Calculation of the sufficiency of natural ventilation by the size of the vents. The height and diameter of the ventilation pipe: we perform the calculation
They design exhaust, natural ventilation from kitchens, sanitary facilities and bathrooms. Natural solution scheme exhaust ventilation kitchens and sanitary facilities with separate insulated ventilation ducts. Exhaust openings are closed with louvered grilles, which are located at a height
0.5 0.7 m from the ceiling. Recommended louvre sizes:
For kitchen 200 250 mm;
For latrines and bathrooms 150 150 mm;
For combined sanitary facilities 150 200 mm.
In brick buildings, exhaust ducts are laid in
thicker walls. The size of the channels is a multiple of the size of the brick min size
140 140 mm. Having placed the channels in the typical floor plan, we transfer them to the attic plan. For each room, the size of the amount of air removed is determined (table 11).
Table 11
| Room type | Air exchange L, m 3 / h | Recommended Channel Sizes a b, mm | Area F, m 2 | d eq, mm |
| Kitchen with stove: two-burner three-burner four-burner | 140 140 140 270 140 270 | 0,020 0,038 0,038 | ||
| Toilet | 140 140 | 0,020 | ||
| Bathroom | 140 140 | 0,020 | ||
| Combined bathroom | 140 270 | 0,038 |
Gravitational natural pressure is determined at an outside air temperature of +5 ºС. With more high temperatures the room can be ventilated with the help of transoms or vents.
Calculation procedure:
1. Determine the natural gravitational pressure for the channel natural ventilation, kitchens with a three-burner stove on the second floor. We start the aerodynamic calculation from the most unfavorably located channel - the channel of the second floor, we display the channels in the form of independent roots
![]() , \u003d 1.27 kg / m 3,
, \u003d 1.27 kg / m 3,
3.4 m - distance from the center of the exhaust hole to the mouth
exhaust shaft (Fig. 14);
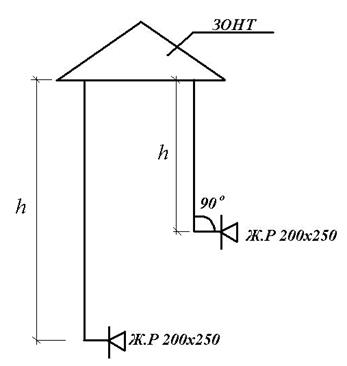
![]() kg / m 3
kg / m 3
The area of the channel is 0.038 m2.
Diameter equivalent d eq=180 mm.
3. Determine the air velocity in the channel
![]() m/s.
m/s.
4. Determine the equivalent channel diameter
5. We determine the pressure loss due to friction per linear meter of the duct according to adj. AND
R= 0.035 Pa/m, m/s at mm.
6. We determine the pressure loss due to friction along the entire length of the brick channel, taking into account the channel roughness coefficient ,
determined by air velocity m/s (app.3), 2.0 > 0.832 Pa
The need for ventilation of premises, both residential and warehouse, and industrial is beyond doubt, is not discussed, and should be present in the project from the very beginning. The lack of properly calculated ventilation on the drawings is an indisputable reason not to accept work from designers. The correct calculation of the natural and exhaust ventilation of the room will provide not only comfort for the people who use it, but also the microclimate necessary to maintain the room in a normal state, because the constant replacement of air masses prevents an increase in humidity and, as a result, a feeling of dampness.
The calculation of natural ventilation, which is most often used in houses and apartments, is possible only if the ventilation system is implemented in a duct way, that is, a system of air ducts is provided in the walls and ceilings, through which air is exchanged in the building.
Natural ventilation of the room can also be carried out in a channelless way - ventilation and natural air infiltration through door and window cracks and wall pores. In this case, the ventilation process is unorganized and uncontrolled, and the calculation of the ventilation system is impossible, since part of the data required for it is constantly changing.
Natural ventilation of the house is based on the property of air rising up when heated, as a result of which the exhausted warm air is discharged through the vent on the roof of the house.
Important! The channelless method of ventilation of any premises is accompanied by significant heat losses, is considered low-efficiency, and in some types of premises cannot be used at all.
Required formulas for calculations
The calculation of the ventilation of the house usually begins with the determination of air exchange or air productivity, which is measured in cubic meters per hour. Also at hand should be a plan of the object indicating the purpose of the premises and their area. All calculations should be carried out in accordance with accepted state norms and standards: SNiP 41-01-2003 or MGSN 3.01.01.
Important! Specialists usually use the norms of SNiP 41-01-2003 in calculations, since they are tougher, therefore, the result obtained is more in the interests of the customer.
It happens that in some rooms natural ventilation is limited for some reason (an old building or an improperly planned ventilation system), however, the conditions for the people living in them must be created as comfortable as possible, for which forced ventilation is installed.

This formula is used to calculate the ventilation performance
In one hour, the air in the room where people are located must be completely updated at least once. If such an update is not enough, it is necessary to calculate how many times it is necessary to replace the exhaust air with fresh air. This is called the definition of air exchange by multiplicity.

Formula for determining air exchange by multiplicity
As a result of the calculations, two indicators are obtained, of which experts recommend choosing the larger one, as the most consistent with safety standards.
When is forced ventilation necessary?
If the air in the room is musty and damp, and ventilation does not solve this problem, most likely, we are talking about insufficient natural ventilation. In this case, it is recommended to calculate the exhaust ventilation, and then install a fan of optimal power. The hood power in the kitchen depends on the type of gas stove used: an electric stove or a 2-burner gas stove will not adversely affect the microclimate of the kitchen if the hood power is 60 cubic meters per hour, for a 4-burner gas stove, the hood power must be at least 90 cubic meters .m/h If the apartment has a combined bathroom, then the exhaust ventilation capacity should be at least 50 cubic meters per hour, and for a separate bathroom and toilet, 25 cubic meters per hour is sufficient.
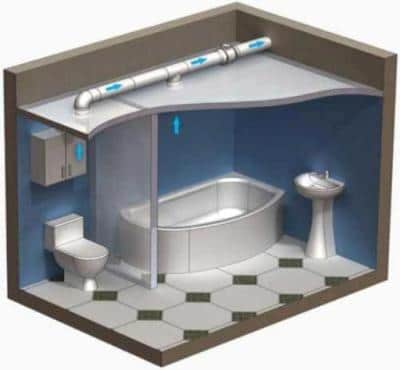
In such a bathroom, it is better to install two exhaust fans of lower power than one larger one, since the screen is an obstacle to air masses
Supply ventilation is an important addition to exhaust ventilation
In the event that the exhaust ventilation power is too high, drafts and problems with heat loss may occur in the room, so it is necessary to calculate the supply ventilation, which will have to compensate for the operation of the exhaust. In houses, cottages, apartments forced ventilation can provide, on average, twice the air exchange, which can be regulated using windows, doors and air conditioners.
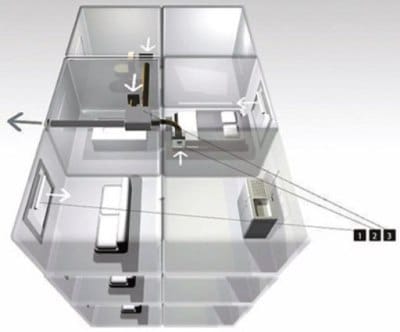
The scheme of supply and exhaust ventilation clearly shows the optimal location of ventilation equipment and the direction of air flow
The optimal calculation of supply and exhaust ventilation is based on the coincidence of indicators, that is, on the balance between incoming and outgoing air.
Aerodynamic calculation of ventilation
Aerodynamic calculation of the ventilation system is carried out for buildings with forced air exchange, which consist of a large number rooms, and the calculation of the natural ventilation of the room shows that it is not able to provide the necessary air exchange to maintain a normal microclimate in the room. Aerodynamic calculation of ventilation is used in the planning of hospitals, educational institutions, office buildings, designed for the constant presence of a large number of people, and it is better to trust the calculations to specialists, since it is very difficult for a person without special skills to correctly build an axonometric projection of a building and take into account all the nuances.
The main task of smoke ventilation
The calculation of smoke ventilation provides for the creation of such an air exchange system that, in case of danger, can block and limit the spread of gases, smoke, combustion products into rooms that are safe for people, as well as evacuation routes.
Important! The smoke ventilation system is effective only in the initial stage of the fire, then it is no longer able to provide fresh air in the required quantities.
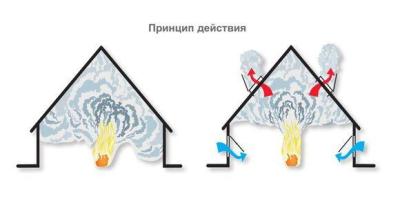
The main task of smoke ventilation is to prevent smoke from entering the premises, based on the effect of heat flow.
In residential premises, it is usually not necessary to install smoke ventilation, it is needed only in those industrial buildings, where the technological process involves the use of fire hazardous technologies. The smoke ventilation system must provide fresh air to limit the spread of smoke.
One of the conditions for creating comfortable microclimate in residential and industrial premises is the presence of an engineering system, thanks to which air is circulated. To ensure its effective functioning, it is necessary to correctly calculate the length and diameter ventilation pipe. For this, several methods are used, depending on the characteristics of the engineering system.
Ventilation scheme of a private house
Consequences of poor ventilation
If the fresh air supply system is not properly organized in the premises, there will be a lack of oxygen and increased humidity. Mistakes in the design of the hood are fraught with the appearance of soot on the walls of the kitchen, fogging of windows and the appearance of fungus on the surface of the walls.
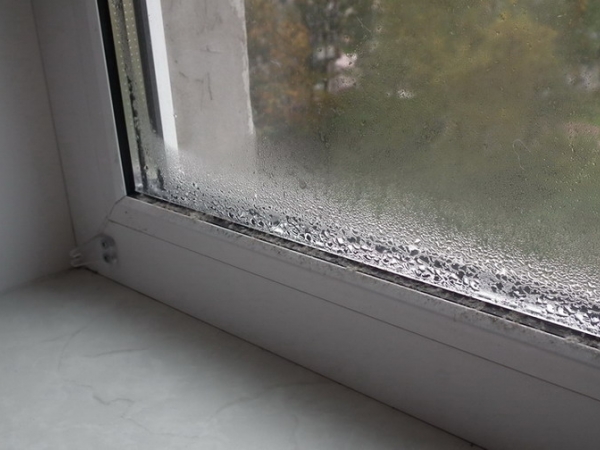

Fogging windows due to insufficient ventilation
It should be borne in mind that pipes of round or square section can be used for the installation of the ventilation system. When removing air without the use of special devices, it is advisable to install round air ducts, as they are stronger, tighter and have good aerodynamic characteristics. Square pipes better to use for forced ventilation.
Calculation of the ventilation system
Normative supply air volume
Typically, natural ventilation systems are used in residential buildings. In this case outdoor air enters the premises through transoms, vents and special valves, and its removal occurs with the help of ventilation ducts. They can be attached or located in internal walls. The construction of ventilation ducts in the external enclosing structures is not allowed due to the possible formation of condensate on the surface and subsequent damage to the structures. In addition, cooling can reduce the rate of air exchange.

Ensuring natural air flow through ventilation
Determining the parameters of ventilation pipes for residential buildings is carried out on the basis of the requirements regulated by SNiP and others. normative documents. In addition, the indicator of the multiplicity of exchange is also important, which reflects the effectiveness of the functioning ventilation system. According to him, the volume of air flow into the room depends on its purpose and is:
- For residential buildings -3 m 3 / hour per 1 m 2 of area, regardless of the number of people staying on the territory. According to sanitary standards, 20 m 3 / hour is enough for temporary residents, and 60 m 3 / hour for permanent residents.
- For auxiliary buildings (garage, etc.) - at least 180 m 3 / hour.
To calculate the diameter, a system with natural air flow is taken as the basis, without the installation of special devices. The easiest option is to use the ratio of the area of \u200b\u200bthe room and the cross section of the ventilation hole.
In residential buildings, 1 m 2 requires 5.4 m 2 of an air duct section, and in ancillary buildings - about 17.6 m 2. However, its diameter cannot be less than 15 m 2, otherwise air circulation is not provided. More accurate data are obtained using complex calculations.
Algorithm for determining the diameter of the ventilation pipe
Based on the table given in the SNiP, the parameters of the ventilation pipe are determined based on the air exchange rate. It is a value that shows how many times during an hour the air in the room is replaced, and depends on its volume. Before determining the diameter of the pipe for ventilation, do the following:
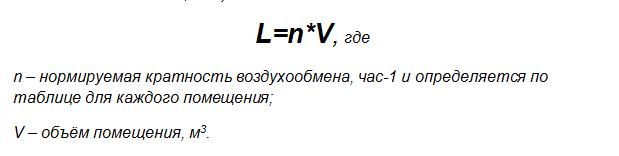
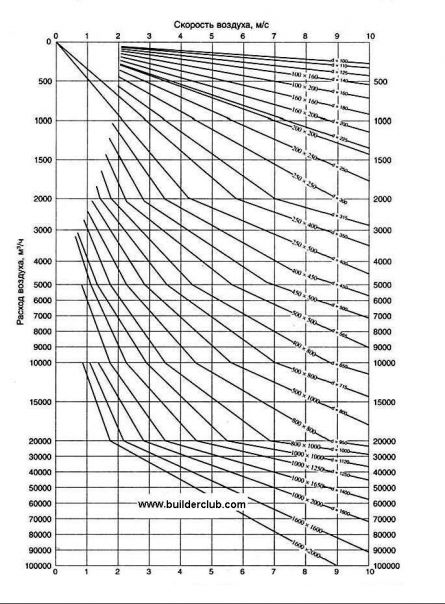
Diagram for determining the diameter of the ventilation pipe
Features of determining the length of ventilation pipes
Another important parameter in the design of ventilation systems is the length of the outer pipe. It combines all the channels in the house through which air is circulated, and serves to bring it out.
Table calculation
The height of the ventilation pipe depends on its diameter and is determined from the table. Its cells indicate the cross section of the ducts, and in the column on the left - the width of the pipes. Their height is indicated in the top line and is indicated in mm.
Selection of the height of the ventilation pipe according to the table
In this case, you need to take into account:
- If the ventilation pipe is located next to, then their height must match in order to avoid the penetration of smoke into the premises during the heating season.
- If the duct is located from the ridge or parapet at a distance that does not exceed 1.5 m, its height must be more than 0.5 m. If the pipe is within 1.5 to 3 m from the roof ridge, then it cannot be lower than his.
- The height of the ventilation pipe above the flat roof cannot be less than 0.5 m.
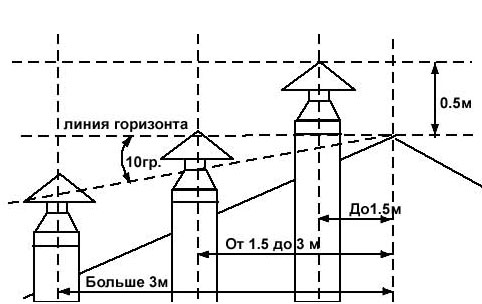
The location of the ventilation pipes relative to the roof ridge
When choosing a pipe for the construction of ventilation and determining its location, it is necessary to provide sufficient wind resistance. It must withstand a storm of 10 points, which is 40-60 kg per 1 m 2 of surface.
Software use
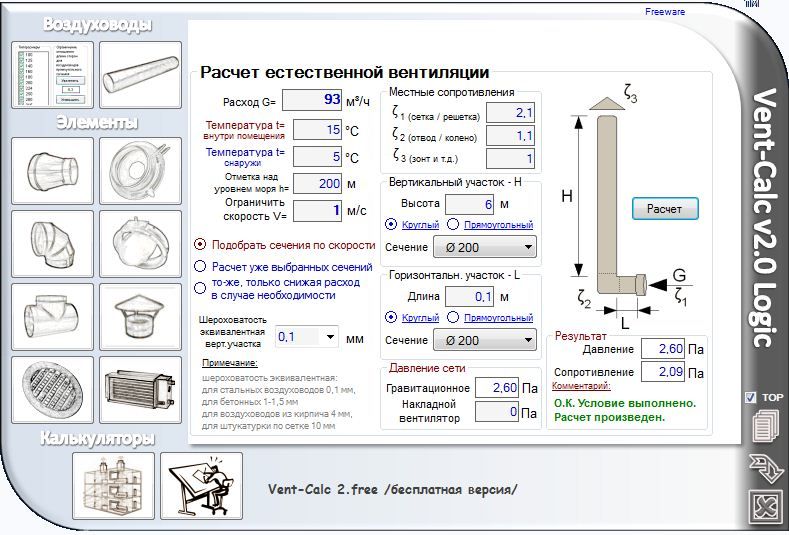
An example of calculating natural ventilation using special programs
The calculation of natural ventilation is less laborious if you use a special program for this. To do this, the optimal volume of air flow is first determined, depending on the purpose of the room. Then, based on the data obtained and the features of the designed system, the calculation of the ventilation pipe is made. At the same time, the program allows you to take into account:
- average temperature inside and outside;
- the geometric shape of the ducts;
- roughness of the inner surface, which depends on the pipe material;
- resistance to air movement.
![]()
Ventilation system with round pipes
As a result, the required dimensions of ventilation pipes are obtained for the construction of an engineering system, which must ensure air circulation under certain conditions.
In the process of calculating the parameters of the ventilation pipe, attention should also be paid to the local resistance during air circulation. It can occur due to the presence of grids, gratings, bends and other design features.
.The correct calculation of the parameters of the ventilation pipes will allow you to design and build an effective system that will make it possible to control the level of humidity in the premises and provide comfortable conditions for living.
The article provides an adapted calculation method autonomous system supply and exhaust ventilation on the example of 3 room apartment. You will learn how to calculate peak throughput values and how to choose the right equipment based on the needs of the apartment.
Like any work related to the installation of engineering equipment, ventilation installation consists of several stages. Consider them on the example of a three-room apartment.
Room analysis and problem setting for the system
Use a sheet of paper or a candle to check if the apartment's exhaust ventilation duct is working, the outlets of which are located in the bathroom and in the kitchen.
To determine the number and performance of air handling units needed in a particular room, you can use two options that are relevant depending on the complexity of the entire system.
Option number 1. Professional engineering online calculator. This method is filled with rather complex terms and formulations and is more suitable for complex layouts with many rooms that have different requirements to air exchange. Full use requires knowledge and professional experience.
Option number 2. Independent calculation, suitable for the requirements of SNiP. The ventilation of an ordinary apartment or a small house has minimal complexity, so any home master can handle its calculation.
Five indicators are necessary for the independent implementation of the project.
Air duct diameter. A complex calculation based on SNiP data, the number of people, room functions at different times of the day, etc. However, from experience it is known that it all comes down to three popular channel diameters (sections) - 100, 125 and 150 mm. Respectively:
- 100 mm - for constant continuous air exchange around the clock with low fan power;
- 125 mm - periodic ventilation while people are in the room (for example, from 18.00 to 8.00) at low and medium power;
- 150 mm - fast ventilation 1-2 times a day for rooms with irregular or rare presence of people.

Accordingly, the diameter of the duct in our case does not depend on the power of the devices, but on the requirements for the room.
Fan performance. Measured in m 3 / hour. According to SNiP 41-01-2003 "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning", air exchange should be provided at least 3 m 3 per 1 hour per 1 m 2 of living space. In other words, the system must pass through itself the entire volume of air in the room in 1 hour. Please note that supply ventilation provides air flow from 5 to 40 m 3 / hour, depending on the set mode.
Shape, section and walls of the channel. There are obstacles that can significantly affect the throughput of the system:
- The corrugated walls of the channel take 7-9% of the fan power. Choose smooth round tubes.
- Right angles (90°) of the channel - each angle takes 2-3% of the fan power. Design the channel with a minimum number of corners.
- Filters and noise absorbers. Their bandwidth and losses are also indicated in the factory documents.
Performance of supply devices. It should be equal to performance exhaust system, otherwise the exhaust fans will work with a load and without the proper result. The numbers of this main indicator are always in the instructions for the air handling units.
Room specifics. You can complicate the task by applying the calculation of air per person or by the frequency of exchange, but in practice there is enough information from the SNiP norm - 3 m 3 per 1 m 2 for bedrooms, living rooms, children's rooms. The same document speaks of fixed norms:
- For the kitchen - 90 m 3 / hour.
- For the bathroom - 25 m 3 / hour.
- For a toilet - 30 m 3 / hour.
- For a combined bathroom - 35 m 3 / hour.

It should be noted that these norms are developed with a huge margin, which is not implemented in practice. The problem of humidity and extraneous odors is solved if necessary - during cooking or a shower, an enhanced hood is turned on. To ensure fixed norms with good draft in a regular ventilation duct, it is enough to provide an inflow. When installing a fan on a regular channel, the inflow must also be increased.
Calculations
Calculation of living rooms
Amount of areas: 12 + 16 + 21 \u003d 59 m 2. Air volume for exchange according to SNiP: 59 x 3 = 177 m 3.
Calculation for bathroom or kitchen
The requirement for the hood is to ensure complete air exchange within 15 minutes. The volume of the kitchen according to the norm: 9 x 7 = 27 m 3, which should be removed in a quarter of an hour. Accordingly, the throughput of the exhaust fan will be equal to at least 27 x 4 \u003d 108 m 3 / hour while the hood is running (40-60 min/day).
In practice, this indicator for most household hoods is much higher - from 220 m 3 / h, however, in 50% of cases they are idle due to the lack of inflow.
Calculation of the bathrooms
Bathroom. Air volume: 4 x 3 \u003d 12 m 3 / hour. Complete air exchange in 5 minutes (1/12 hour). Bandwidth - 12 x 12 = 144 m 3 / hour.
Toilet. Air volume: 2 x 3 = 6 m 3 / hour. Complete exchange in 5 minutes (1/12 hour). System throughput — 6 x 12 = 72 m 3 / hour.
Recall that the calculated indicators refer to the throughput of the inflow, on the basis of which the exhaust equipment is selected.
The resulting data can be combined into a table:
| room | Area, m2 | Exchange according to the SNiP norm, m 3 / hour | Optimal channel diameter, mm | Number of knees, pcs. | Influx source | Note |
| Bedroom | 16 | 16 x 3 = 48 | 125 | 1 | Window/wall valve | Periodic ventilation 10 hours a day (from 22.00 to 08.00) |
| Children's | 12 | 12 x 3 = 36 | 100 | 2 | Constant ventilation | |
| Living room | 21 | 21 x 3 = 63 | 125 | 2 | Constant ventilation | |
| Kitchen | 9 | 90 (108 at peak) | 150 | 3 | Window/wall valve through living spaces | Constant ventilation with periodic amplification (hood) |
| Bathroom | 4 | 25 (144 at peak) | 150 | 2 | ||
| Toilet | 2 | 30 (72 at peak) | 150 | - | Periodic enhanced ventilation |
Question. How to ensure the flow of 144 m 3 / hour into the bathroom, if maximum ability supply valves - 40 m 3 / hour?
Answer. Connect the bath and toilet inlet to the combined extract from the living rooms. The air quality is quite suitable for enhanced ventilation, and a total of 120 m 3 / hour of inflow will ensure the normal efficiency of the hood.
The number of elbows is an indicator of the power loss of the exhaust fan (2% per elbow), take this into account when selecting equipment.
Based on the given data, it is possible to select equipment - window and wall valves, fans and hoods, channels. The main thing is to follow the rule - the volume of inflow must be equal to the volume of air exhaust. It is advisable to use a centralized multi-channel system with taps to each room (300-700 cu), and install power controllers and turn-on timers (from 15 cu/piece) to separate rooms.

Using the adapted methodology given in the article, you can save on the services of professionals. This is quite acceptable, given the low complexity. Now it remains to choose equipment, the price of which will depend only on the quality of the product and the noise level. We will tell you how to mount the system in the next article.
Vitaly Dolbinov, rmnt.ru
Until recently, natural supply and exhaust ventilation systems have been the favorites of industrial and civil engineering. The combination of simplicity and reliability attract both professionals and homeowners.
Penetrating into the house through leaky window blocks, cracks or specially installed ventilation devices, the air is drawn out due to the laws of physics. Before calculating natural ventilation, read existing species, advantages and disadvantages. With the help of our tips, you can easily and competently design the natural ventilation of a private house with your own hands.
How natural ventilation works
We will tell you in detail how natural ventilation works so that the apparent simplicity does not deceive anyone.
In cold weather warm streams are actively drawn out of the premises through the ventilation ducts. An area of low pressure is created, which is equalized by sucking in air masses from the outside. The cool outdoor air is warmed up, the cycle of work is repeated according to the same principle, until the temperature outside and the house is equalized.
Therefore, we feel a special closeness: our natural ventilation is not able to provide sanitary standards.
In the summer when atmospheric air hot, natural exhaust ventilation stops working.
Successful work is directly ensured by the following conditions:
- ventilation ducts are installed in rooms with maximum heat gain (kitchen, bathroom);
- ventilation shafts are designed strictly vertically, channels from apartments are connected to them;
- an uninterrupted supply of air from the street is provided to each of the rooms of the house (supply valves, ventilators, leaky wooden windows);
- air between rooms moves freely. To do this, a gap of 1.5 cm is left under the doors or a ventilation grill is installed in the lower half of the door leaf.
The operation of the system is based solely on a significant difference in climatic indicators in the building and on the street.
Types of natural ventilation
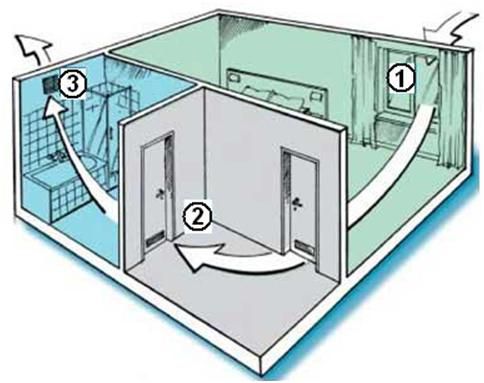
In buildings with natural supply and exhaust ventilation, the use of any kind of fans is completely excluded.
There are two types:
- Disorganized or spontaneous. Air currents enter the house through specially designed cracks, and are removed through the chimney. No ventilation vents do this.
- Organized. Air enters the building and leaves it through specially equipped vents. The location of the vents and their diameter are calculated depending on the volume of the room. The movement of air masses is regulated in different ways, depending on which the system can be:
- gravity;
- longline;
- aeration.
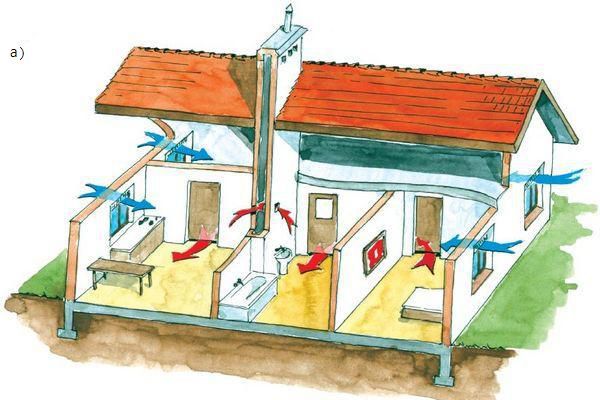
The device has many advantages:
- it is realistic to equip the natural ventilation of a private house with your own hands, spending a little money and having minimal knowledge in physics;
- works effectively under certain conditions and proper design;
- calculating natural ventilation for a private house is quite simple.
A simple but not always reliable principle of natural ventilation is used in residential buildings, public buildings old buildings, small warehouses, workshops. But when natural ventilation is not able to maintain the desired microclimate, while maintaining it, auxiliary fans are connected, which can increase the supply or exhaust of air.
Natural ventilation schemes
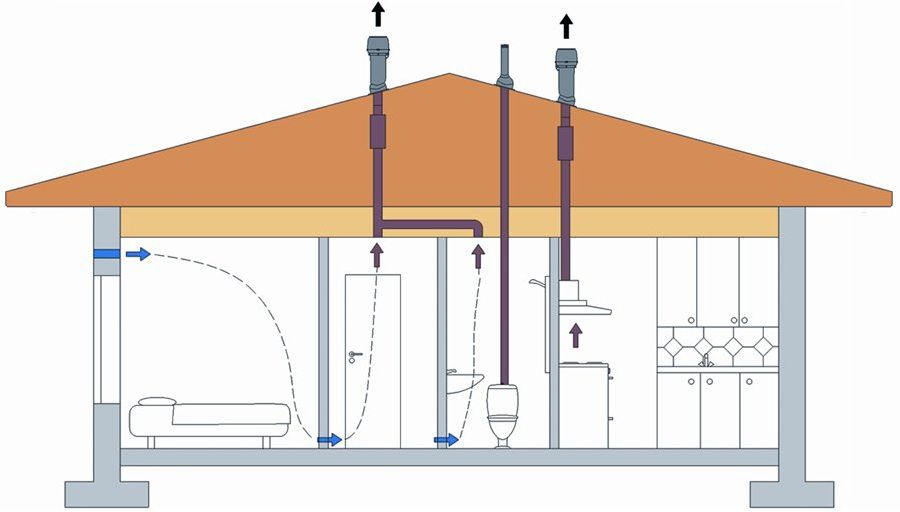
There are several types of schemes for a private house:
- channelless;
- channel;
- permanent;
- periodic.
Air enters the house through “dry” rooms: bedroom, guest room, and is removed through “wet” rooms with any ventilation device.
Projects without the use of ventilation ducts are more often done for industrial premises. The constant pattern is characterized by continuous air movement. Periodic chart natural ventilation means periodic ventilation.
The well-known channel scheme of natural ventilation of a private house is quite simple, it consists of shafts located vertically. The lower ends of the shafts go into the premises and are covered with ventilation grilles. The upper ones are raised above the level of the roof.
Most of all, bathrooms, toilets, kitchens, pantries, and boiler rooms need exhaust ventilation. With this in mind, the scheme is calculated.
Supply devices are located at the level of the top of the sash. Exhaust - as high as possible to the ceiling. For the free movement of air around the house under interior doors leave gaps.
If it is necessary to ventilate the basement or attic floors, additional air ducts are equipped.
Usually, all calculations and the scheme are prepared during the design of the building. During construction, cavities or shafts are provided.
The thrust force directly affects the speed of the air flow.
Which largely depends on the properties of the ventilation ducts:
- sections;
- height;
- thermal insulation;
- the number of turns.
Air ducts suitable in size for natural are installed during the construction of walls. Often they hide quite imperceptibly inside the partitions.
The higher the head of the ventilation duct rises above the roof, the higher the air speed. This is due to the greater difference in pressure below and above.
Air exchange rates for natural ventilation
The norms according to ABOK-1-2002 are:
The project was originally based on sanitary standards. The natural ventilation scheme will not provide a healthy microclimate in the house if they are not taken into account. So, with excessive air exchange, residents expect drafts and colds, and with a weak one - stuffiness, accumulation of dust and allergens.
Calculation of natural ventilation ducts
Air ducts are one of the main components of the natural ventilation of an apartment or house. Exhaust air is removed from the premises through them. For the system to function correctly, pipe cross-sections must be calculated.
Formula 1. First, specific losses are calculated:
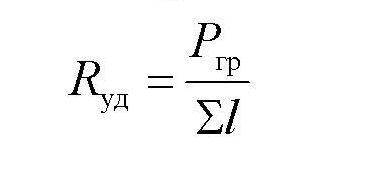
The numerator is the gravitational pressure, the denominator is the design length of the route in meters.
Formula 2. Gravitational head in Pascals:
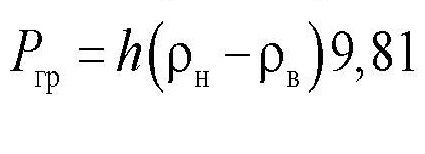
here h- height of the air column, R in is the density of the air in the room, R n- air density in the street in kg / m3.
Pipe dimensions are calculated as follows:
- Designation of ducts and ventilation grilles on the natural exhaust ventilation plan;
- Drafting axonometric diagram.
When drawing up an axonometric diagram, the vertical channels must be placed evenly and ensure the movement of the same volumes of air.
Do-it-yourself aerodynamic calculation procedure for a private house system:

For calculations, averaged indicators of air velocity in natural ventilation are taken: from 0.5 to 1 m / s.
As air ducts for natural ventilation, choose plastic round pipes.
Their smooth inner surface freely passes through itself air, without creating obstacles. They fit together easily and are easy to maintain. It is advisable to treat plastic pipes with an antistatic solution before arranging natural ventilation in a private house.
Natural ventilation problems

Even properly calculated natural ventilation has several disadvantages. We have already mentioned the dependence on external conditions.
And the last factor that nullifies the presence of natural exhaust ventilation: sealed windows. Air does not enter through PVC window seals; modern wall materials completely isolate housing. Therefore, common house hoods do not work.
Checking the effectiveness is very simple:
- Open the window in the kitchen;
- Bring to exhaust grille a piece of thin paper the size of a palm for a ventilation duct;
- If the sheet is held, then natural ventilation works like a clock.
It is also common to check natural ventilation with a lit match. This method is dangerous and may cause a fire or explosion in the ventilation shaft. Therefore, professionals check only with a paper sheet.
Heat is removed from an apartment or cottage along with stale air through natural ventilation ducts. Outdoor air carries dust and allergens. And in the kitchen natural supply and exhaust ventilation can't handle the steam and heat on big cooking days.
Solution of problems

You can create a constant or adjustable air supply for the natural ventilation of the apartment by installing a supply valve. Supply valves are wall or window. With some skills, it is really possible to normalize the work of natural ventilation with your own hands.
Supply devices must be equipped with nets that will not let dust and insects into the apartment.
Hoods are widely used as an auxiliary exhaust device. Must be properly connected kitchen hood maintaining natural ventilation. The ventilation grill in the kitchen does not overlap, as there is a separate outlet for the hood. The natural one is preserved, while the fan intensively drives moist air saturated with fat particles from the room.
Take the end of the duct to the street. This is the most reasonable option for those who want to connect a kitchen hood while maintaining natural ventilation.
Outside, the air duct is covered with a check valve, its surface is covered with thermal insulation. The method is more expensive, but competent.
Video on how to install yourself:



