technology and feature low power consumption, high light output, small size and high style. Suitable for organizing the main and auxiliary lighting in the interior.

Energy saving lamps - pros and cons
Energy-saving ones include fluorescent compact light sources that can be screwed into a conventional cartridge, traditional fluorescent models and LEDs. With equal power, the luminous flux in them can be 3-5 times greater. This indicator depends on the manufacturer and the emitted spectrum. For living quarters where you can stay in the light for a long time, it is advisable to select options with a warm glow, which, in perception, is very close to natural sunlight.
The main disadvantages of energy-saving light sources are their high price and special disposal requirements, since if such products are damaged, the environment is harmed. But technologies are developing rapidly, and perhaps in the near future we will see products on store shelves that are devoid of these shortcomings.
Currently, a large selection of different lamps is available, each with its own unique characteristics. For certain operating conditions, you can choose the most suitable lighting device.
The following main types are on the market:
- Incandescent:
- vacuum;
- halogen;
- krypton;
- Discharge:
- mercury
- DRL;
- DRI (metal halide);
- xenon;
- neon, argon, etc.
- mercury
- LED.
Characteristics

At detailed description We will take into account the following characteristics:
- base (cartridge) - the place of attachment of the flask;
- color rendering;
- light output (light efficiency);
Light output
Shows how many lumens the light source gives out at a power of 1 watt. For example, a standard incandescent lamp has a light output of 10 lm / W, a fluorescent lamp - 70 lm / W, which means that at the same power, the latter will glow 7 times brighter.
When talking about light output, it is necessary to mention the so-called energy-saving technologies.
Essentially, energy saving means: we consume little - we shine a lot. In this context, sodium light sources are the most energy efficient (see comparison table).
However, it is customary to call either LED or fluorescent lamps.
Color rendering index (Ra)
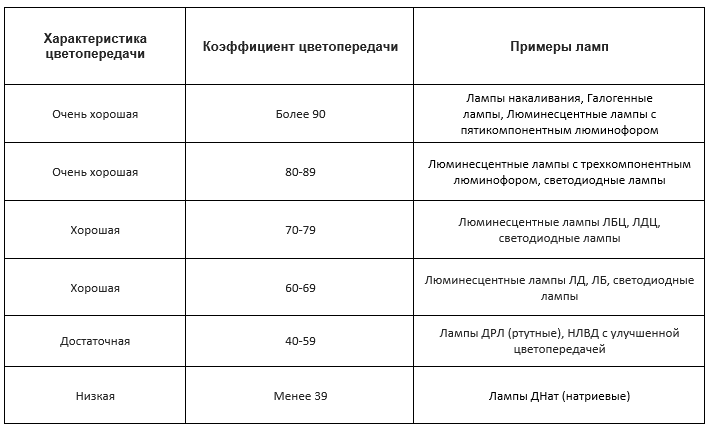
Shows how natural the colors look in the light emitted. The larger this number, the better performance source, the closer its light to natural light.
Qualitative gradations of the coefficient are indicated in the table:
| Ra | color quality |
| <39 | not enough |
| 40–59 | enough |
| 60–79 | Good |
| >80 | very good |
Colorful temperature
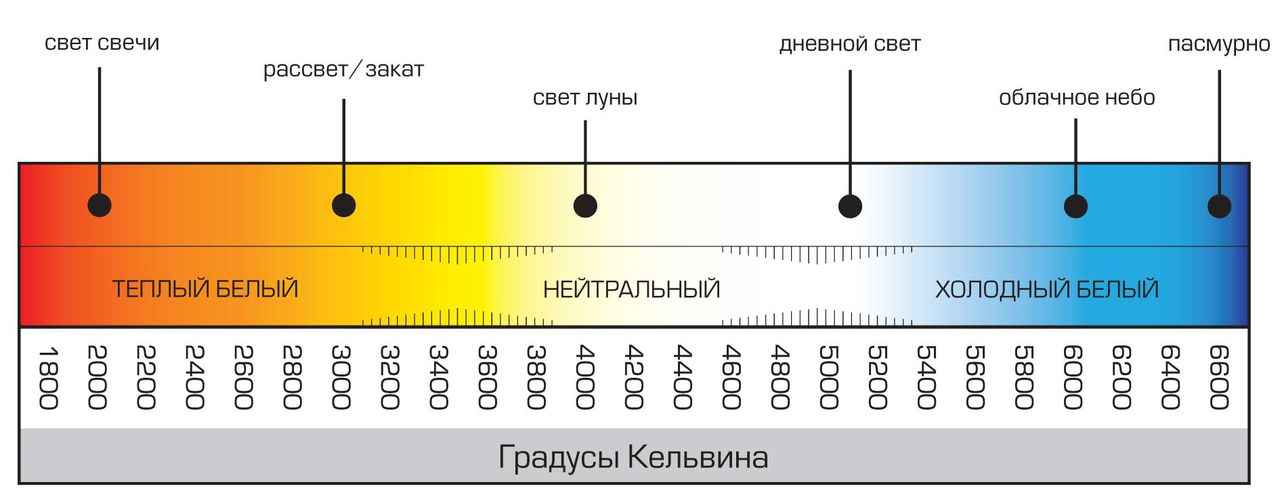
Specifies the color of a glowing object, measured in degrees Kelvin (K). Depending on the temperature of the light, the surrounding objects look somewhat different.
Ordinary White list paper can have shades from warm and yellowish at 2500 K (candle), to radiant blue - at temperatures from 6500 K.
There are the following shades of light:
Light of different temperatures affects the perception of a person in different ways (let us recall, for example, theatrical performances and various installations where light plays essential role in conveying an emotional state).
Warm white (2700 - 4200 K) light helps to relax, sets in a calm mood. Suitable for lighting bedrooms, living rooms and dining rooms.
Daylight (4200 - 5500 K) helps to concentrate on tasks, most suitable for office space and for lighting working area(including in the kitchen), for dressing rooms.
Cold white light (5500 - 6000 K) is energetic enough, suitable for bathrooms, kitchens (worktop, but not a dining table).
Classification
Incandescent lamps
In the recent past, the most common type. Lighting devices of this type can be used both on stationary and portable devices (for example, hand-held flashlights).
Light is emitted by a heated tungsten filament placed in a flask (cylinder), from which air is pumped out (hence the term "vacuum").
According to the composition of the gas in the cylinder, incandescent lamps are divided into vacuum, krypton, and halogen lamps.
vacuum

The surface of the flask can be either transparent or opaque, which allows you to get softer light without the use of a protective cap. Also, the top of the bulb can be covered with mirror paint to direct the light downwards (in case of ceiling lighting).
Lamps for portable sources operate on voltages of 12, 24, 36 V.
For stationary- 220 V, 50 Hz (city electrical network).
The main disadvantage of such light sources is low efficiency: only 2-3% goes to lighting. The rest of the energy is dissipated as heat (hence the low light output).
Type of fastening used - Edison base (E-base); differs in its diameter (in mm), indicated in the marking:
- E10 - used for flashlights;
- E14, also called "minyon" (small);
- E27 - standard;
- E40 is used for outdoor lighting;
Pros:
- wide distribution of equipment;
- low price;
- ease of installation;
Minuses:
- low efficiency;
- short duration of work (500–1000 hours);
- fire hazard (cannot be used in plastic and wooden structures);
Characteristics:
krypton lamps

An incandescent lamp with krypton (an inert gas) added to its bulb. They are smaller and big time work compared to vacuum (1000–2000 hours), are not sensitive to voltage drops.
Characteristics:
Halogen lamps

As the name implies, the flask contains a pair of halogens (elements of the 17th group of the periodic table - bromine or iodine). The addition of these gases can significantly increase the operating time and increase the light output, compared with vacuum counterparts.
An E- or G-base is used (see fluorescent lamps).
Pros:
- Service life up to 2000-4000 hours.
- Small size, the possibility of using in plasterboard structures (for example, suspended ceilings).
Minuses:
- Sensitivity to pollution(installation must be done with gloves, if fat gets on the surface of the flask, the device fails very quickly).
- Sensitivity to voltage drops.
Currently, a new type of halogen sources with an infrared coating has been developed, which transmits visible light and reflects thermal radiation, they have reduced power consumption and increased operating time compared to uncoated analogues.
Characteristics:
Discharge lamps
The physical basis of the glow is an electric discharge passing through a gas hermetically sealed in a tube.
Depending on the internal contents of the tube, the following types are distinguished:
- Mercury:
- DRL;
- luminescent;
- sodium.
- Neon, xenon, argon, etc.
The glow process must be started using a special ballast (PRM). Currently, luminaires are produced, where the PRM can be either built into the cartridge or mounted separately.
Mercury

All mercury-containing devices are highly toxic and must be disposed of through hazardous waste collection points. In accordance with the Minamata Convention on Mercury, the manufacture, export and import of certain mercury-containing lamps will be prohibited from 2020, along with a similar ban on mercury-containing batteries and thermometers.
Lamp DRL (arc mercury fluorescent)

mercury lamp high pressure, should not be used in rooms where people stay for a long time (apartments, offices).
These lighting devices find their application in street lighting, in automated industrial workshops, in agriculture.
Minuses:
- Low Ra: 40 – 59.
- Long turn-on time(up to 15 min), depending on the ambient temperature (the colder, the longer the illumination process takes).
- Strong heating of the tube.
- Sensitivity to voltage drops: with frequent short-term power outages, the device will go out, and then, after restarting, for a long time to enter the operating mode.
Classic DRLs are gradually falling out of use.
Currently, devices of a combined type are produced for domestic use (for example, by OSRAM).
DRI lamp (arc mercury with emitting additives)
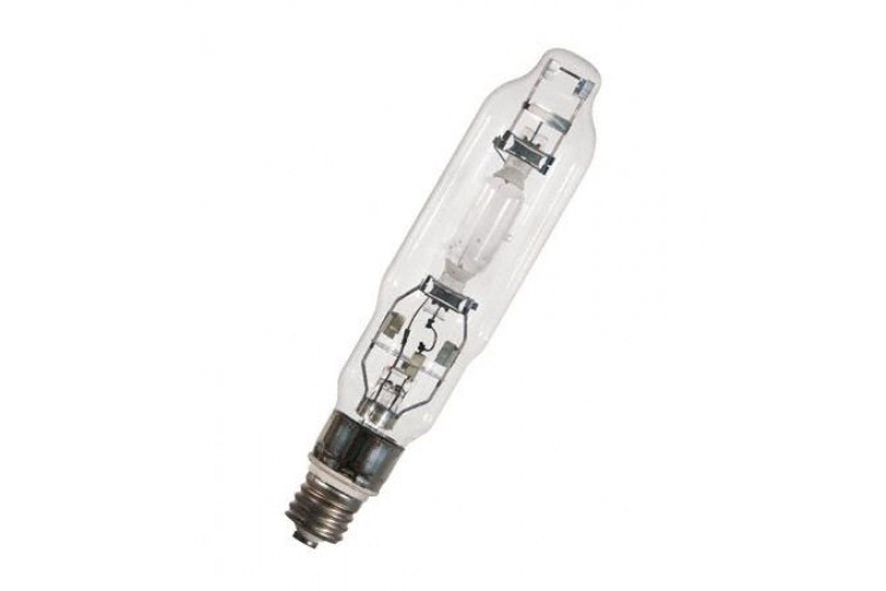

Also called metal halide.
DRL lamps, in the flask of which halides of certain metals (sodium, indium, etc.) are added.
Base E27, E40, R7S (base with recessed contact, used mainly in high-intensity lighting installations, after marking the base, the bulb length is indicated in mm - 78 or 118):
Mercury-quartz lamps (PRK, DRT)

Arc HRVD type DRT (arc mercury tubular, obsolete - direct mercury-quartz, PRT) are used in medical equipment (the same quartz cabinets) for disinfecting air and products. DRTs are also used in some technological processes (such as, for example, photopolymerization).
Fluorescent lamps

Or otherwise fluorescent lamps.
The marking of domestic devices indicates the spectrum of luminescence:
After the letter marking, numbers follow: the first indicates the degree of color rendering (the higher it is, the more natural the light looks, range 6–9), the next two indicate the color temperature:
- 30 (3000 K) - warm white;
- 35 (3500 K) - white;
- 40 (4000 K) - cold white;
- 54 (5400 K) - daylight;
- 65 (6500 K) - cold daytime;
A G-base is used, which is a socket where a balloon is attached with pins. It is used for halogen and fluorescent compact lamps (to reduce the size). There are a large number of markings for this type of plinth, so each time it is necessary to compare the type of fastening (it is indicated on the flask), the plinths are not interchangeable.
Pros:
- Low operating temperature(you can safely touch).
- Soft light.
- Operating time up to 30,000 hours
- Modern compact models can be connected to a conventional cartridge (fluorescent lighting devices of the past generation were made in the form of tubes and required the use of special cylinders for their connection).
Minuses:
- Source operation is not silent(the glow process is accompanied by a hum).
- Plus operating temperatures environment.
- Toxicity– Disposal to special landfills is required (free of charge for the population through hazardous waste collection points).
- Sufficiently long turn-on period, during which the light reaches its maximum.
- Sensitivity to frequent switching on and off.
From the listed features it can be seen that it is advisable to install such equipment in places where it is necessary to provide illumination for a long time with a minimum number of inclusions. For example, on the first floors of stairs.
If the mode of use implies a short period of work with frequent switching on (for example, in bathrooms), it is better to choose another source.
Characteristics:
Sodium lamps
Sodium vapor discharge lamps
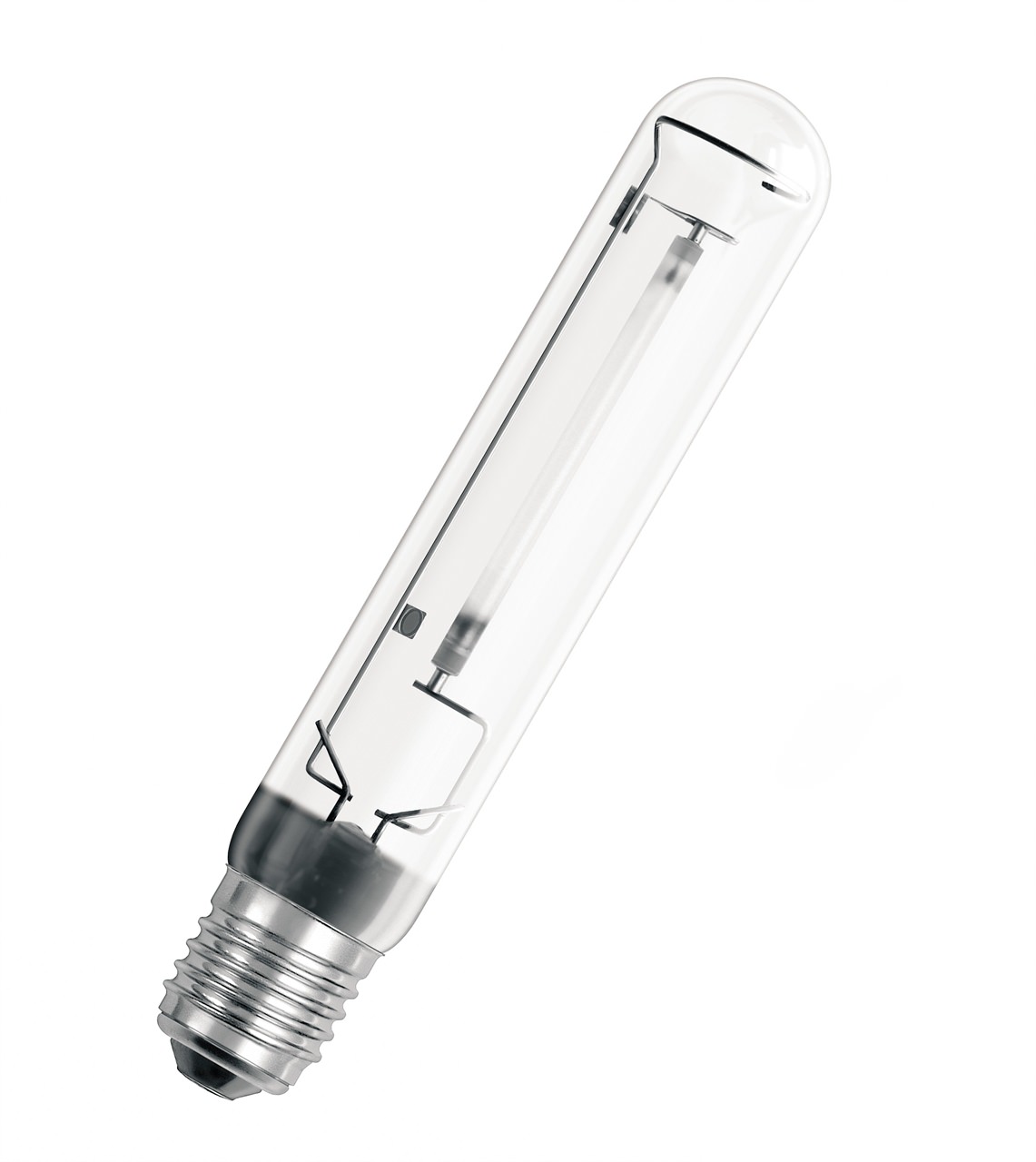

These lamps produce monochrome yellow light. They are used where a high color rendering index is not required: in street and road lighting, when illuminating buildings, etc. High pressure lamps (HLPH) are used in agriculture for additional illumination of plants in the winter.
There are several markings for domestically produced arc sodium (DN) light sources:
- DNaT - DN tubular;
- DNaS - DN in a light-scattering flask, are a replacement for DRL;
- DnaMT - frosted;
- DNaZ - mirror;
xenon lamps
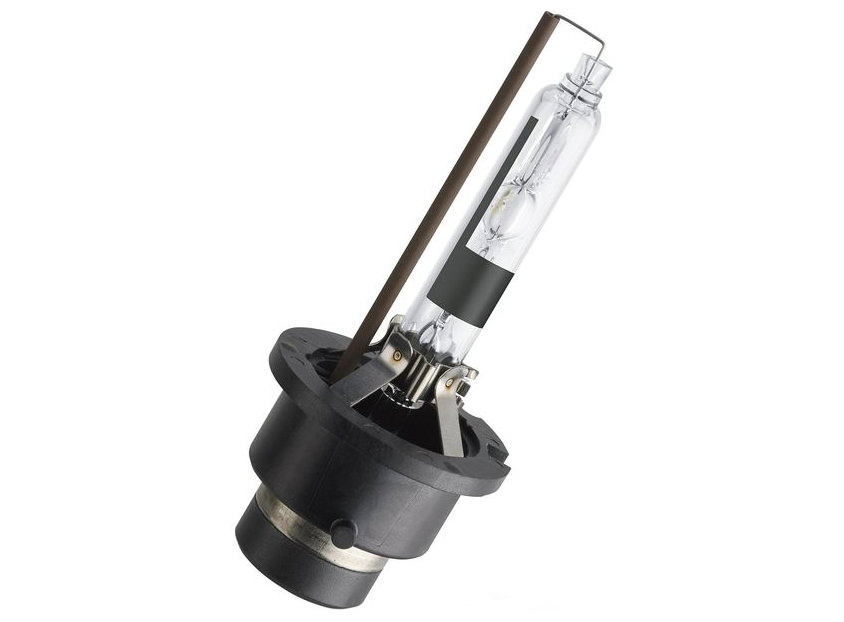

They provide very good color reproduction.
They are used in car headlights, as well as in projectors, flashlights and other lighting devices.
Depending on the application, the price for them varies from several hundred to several thousand rubles. They have a specific purpose.
Characteristics:
Neon, argon, etc.
![]()
Discharge lamps, the bulb of which is filled with an inert gas.
They have a long operating time (up to 80,000 hours), depending on the composition of the gas mixture, they make it possible to obtain light sources of various shades (from blue-green to red-orange). Used for advertising lighting, for indicating the voltage in the network.
LED lamp

They are also called LED.
This type of sources has one significant drawback: high cost. However, they can further significantly reduce energy costs. In economic terms, such lighting devices are very attractive, as they have a long period of operation.
At the moment, LEDs are used to illuminate streets, in common areas (often together with), to illuminate museum exhibits.
Pros:
- Environmental friendliness.
- Long service life (30,000–50,000 hours).
- Small dimensions.
- Small heating source.
- Resistance to mechanical impact.
Minuses:
- Price.
- Narrow beam of light.
- End of service life the brightness of such sources decreases (so-called LED burn-in).
Characteristics:
Comparison table:
| Type of | Price,R | Power, W | Light output, lm/W | Color reproductionRa | light temperature,To | Service life, h | Key Features |
| vacuum | from 10 | 5 – 500 | 7 – 17 | over 90 | 2 700 | 500 – 1000 | fire hazard |
| halogen | from 20 | 20 – 1500 | 14 – 30 | over 90 | 3 700 | 2000 – 4000 | can be mounted in drywall, high sensitivity to contamination of the surface of the flask |
| krypton | from 40 | 5 – 500 | 8 – 19 | over 90 | 2 700 | 1000 – 2000 | fire hazard |
| DRI | from 500 | 20 – 2000 | 70 – 95 | over 90 | 3500 – 6000 | 8000 – 10 000 | long turn-on time, toxicity, bulb does not heat up (luminescent) |
| luminescent | from 100 | 4 – 140 | 40 – 90 | 60 – 90 | 3000 – 6000 | 30 000 | |
| sodium | from 200 | 50 – 100 | 150 – 200 | less than 39 to 59 | 3000 – 6000 | 30 000 | plant lighting |
| LED | from 200 | 2 – 2000 | 40 – 120 | 60 – 89 | 3000 – 6000 | 30 000 – 50 000 | energy efficient |
When choosing lighting sources, it is necessary to take into account their performance characteristics.
The right choice will save you money and extend the life of the lighting fixture.
The plinths themselves are made of metal or ceramic. Inside them there are contacts for supplying current to the working element of the lamp. Each luminaire is equipped with one or more lamp sockets. The bases of the purchased light bulbs must correspond in shape and size to them. Therefore, when buying a lamp, it is important to be guided by what types of light bulbs and types of socles are suitable for it.
In addition, most lamps need to be replaced from time to time as they do not last very long. In order to make the best choice and not get lost in all their diversity, it is important to know what types of lamps and types of socles generally exist. In addition to the base, when buying a lamp, you must also take into account the power consumption of the lamp, voltage, its dimensions and the connection scheme to the chandelier.
What are the types of plinths
There is a wide variety of types of lamp bases that are used today in certain areas. In this regard, there is their classification, according to which all types can be divided into several groups. At the same time, in Everyday life we most often encounter only two of them: threaded and pin. Let's take a closer look at each of these two types.
Screw base
It is considered traditional to consider a threaded base, or in another way - a screw base. It is marked with the Latin letter E. This type of base is widely used in many types of lamps, including most household ones. After the letter, there must be a number that indicates the diameter of the threaded connection. In household light bulbs, two sizes of threaded connection are used - E14 and E27. For more powerful lamps, for example, street lighting there are E40 socles.
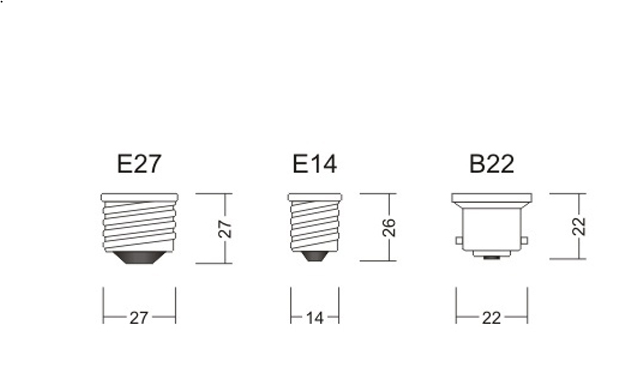
We are used to seeing the threaded type of the base in almost all home lighting fixtures. Most modern lamps are equipped with just such a connection design. It is considered the most convenient for general consumption. The dimensions of the threaded connections for lamps have not changed for several decades, so even modern light, which you purchased today, may well be screwed into an old rare chandelier from the 30s and 40s of the last century. This is very important for those who are fond of the revival of antiques.
In the US and Canada, plinth sizes are not the same as in Europe. This is due to the fact that there the voltage in the network is 110 V. Therefore, in order to avoid accidentally screwing in European bulbs, their diameter is: E12, E17, E26 and E39.
Pin base
This is also a fairly popular base, which is successfully used in various types of lamps. It consists of two metal pins that simultaneously play the role of electrical contacts. Holding the lamp in the socket is carried out by these pins, as they are inserted into the socket quite tightly. The pins can be different in diameter and distance between them. Hence the marking with the letter G, which means that this is a pin base, and the number after it determines the gap between the two pins. For example, plinths G4, G9 or G13.
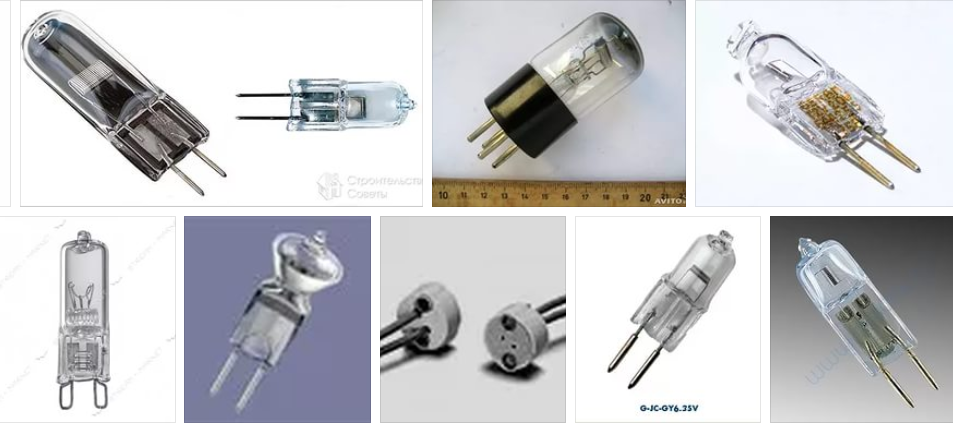

This type of base is found in almost all types of lamps: incandescent, fluorescent, halogen, LED.
In addition to the traditional ones listed above, there are several more rare types of socles that are less popular, but, nevertheless, are used in some types of lamps.
- Plinths with recessed contact (R). They are mainly used in high intensity appliances that are powered by alternating current.
- Pin bases (B) make it possible to most conveniently and quickly replace the light bulb in the cartridge due to the fact that their side contacts are asymmetrical. In fact, this is an improved analogue of the threaded type of base.
- Single-pin (F), which come in three different subspecies: cylindrical, with a corrugated surface and a special shape.
- Soffit bases (S) are used in lamps of various hotels and car lighting fixtures. They are distinguished by a peculiar bilateral symmetrical arrangement of contacts.
- Fixing (P) bases are used in special high-power spotlights and lanterns.
- Telephone (T) bases are equipped with light bulbs for various control panels, one or another backlight, signal lamps mounted in automation panels.

Often, available on the base, the marking of the lamp consists of several letters. The second letter most often means a subspecies of this lighting device:
- V - base with a conical end.
- U - energy-saving fluorescent.
- A - car light bulb.
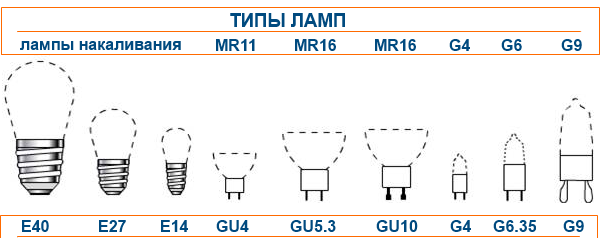
Types of lighting bulbs
We will talk about the most common lamps that we usually use at home, in offices and various industrial premises. These include incandescent, energy-saving, halogen, fluorescent and LED lamps. Let's take a closer look at each of these types.
Ordinary incandescent lamp
This is probably the most common lamp, despite the fact that its age is already more than 150 years old, and over the past 100 years it has hardly undergone significant changes, we still use it. The thing is that its production is very cheap, and the design is simple. It is a flask without air, in which a tungsten filament is placed. Under the influence of an electric current, it heats up to high temperatures and emits light. Modern incandescent lamps with a tungsten filament have one feature: when room temperature the resistance in the tungsten filament is very low, about 15 times lower than the working one, which increases the risk of its burnout when passing a stronger current at the moment of switching on. The first lamps used graphite filaments, the resistance of which, on the contrary, decreased with increasing temperature. This had the effect of gradually increasing the brightness. At the same time, graphite threads developed their resource faster.

By their own technical specifications incandescent lamps are much inferior to other types of lamps. The life of a typical light bulb is about 1000 hours. It is noteworthy that in the fire department of the small town of Livermore, California, there is a light bulb that has been continuously lit since 1901. This, of course, is an exception to the rule. In addition to a short service life, incandescent lamps become cloudy over time due to the vapors formed in the bulb. This greatly reduces their luminosity. Incandescent lamps emit yellow light, which is close to the spectral characteristics of sunlight. Almost all incandescent lamps are produced with E14 and E27 sockets. The exception is small light bulbs, which a couple of decades ago were screwed into lanterns and Christmas tree garlands. Today it is already difficult to find a cartridge for such light bulbs.
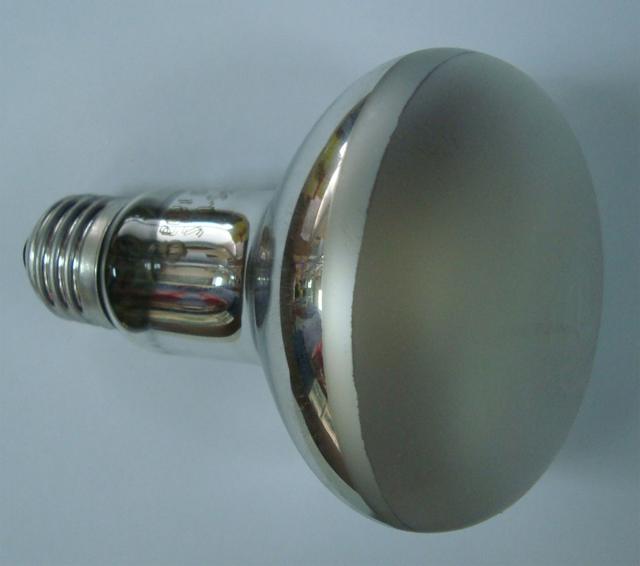
Among lamps of this type there are special reflector lamps. Their distinguishing feature is silver plated inner surface flasks. Such devices are used to create a beam of directional light when it is necessary to illuminate an object. On store shelves there are reflector lamps that are marked R50, R63 and R80, where the number is the diameter of the lamp. As for the base, it is the same as that of simple incandescent lamps. Some light bulbs have frosted glass for more diffused light. There are also multi-colored lamps used to create various lighting effects.
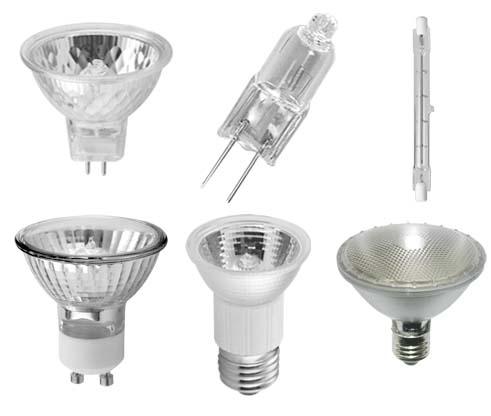
Halogen lamp
Such a light bulb can last about four times longer than a conventional incandescent bulb. Manufacturers claim that its service life can be about 4000 hours, and the so-called color rendering index is 100%. According to its design, such a lamp is not much different from a conventional one, but vapors of substances such as iodine or bromine are added to the flask. This greatly improves light output and service life. Modern halogen lamps have a light output of 20-30 lm / watt, which is maintained throughout the intended life and is not lost over time, like a conventional incandescent bulb.

Most often, halogen lamps are much smaller than conventional ones in size. They have many different shapes, and plinths are: G9, G4, R7S, GU10. There are even halogen lamps built into the bulb of a conventional light bulb with an E27 base.

There is only one drawback with halogen lamps - this is low-frequency noise when used in conjunction with dimmers that control the luminosity. This type of lamp has found the widest application in the automotive industry. Modern car headlights are equipped with halogen lamps.
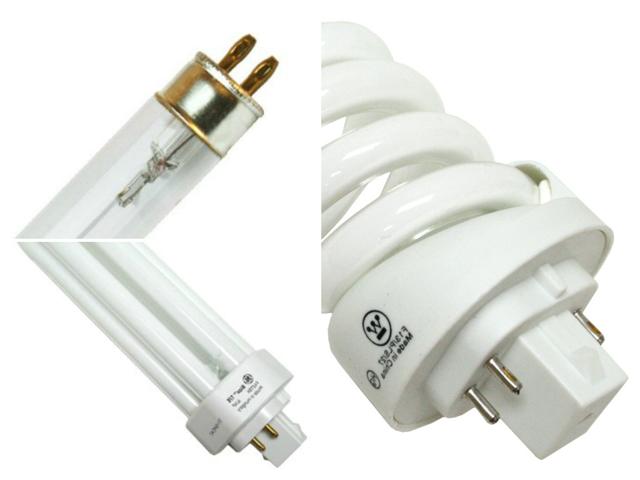
Fluorescent tube lamps
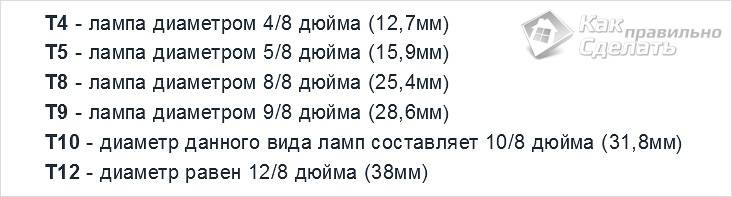
These light sources have a characteristic elongated shape in the form of a tube of various lengths and diameters. The latter is indicated by the letter T on the label. For example, T12 (diameter 12/8 inch=3.8 cm). For such lamps, special lamps with a starting device are required. It is required in order to create an electromagnetic field inside the bulb that can cause the phosphor to glow under the influence of mercury vapor. In such lamps, there are no incandescent parts, which significantly increases their efficiency and efficiency, since there is no need to heat up the substance and almost all of the energy is converted into a luminous flux. The bases of this type of lamp are most often pin and located on both sides of the bulb.

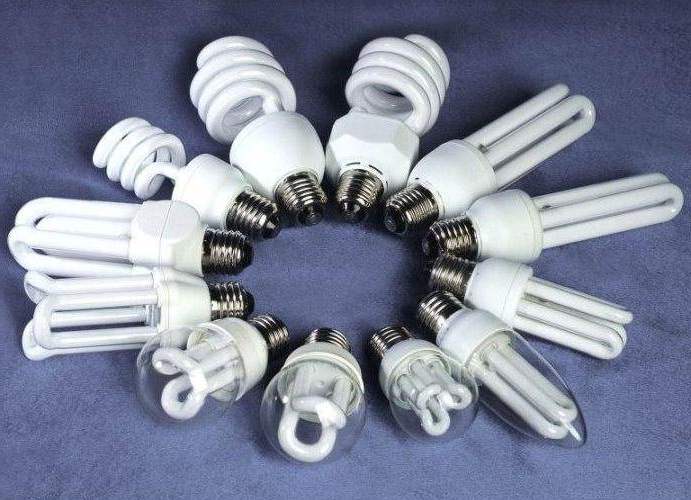
Energy saving types of lamps
This term is commonly used for small fluorescent lamps. They have gained high popularity today, as they are able to reduce energy costs very significantly. They are sold in any stores, and installing them in a regular threaded cartridge is not a problem, since they are equipped with the same bases.
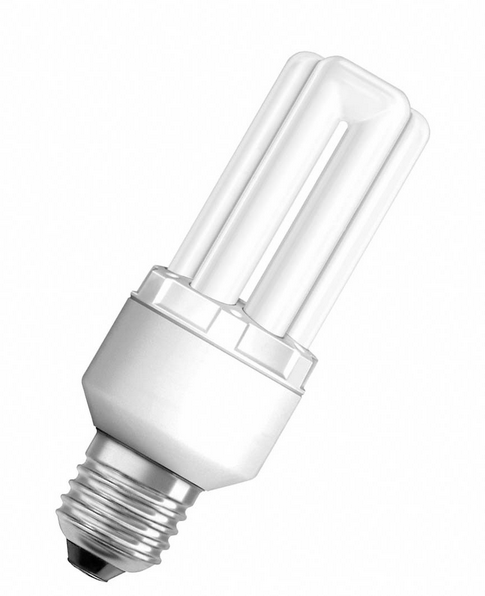

Thanks to modern technological developments, energy-saving light bulbs have a very compact size, various power variations, a large variety of shapes, but definitely a long service life and extraordinary efficiency. However, it must be remembered that such lighting devices “do not like” turning on and off too often, and, like all fluorescent lamps, require special disposal conditions, since the mercury vapor they contain is very dangerous for humans and the environment. Today there are energy-saving lamps with any type of socles: E14, E27, GU10, G9, GU5.3, G4, GU4.
They can also be called "energy-saving", but this is not their main advantage. With significant energy savings, they have a truly enormous service life, which can amount to tens of thousands of hours and years. From 25,000 to 100,000 hours, an LED lamp will last, which is equal to 3-12 years of continuous operation. In addition, their light output is almost one hundred percent. LEDs do not use heat, so these lamps are completely safe in the fire sense. Most LED lamps are equipped with standard sockets, which allows them to be used in any fixtures. They are completely environmentally friendly, as they do not contain any harmful substances.
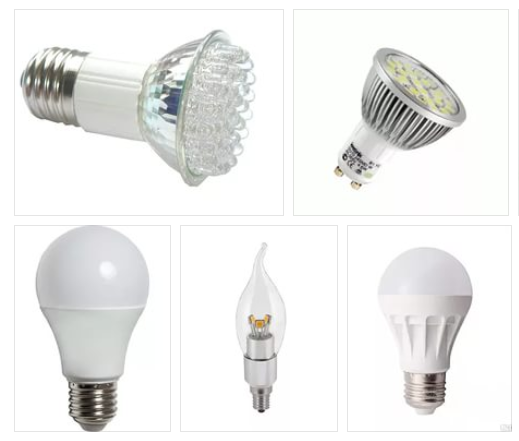

Of the shortcomings, only a very high cost should be noted. This, of course, is offset by a very long service life. It is not recommended to purchase cheaper LED lamps, because due to savings on capacitors, they shine with an invisible flicker, which in a hidden form affects vision. Another disadvantage can be considered shifted to the side of blue color radiation spectrum that does not correspond to natural sunlight. LEDs shine with a rather cold unnatural light.
Using energy-saving lighting sources can save a lot on electricity. At the same time, when buying them, you should be attentive to the choice of manufacturer and buy only well-known models, otherwise many advantages become not so obvious.
When buying a lamp, it is important to know what type of lamp is suitable for it, because in the vast majority of cases, complete with lighting fixture she is not included. Today, lamps are presented in stores in a large assortment. They differ in shape, size, power consumption and plinth. A base is a part of an electric light bulb that allows it to be mounted in a lamp socket, and through which current is supplied.
Plinths are made of metal or ceramic. Inside they are filled with electrodes (part of the lamp), and outside there are contacts. For each lamp, a specific socket is used, in which a lamp with a suitable base is installed. Before buying a chandelier, it is important to know what type of cartridge is suitable for it, and, accordingly, which lamp.

In addition, the lamps have to be changed periodically, as they are not durable. To do right choice and not to get confused in all the variety of light sources, it is important to know what types of light bulbs and types of socles exist. In addition to the base, when buying a lamp, it is also important to take into account the maximum lamp power, voltage, dimensions and chandelier connection scheme.
What are plinths
Due to the variety of socles known today, a classification has been developed, according to which all types of lamp socles are usually divided into groups. Among them, two groups are considered the most common: threaded and pin.

The threaded base is considered traditional, or, as it is also called, the screw base. It is denoted by the Latin letter E. The threaded base is widely used for many types of lamps, including household ones. The letter, as a rule, is followed by a number, it indicates the diameter of the thread. The most common screw bases are designated E14 and E27. For high-power lamps, there are also bases, for example, E40.
A little less popular is the pin base, it is denoted by the letter G, which shows the gap between the contacts in millimeters. The scope of the pin base is also wide - suitable for many lamps: halogen, fluorescent and ordinary incandescent lamps.

In addition to the traditional ones, there are several more types of socles that are less common, but, nevertheless, are used for various types of lamps.
- Plinths with recessed contact (R). They are used mainly for high-intensity appliances that operate on alternating current.
- Pin (B). They allow you to quickly replace the lamp in the cartridge due to asymmetrical side contacts. They are an improved analogue of threaded plinths.
- With one pin (F). Such plinths come in three subspecies: cylindrical, corrugated and special shape.
- Soffit (S). Most often, light bulbs with such a base are used in hotels and cars. Them distinguishing feature– bilateral arrangement of contacts.
- Fixing (P). Scope - special spotlights and lanterns.
- Telephone (T). They are equipped with control panel lamps, backlights, signal lamps in automation panels.

Often the marking of the lamp consists of more than one letter. The second letter usually indicates a subspecies of the lighting device:
- V - base with a conical end
- U - energy saving
- A - automotive.

In this video, a specialist will talk in detail about the different types of plinths:
Types of light bulbs
We will talk about the most common lighting lamps, those that are usually used in home and industrial premises. These include incandescent, halogen, energy-saving, fluorescent and LED lamps.
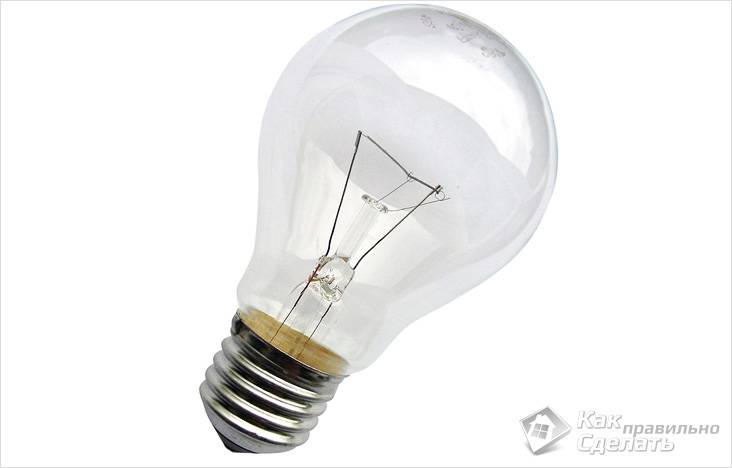

It is rightfully considered the most massive of all types of lamps and is probably familiar to everyone. It has gained popularity due to its low cost, simplicity of design and familiarity. It is used in the simplest models of lamps. However, despite its wide popularity, the incandescent lamp is inferior in terms of technical characteristics to its "brothers". Its service life is approximately 1000 hours, but this is not the most serious drawback. The fact is that during operation, vapors are formed inside the lamp, which provoke clouding of the bulb, so the brightness decreases over time. The color rendering index is approximately 90%. The predominant tones in the glow spectrum are yellow, so the light from an ordinary incandescent lamp resembles sunlight. Most, if not all, incandescent lamps come with E14 and E27 bases.

There are incandescent reflector lamps. Their main and only difference from ordinary lamps is the silver-plated surface. This helps direct the light to a specific point, which is why such lamps are used to create directional light. In stores you can find reflector lamps with the designation R50, R63 and R80, where the number is the diameter of the lamp. Also, like simple incandescent lamps, reflex lamps have an E14 or E27 threaded base.
Halogen lamp
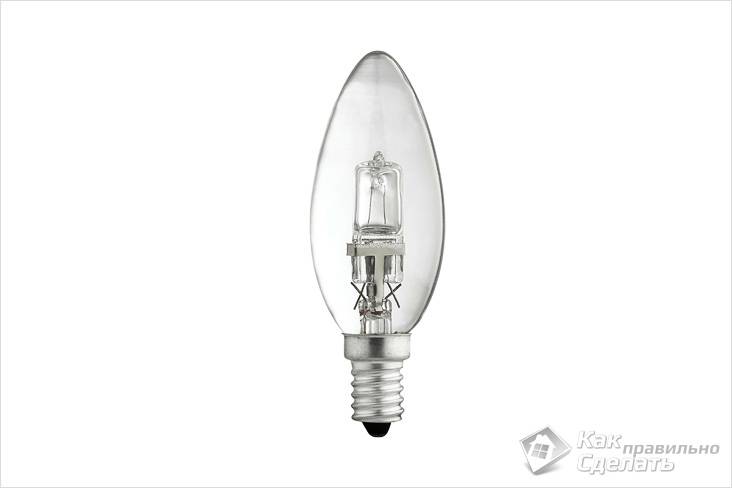

Able to last four times longer than an incandescent lamp. Its life span is approximately 4000 hours. Color rendering index - 100%. The technological process for the production of halogen lamps involves the addition of a certain amount of iodine or bromine. This contributes to a better light output, which is 20-30 lumens / watt. Moreover, a consistently high light output is maintained throughout the entire period of operation and does not decrease, as with a conventional incandescent lamp.
Being smaller in size than conventional lamps, they are more diverse in shape, respectively, their scope is wider. Their bases can be as follows: G9, G4, R7S, GU10.
Energy-saving lamps

This term is usually used when talking about a small fluorescent lamp. Such light bulbs have gained extraordinary popularity due to the fact that they can reduce energy costs. They are sold everywhere, and install them in place old lamp incandescent is not a problem, since it does not require any alterations.
Thanks to the latest production technologies, energy-saving lamps have a compact size, various power options, a variety of shapes, but consistently long life and efficiency. However, it is important to remember that such lamps "do not like" frequent switching on and off. There is an opinion that this shortens their life.
Today, compact energy-saving lamps can be purchased with almost all types of socles: E14, E27, GU10, G9, GU5.3, G4, GU4.
Fluorescent lamps

They are sometimes called tubular or linear due to their characteristic shape. The T on the tube is the diameter, and the number after it is the diameter in inches (eighths). For example, T12 (diameter 12/8 inch=3.8 cm).
LED lamp
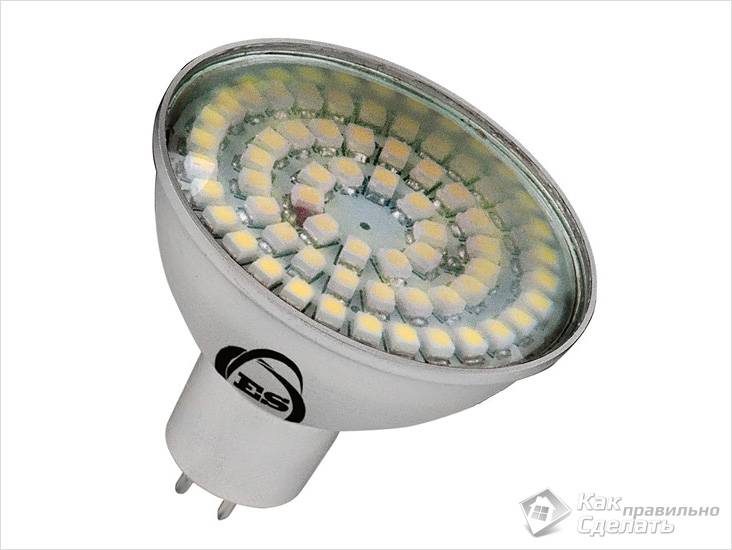

The term "energy-saving" is also applicable to them, but this is not their main advantage. The main thing is an incredibly long service life, which ranges from 25,000 to 100,000 hours. If we translate this number into years, we get 3-12 years of continuous work. Light output is almost 100%.
In addition, LEDs do not heat up to a significant extent, so it is advisable to use such lamps in rooms where the temperature regime is strictly observed. Standard bases allow the use of LED lamps.
Video
This video demonstrates different types lamps:



