How to choose a ventilation duct based on the volume of the room. Ventilation in the kitchen in a private house: a rational solution to complex problems. What schemes are used to organize effective ventilation in a private house
Comments:
Comfort in the house is determined not so much by the convenient location of the premises and the presence of comfortable furniture, but by the microclimate in it. Clean air and its temperature not only create a favorable microclimate in a private house, but also affect human health. Properly organized ventilation systems of a private house can contribute to health, and incorrect calculation and arrangement can cause irreparable harm.
The more inconspicuous ventilation and the lower the speed of movement of the air mass, the more comfortable microclimate for the person in the room.
Previously, when the construction of residential buildings was carried out exclusively from wood materials, calculation and arrangement of ventilation were not required due to the fact that the exchange of air mass in the premises of the house occurred due to infiltration. The inflow and outflow of air occurred through wood pores and cracks in wood, leaks window frames. The same was true for doors. A large area of infiltration provided sufficient air exchange. Therefore, the microclimate of a wooden private house is most favorable for a person. The emergence of modern materials contributed to greater sealing of the premises, which led to the need for arrangement in private homes various systems ventilation.
Natural ventilation of premises

The most favorable for a person is natural ventilation in a private house, when the air velocity is minimal. The normal volumetric air velocity for this type of ventilation is 1 m³/h. This ventilation does not require the use of forced air supply, and its operation is based on elementary physical laws. For this type of air exchange, exhaust ducts are installed in rooms where the air is polluted the most. As a rule, this is a kitchen, bathroom and toilet. The channel starts indoors and ends outdoors, above the ridge of the roof of the house. The influx of fresh air mass occurs due to infiltration, and if there is not enough air exchange through infiltration, then due to ventilation or installation of infiltration valves. Ensuring the flow of ventilation has some disadvantages:
- large heat losses during the cold period;
- freezing and the appearance of condensate on window blocks during prolonged ventilation;
- strong dust content in the air during warm periods;
- high air flow rate, which can cause illness to a person when he is in the room.
A more favorable climate can be created by using infiltration valves, which are included in the manufacture plastic windows or installed separately in the walls of a private house. The infiltration damper is a round pipe, mounted through the outer wall and closed at both ends with grilles for air filtration.
The inner grille has an adjustable passage section. Separate infiltration valves can be installed in the area of heaters in the house so that the air is immediately heated.
When installing valves, it is necessary to observe the condition that the supply air flows in the direction from rooms with cleaner air to household rooms with more polluted air, for example, from a bedroom to a kitchen.
Infiltration valves can be equipped with humidity and temperature sensors and have different throughputs. The number of valves required is determined by calculating the air exchange required for the ventilation system.
For the correct functioning of the natural ventilation system interior doors must be equipped with overflow gratings located at the bottom, or have a gap between the door and the threshold.
Back to index
Forced ventilation of premises

Sometimes the premises are so large or complex that the use of a natural ventilation system based on infiltration valves will require them in large numbers or will not work at all. In such cases, forced ventilation of the premises is used. She, in turn, happens:
- supply direct-flow;
- exhaust;
- supply and exhaust recuperation.
Supply once-through ventilation system consists of a network of ventilation ducts and equipment for air supply. The design and calculation of channels are carried out at the design stage of the walls, since it is better to place them in the walls.
If it is impossible to arrange channels in the walls, they are made in the form of separate ventilation shafts, hanging boxes hidden behind a false ceiling. Often the ventilation system in a private house is located in the attic. Force feed equipment includes:
- input filter. It serves to clean the air from mechanical particles at the inlet to the ventilation system.
- Heater. It is installed to heat the air during the cold period. Heaters are electric and water. The latter are somewhat more expensive than electric ones in installation, but cheaper in operation.
- A fan for forcing air mass into the system. There are a lot of fan designs for ventilation systems.
- Fans with a plate for mounting, in a housing for cylindrical systems, for installation on rooftops and for installation in ducts, as well as jet, centrifugal, monobloc units.
- Noise suppressor. Serves to reduce the noise pressure generated by the fan. Its design resembles a car muffler: it consists of a ventilation box with plates installed in it that change the direction of air movement.
The exhaust system has a set of elements similar to the supply system, but the fan is installed at the end of the ventilation system of a private house and works for extraction.

Supply ventilation is used for rooms with unpolluted air, and exhaust ventilation is used for rooms with a high level of indoor air pollution.
To reduce the operating costs used to heat the supplied air, supply and exhaust ventilation systems with recuperation are used. The principle of operation of the recuperation effect is to heat clean air with exhaust air. To do this, a heat exchanger is additionally included in the ventilation system, which provides heating of the supply air by the exhaust air through the heat exchange system, without mixing with it.
Back to index
Calculation of the ventilation system
Having decided on the type of ventilation system, it is necessary to calculate its air exchange. An elementary technique is to calculate the exchange of air over the area. For this, it is assumed that normal air exchange in any house should be 3m 3 per 1m 2 of the house area. To put it simply, 3 times more air than its area should be delivered to the premises every hour. And the same should be removed.

The second method of calculation is carried out according to the norms of sanitary hygiene, according to which for each person staying in the room a large number of time, there should be 60 m³/h of fresh air. Each person who is temporarily adds another 20 to the air exchange.
A more accurate method is the calculation of the ventilation system in a private house in accordance with SNiP 2.08.01-89 "Residential buildings". These SNiPs offer norms of hourly exchange or multiplicity for each type of premises. The multiplicity is an indicator of the multiplicity of the exchange of air mass in a particular room per hour (in simpler terms, how many times during an hour the air in the room should completely change). For residential buildings, these indicators are as follows:
- residential - 3 m 3 / h for each 1 m 2 of residential premises;
- bathroom - 25 m 3 / h;
- toilet - 50 m 3 / h;
- bathroom combined with a toilet, 50 m 3 / h;
- kitchen - 90 m 3 / h.
These data regulate the volume of air drawn from the room. In addition, SNiP provide for the supply air ratio, the minimum value of which for these premises is equal to one.
Based on the standards, it is calculated total area living rooms and multiplied by 3, resulting in the total air exchange of the premises. This volume is added to the volume of air mass exchange in the rest of the house, and the total volume of air output per hour is obtained. The amount of air supplied, according to calculations for residential premises, is always less than the amount removed, therefore, in order to satisfy the balance equation, according to which the amount of supply air must be equal to the amount of exhaust air, it is necessary to take the required amount of air equal to the calculated exhaust air.
The power of the fan is selected according to this indicator. exhaust system, and according to the "Diagram for the selection of sections of air ducts for ventilation", their section for each of the premises and the section for the common branches of the system are selected. Depending on the configuration of the ventilation system scheme, the length of the duct of each section is calculated.
The ventilation system in a private house plays an important role in creating a favorable microclimate in the home, ensuring comfortable living for people. With its help, oxygen enters the house, polluted air is removed, and the temperature and humidity of the air that the residents need is maintained. For effective operation, it is necessary to correctly calculate the main parameters of the system, as well as high-quality installation of ventilation in a private house and setting up all its main components.
Choosing the type of ventilation for a private house
The ventilation device in a private house provides for several successive stages, of which the main one is the choice of the type of ventilation. It depends on many different factors, including:

- at what stage the installation of the ventilation system is carried out - during the construction of a new house, or already in a built dwelling;
- type of building materials from which the house is built (brick, foam concrete, wood, etc.);
- the total area of the house and the volume of each individual room;
- financial capacity of the owner of the house.
Ventilation systems that are usually used in a private house can be of two main types:
- natural ventilation, the advantage of which is the simplicity and low cost of its installation and operation, no need to install additional equipment and its Maintenance. However, such a system cannot function in houses with high airtightness, in large rooms and is largely dependent on climate and other natural phenomena (outdoor temperature, wind, etc.). In addition, its operation often requires the use of large ventilation openings and increased diameters of air ducts, which is not always possible, especially in an already built building.
- Forced ventilation, in which air circulation is carried out due to the operation of exhaust and / or suction outdoor air fans. It can be: exhaust, supply, balanced (supply and exhaust), as well as a system with recuperation (heat recovery). Such systems can provide complete control of the ventilation system, filtering the intake air, regulating the required temperature and humidity in the room, saving the cost of heating the house. At the same time, the disadvantage of these systems is the rather high cost of equipment, the relative complexity of installation and maintenance, as well as the additional consumption of electricity.
Ventilation system design

After the type is defined ventilation system, it is necessary to design ventilation in a private house, determining all the necessary elements of the system and their relative location for each individual room and throughout the building as a whole. In this case, special attention should be paid to domestic and technical premises (kitchens, bathrooms, boiler rooms, etc.), where the most intensive air ventilation is required.
For a house under construction, it is best to include the ventilation project of a private house in the overall project of communications of the future building, providing for the location of ventilation ducts built into the walls and technological openings for air inlet and outlet, as well as installation sites for additional elements.
When developing a system natural ventilation it must be borne in mind that the ventilation scheme in a private house should provide for the location of the outlets of the exhaust ducts above one meter above the level of the roof of the house, and the distance from the inlet to the outlet exhaust grille should be 5-6 meters. This ensures the creation of the necessary draft in the exhaust air ducts and contributes to effective work the entire system.
Laying ventilation in a private house should be carried out in such a way as to ensure minimum dimensions the length of the air ducts, the least number of their bends and other possible obstacles that prevent the free passage of air flow through them.
Calculation of the ventilation system
The calculation of the ventilation system of a private house is based on determining the required air exchange in each room of the house, measured in cubic meters per hour. To make such a calculation, a complete floor plan is required, indicating the area and purpose of each room in the house. Definition required amount Air exchange in a separate room is carried out in two main ways:
- Taking into account the coefficient of air exchange, which is multiplied by the volume of the room. This coefficient depends on its purpose and is equal to "1" in living rooms (bedroom, living room) and "3" in household rooms (kitchen, bathroom, etc.). For example: in a bedroom with an area of 20 sq.m and a ceiling height of 2.5 m, the amount of air exchange should be 50 cubic meters per hour (20x2.5x1); in the kitchen, with a size of 10 sq.m and the same ceiling height, taking into account a three-fold coefficient - 75 kbm / h (10x2.5x3).
- Taking into account the number of people present in the room. The standard for air consumption by one person, according to sanitary and hygienic rules, is: for a bedroom - 20 kbm / h, for other residential premises (living room, children's room) - 40 kbm / h, for the kitchen and other household premises - 60 kbm / h. Thus, in a bedroom for two people, the required air flow will be 40 kbm / h (20x2), for a kitchen in a house where 3 people permanently live - 180 kbm / h (60x3).
The scheme of the ventilation system of a private house should provide the house with such a volume of fresh air that corresponds to highest value calculated using these two methods.
After that, it is necessary to calculate the parameters of individual elements of the ventilation system: the type and required size of the through holes of the supply and exhaust devices, the diameter of the ventilation ducts, the power of the fans (for a forced ventilation system).
Proper organization of ventilation in a private house depends on the type and diameter of the air ducts of the ventilation ducts. They can be built into the inside as a shaft in the wall or installed outside in the form of metal or plastic pipelines of round or rectangular cross section. To make channel bends and connect various ventilation equipment, corrugated pipes. In unheated rooms and outside the house, the air ducts are insulated to prevent the formation of condensate inside the pipes. A special deflector in the form of an umbrella is installed at the outlet of the exhaust channel so that atmospheric precipitation and foreign objects do not get inside.
When calculating ventilation in a private house, it must be taken into account that the diameter of the ventilation ducts must provide the necessary pressure and air flow rate to create the required amount of air exchange in the room. For example, in order to ensure air exchange in the room in the amount of 300 kbm / h, a channel section of 250x400 mm is required with natural ventilation or 160x200 mm with a forced system. The minimum allowable diameter of the ventilation duct for natural ventilation must be at least ten centimeters, for forced ventilation systems - from 6 cm.
Ventilation in a private house, the price of which directly depends on the type of system chosen, can be designed and installed independently or by specialists in this field. In any case, it is better to entrust the verification of the correctness of the scheme and calculations of the parameters of the ventilation system to a person with relevant knowledge and experience.
One of the most important indicators determining the degree of comfort of housing is a favorable microclimate, which directly depends on the quality of indoor air and ventilation. That is why proper and thoughtful ventilation of a private house will improve the quality of life and create a healthy atmosphere.
How to do the ventilation of a private house with your own hands?
For the manufacture and installation of a ventilation system for a private house, it is necessary to decide which system is most effective for a given building.
Important! If the building has small dimensions and the number of people living in it is small, that is, its area does not exceed 200m2, and the number of residents is not more than 5-6 people, then it is used for ventilation with natural draft.
In other words, the project provides for ventilation ducts that produce air exchange due to the laws of physics, which force warm air masses to leave the room, rising up, and cold air to enter the building through window and door openings. In this case, additional ventilation equipment is not provided, which significantly saves the developer's money, but does not exclude the ingress of foreign odors and various microelements and dust along with outdoor air. The efficiency of work in this case will significantly depend on weather conditions and climatic features of the construction region.
A supply system is often used, which involves pumping outside air into special filters. After cleaning, the air is heated to the required temperature, its humidity is adjusted and supplied to the premises.
The exhaust system is similar to the supply system, with the difference that the pump does not supply outside air, but removes air from the premises to the street through the ventilation shafts.
The most suitable for modern houses with an area equal to 300 - 500 m2 is a ventilation system that combines the properties of a supply and exhaust with a heat exchanger. In other words, a system is being created that fully regulates the supply of air, its processing and distribution to the premises of the house, the removal of exhaust air to the outside and a partial mixture of warm air with outdoor air (recovery) to reduce the cost of heating it.
After choosing a ventilation system for a private house, it is possible, based on the calculations made, to purchase materials and install equipment. The most rational thing would be to fix the main exhaust pipe on one of the internal load-bearing walls, and from it to separate the ventilation ducts throughout all the premises of the floor. The material of pipes for ventilation ducts can be very diverse. Do not forget that in the very recent past they were knocked down from wooden boards, and today plastic pipes have become the most practical material. Their weight allows the pipes to be fixed in any convenient place, they are not subject to corrosion, they are easy to install, and they are relatively cheap.
The market offers huge selection filters, but it is most rational to use combined filters consisting of two components - for dust particles and for gases. They do not allow airborne particles, smog odors, decaying organic particles, food and smoke odors to enter living spaces.
Of all the types of recuperators offered by manufacturers for the ventilation of a private house, a plate-type heat exchanger is the most suitable. It is very easy to install, which will allow you to do all the installation work yourself, a simple design and the absence of dynamic loads from rotating or moving parts eliminate breakdowns, does not require power supply and has excellent efficiency.
Heaters for ventilation of a private house must be selected in such a way that they provide the necessary design temperature supply air and were quite economical in energy consumption. Not only electricity, but also natural gas can serve as power, which will help save costs for the maintenance and operation of the entire system.
The place for the installation of fans can serve as an attic or technical floor. The main indicator of fans is its power, which is determined by calculation. When choosing, special attention should be paid to noise indicators.
When installing the ventilation system of a private house, you need to think about how it will be decorated. The best option will hide all ducts and equipment above the ceiling. If the house has several floors, then you can use dropped ceilings Armstrong type. At the right combination ceiling elements and diffusers, they can give the room style and originality.
Calculation of ventilation of a private house
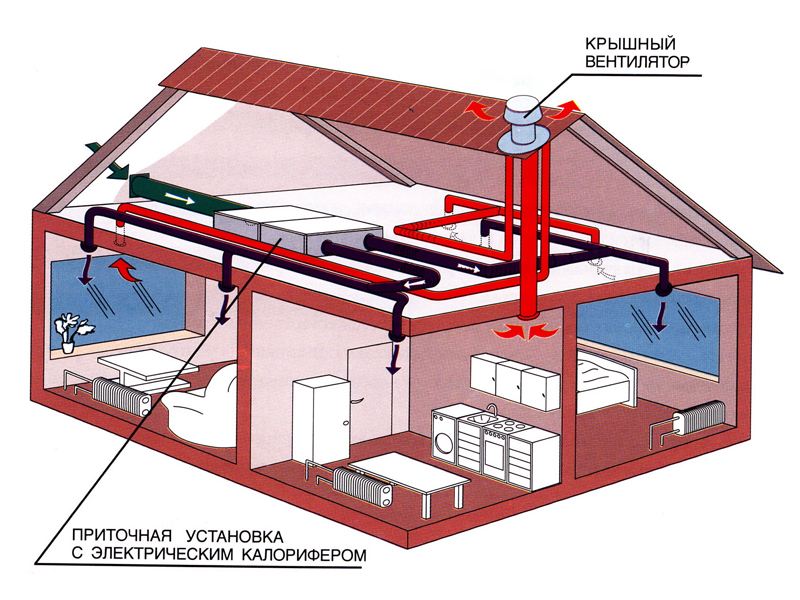
Diagram of a ventilation device with a heater
Only a qualified engineer can perform an accurate calculation of the ventilation system, but any educated person can calculate the ventilation of his small house.
Let's take the following performance characteristics for calculation:
- The area of living rooms is 100 m2;
- Kitchen area - 20 m2;
- Bathroom and toilet area - 10 m2;
- Wardrobe area - 10 m2;
- Other premises - 40 m2;
- Floor height - 3 m.
We determine the required performance of the ventilation system
It is calculated based on the required air exchange in the premises of the house. So in living rooms, air exchange is 3 m3 / h per 1 m2, in the bathroom 25 m3 / h, in the kitchen the air exchange rate is 6, i.e. we multiply its area by the height of the room and by the multiplicity, in the dressing room the multiplicity is 1.5, in other rooms 1.
We calculate the performance:
100x3+25+20x3x6+10x3x1.5+40x3x1=850 m3/hour
Calculation of heater power
To select a heater, we calculate its power.
To do this, we multiply the difference in air temperature at the inlet and outlet of the heater (for the Moscow region it is 44 ° C) by the previously obtained productivity (850 m3 / h) and the volumetric heat capacity of the air (0.336 W * h / m3 / ° C), and then the obtained divide the value by 1000.
44x850x0.336/1000=12.57 kW.
Based on the received power of the heater, it is possible to perform a calculation and determine the power of the current necessary for its operation. To calculate, you need to decide what current will be used to power the unit - single-phase or three-phase. We accept single-phase current with a voltage of 220V as a power supply.
12570/220=57 A
Attention! The resulting current strength will significantly load the electrical network of the house, provided that single-phase power is used.
Selection of the section of air ducts for ventilation of a private house

Air ducts for ventilation
We determine the cross-sectional area of the duct by multiplying the system capacity (850 m3 / h) by a factor of 2.778 and dividing by the air velocity, which is assumed to be 5 m / s.
850x2.778/5=472.26 cm2
Since it is intended to be used as an air duct plastic pipe we calculate its diameter, which is equal to the square root of the product of the area (472.26 cm2) by the constant 400 and divided by the number pi (3.14).
√472.26x400/3.14=245.28mm.
Since pipes with such a diameter are not produced, we accept a typical pipe d = 250mm. At an air speed of 5 m/s, a pipe with a diameter of 250 mm provides a capacity of 900 m3/h, i.e. its application completely provides ventilation of the house.
Ventilation of a private house should be based on the calculation and proper selection of materials.




