Maintain a comfortable indoor climate. The optimal microclimate of the room where the child is located. The impact of the factor on the human body
The concept of microclimate
Under the microclimate industrial premises understood climate human environment the internal environment of these premises, which is determined by the combinations of temperature, humidity and air velocity acting on the human body, as well as the temperature of the surfaces surrounding it.
The impact of the factor on the human body
The microclimate of industrial premises mainly affects thermal state the human body and its heat exchange with environment.
A hooded chair can protect the body from the colder parts of the room. "Chairman Arend Kaigan", Marian van der Pol. Localized insulation, such as a hooded chair or screen, can protect the enclosure from the colder parts of the room, improving the comfort of the room without insulation.
Heat sources that produce warm microclimates also consume energy, which of course must be taken into account. Conductive heating systems can be even more efficient. Although localized heating systems may be more sustainable and save a lot of money, this effect is not guaranteed. There are situations when localized heating will consume more energy than air heating. The exact amount of energy used depends on many factors: the volume of the room, the number of people in it, the degree of its occupancy, the level of insulation of the building, ventilation requirements, the efficiency of the air heating system and the localized heating system.
Despite the fact that the parameters of the microclimate of industrial premises can vary significantly, the temperature of the human body remains constant (36.6 ° C). Property human body maintaining heat balance is called thermoregulation. The normal course of physiological processes in the body is possible only when the heat released by the body is continuously removed to the environment.
Most important factors are the amount of space and the number of people who occupy it. Obviously, the larger the space and the smaller the footprint, localized heating will be more attractive than an air heating system. Localized heating systems are also beneficial in areas with high ceilings. Hot air rises, which reduces the efficiency of the air heaters. It is no coincidence that the churches of the northern countries have been heated for centuries by huge brick slabs.
Another factor is the power supply to the localized heating system. The radiant heater is not tied to a primary energy source. For example, hot water used by hydronic radiant panel can be supplied solar collector, electric heater, heat pump or gas, coal or wood heater. Of course, the choice of primary energy source will affect the energy efficiency of the heating system. Use may be viewed with a grain of salt as it is generally believed that electric heating not sustainable: burning fossil fuels to produce electricity and converting it back into heat has large energy conversion losses that could be avoided with direct.
The release of heat by the human body to the external environment occurs in three main ways (paths): convection, radiation and evaporation.
A decrease in temperature, under all other identical conditions, leads to an increase in heat transfer by convection and radiation and can lead to hypothermia of the body.
At high temperatures, almost all the heat that is released is given off to the environment by evaporation of sweat. If the microclimate is characterized not only by high temperature, but also by significant air humidity, then sweat does not evaporate, but drips from the surface of the skin.
Our energy self-sufficiency project makes sense in our efforts to promote the savings and use of resources to promote responsible and sustainable tourism, and to help keep the planet healthy. Our sustainable project is about economy and health for us and for our environment, sustainable rural tourism is the only form of tourism that is viable in the long term, both ecologically and economically.
Encourage responsible tourism to protect local natural resources and biodiversity. Our mission is to promote sustainable tourism and quality. During the colder months, the water is heated with the help of biomass, as well as biomass, which is responsible for heating all the radiators in the house. The biomass boiler maintains the temperature of the boiler in the house, during the cold months the temperature is maintained at both plants up to 22 degrees to save energy.
Insufficient moisture leads to intensive evaporation of moisture from the mucous membranes, their drying and erosion, contamination by pathogenic microbes. Water and salts excreted from the body afterwards must be replaced, since their loss leads to blood clotting and disruption of the cardiovascular system.
Increasing the speed of air movement enhances the process of heat transfer by convection and evaporation of sweat. Prolonged exposure to high temperature in combination with significant humidity can lead to heat accumulation in the body and to hyperthermia, a state in which body temperature rises to 38–40 °C.
Rainwater is reused, collected in channels on the roof of the house and returned to a well used to irrigate the entire garden and olive grove with a drip system, as well as to fill the outdoor pool when needed. Both are well water, which is potable as running water is decalcified to come with less chlorine and heavy materials. The water collected by the spa room dehumidifier is filtered and reused in the heated pool, houseplants of the rocky area of Spa form a small microclimate that also helps to collect indoor humidity and ensures optimal indoor air quality, given the cleansing effect of vegetation.
At low temperatures, significant speed and humidity, hypothermia of the body occurs (hypothermia). Cold injury may occur due to exposure to low temperatures. Microclimate parameters also have a significant impact on labor productivity and injury rates.
Factor classification
In accordance with current classification given in Guideline R 2.2.2006-05 "Guidelines for the hygienic assessment of working environment factors and labor process. Criteria and classification of working conditions "microclimate is divided into heating and cooling.
The two pools, both the heated indoor spa and the summer outdoor pool, operate with electrolysis and salt water, making necessary quantity the chlorine required to maintain the water is minimal. Chlorine is a very polluting product for the environment and very harmful to nature.
In the restoration of the house, the original building elements were respected, such as thick stone walls, very good cold and heat insulation, the house is completely insulated to maintain good temperature both in winter and summer and save energy. In addition, new elements with sustainability and energy saving have been included in the building: all windows in the house have double glazing and an air chamber with aluminum eco-carpentry, and wood floors are lined with warmth for the whole house. The lamps are low power LEDs.
Heating microclimate - a combination of microclimate parameters (air temperature, humidity, speed of its movement, relative humidity, thermal radiation), in which there is a violation of heat exchange between a person and the environment, expressed in the accumulation of heat in the body above the upper limit of the optimal value(>0.87 kJ/kg) and/or an increase in the proportion of heat loss by sweat evaporation (>30%) in overall structure thermal balance, the appearance of general or local uncomfortable heat sensations (slightly warm, warm, hot).
Automatic stop settings in outdoor lighting and spa switches. Water recirculating switches have been introduced in the Spa and in the bathroom to avoid wasting so much water for it to heat up. The materials used in the body, stone and wood, as well as the quality furniture, were designed to last, as the longer the materials and objects are better suited to the environment.
To maximize the use of natural light, a bull-eye was installed on the top floor with solar tubes that gather maximum light and clarity during the day, as well as a skylight window on the ground floor bathroom or a large archway overlooking the south facing kitchen that helps bring in natural light. . Also, the spa roof skylight is a resource that allows you to use the maximum solar radiation, making the room a bright and very bright space. In the bedrooms, very bright and well-ventilated cotton and thread clothes are used, and the curtains are translucent to wake up in the sun, very healthy.
Cooling microclimate - this is the state of the microclimate in the production room, in which the air temperature in the workplace below the lower limit of admissible. There is a deficiency of heat in the body, a person feels cold.
Normalized factor indicators
The list of normalized microclimate indicators is given in Table 1.
The house has a anti-human system, recycled trash, and uses organic and non-toxic products for home cleaning and garden care, as well as garden waste compost to make fertilizer for their plants. European Union environmental label in recognition of efforts to help save our planet.
Human bioclimatology and habitat. This favorable result is achieved due to the presence of a patio, which determines the internal structure of the whole house. The concept of human bioclimatics and habitat. Photo - Patio in Cordou. The widespread use of new building methods has allowed for a certain homogenization of architectural typologies. The change has been so rapid that it is now possible to recognize some architectural elements that have partially or completely lost their function of the past, due to the widespread use of new technologies, such as the balcony, which is so characteristic of the Andalusian house.
Table 1
Standard values
Optimal and permissible values of microclimate parameters for industrial premises are established Sanitary regulations and SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96 " Hygiene requirements to the microclimate of industrial premises. Their values depend on the period of the year (cold or warm), as well as the category of work performed by the employee.
Nowadays, who pays attention to the existence of a balcony in the entire building? Probably very few people. Street noise and, above all, the installation of air conditioners inside buildings has reduced this architectural element to a mere rank of a decorative element, which has led to it losing most of its climatic function, traditionally filled, especially in the summer season, long and hot. It should be noted that during the summer period, which lasts almost five months, at dusk, when the lush vegetation that adorns the facade of the house is watered abundantly, the balcony functions as a kind of natural temperature and humidity conditioner inside the building, since it allows hot and dry air to penetrate from the outside, and then moisturizes and refreshes it as it passes through abundant vegetation.
To category Ia include work with an intensity of energy consumption up to 120 kcal / h (up to 139 W), performed while sitting and accompanied by slight physical stress (a number of professions in precision instrumentation and engineering enterprises, in watchmaking, clothing production, in management, etc.).
To category Ib include work with an energy consumption intensity of 121 - 150 kcal / h (140 - 174 W), performed while sitting, standing or walking and accompanied by some physical stress (a number of professions in the printing industry, in communications enterprises, controllers, craftsmen in various types of production and etc.).
At present, the difference between the balconies of cities and villages is very disturbing. On the latter, it is easy to find plants grown in all kinds of containers, whether they are terracotta pots or simple jars. This is a custom that practically does not exist in the city.
Rice. - Indoor thermal gradient of a one-story family house in summer. The degrees Celsius do not represent actual temperatures, but average relative thermal gradients. It should not be forgotten that the fact of leaving the balcony in desolation is equivalent to giving up even more the opportunity to create another pleasant place in the house.
To category IIa include work with an intensity of energy consumption of 151 - 200 kcal / h (175 - 232 W), associated with constant walking, moving small (up to 1 kg) products or objects in a standing or sitting position and requiring a certain physical exertion (a number of professions in mechanical assembly shops engineering enterprises, in spinning and weaving, etc.).
Since almost always, in order to cope with the disadvantages imposed by the natural environment, folk wisdom has used either architectural elements - a balcony alone - or methods such as whitewashing. The beneficial effect of the latter is widely known in Andalusia: White color has a high albedo and therefore absorbs less heat than black or dark bodies, and as a result of reflections of solar radiation are amplified in summer. which prevents heat from entering the house.
Currently the view is different and the most common idea is that any building under construction can solve their comfort problems later using artificial systems, which make it possible to forget the characteristics of climate and place in exchange for expensive investments and high energy consumption, which are difficult to maintain indefinitely. Perhaps this led to the last years concept Bioclimatic architecture is beginning to take on a new dimension, and it is a new way of understanding architecture and urban planning, which aims to capture some of the architectural features of the past that are worthy of interest and are currently scarce.
To category IIb include work with an energy intensity of 201 - 250 kcal / h (233 - 290 W), associated with walking, moving and carrying loads up to 10 kg and accompanied by moderate physical stress (a number of professions in mechanized foundry, rolling, forging, thermal, welding shops of machine-building and metallurgical enterprises, etc.).
The characteristic of bioclimatic architecture is basically that it itself tries to optimize the energy relationship with the environment: in this way it uses the winter sun and rejects the summer; it takes advantage of aeration to combat moisture and release annoying hot air; it uses insulation to reduce heat transfer from the outside and, in particular, heat loss in cold weather. In traditional architecture, this climate regulation is achieved through a combination of all kinds of means and resources: in the form of the city itself, which includes allotted places warmed by the winter sun and protected from the cold wind; thanks to some architectural elements such as arcades and large awnings that enrich the public space and extend the time of use; through protective accessories such as awnings and even vegetation, all of which make the traditional city reflect a process of successive attempts to reconcile urban forms with certain physical conditions, location and climate, in the most functional and economical way.
To category III include work with an energy intensity of more than 250 kcal / h (more than 290 W), associated with constant movement, moving and carrying significant (over 10 kg) weights and requiring great physical effort (a number of professions in blacksmith shops with manual forging, foundries with manual stuffing and casting molding boxes of machine-building and metallurgical enterprises, etc.).
The optimal values of the microclimate indicators at the workplaces of industrial premises are shown in Table 2.
table 2
| Period of the year | Category of works | Air temperature, °С | ||
| Cold | Ia | 22 – 24 | 60 – 40 | 0,1 |
| Ib | 21 – 23 | 60 – 40 | 0,1 | |
| IIa | 19 – 21 | 60 – 40 | 0,2 | |
| IIb | 17 – 19 | 60 – 40 | 0,2 | |
| III | 16 – 18 | 60 – 40 | 0,3 | |
| Warm | Ia | 23 – 25 | 60 – 40 | 0,1 |
| Ib | 22 – 24 | 60 – 40 | 0,1 | |
| IIa | 20 – 22 | 60 – 40 | 0,2 | |
| IIb | 19 – 21 | 60 – 40 | 0,2 | |
| III | 18 – 20 | 60 – 40 | 0,3 |
Permissible values of microclimate indicators at workplaces of industrial premises are given in Table 3.
Table 3
| Period of the year | Category of works | Air temperature, °С | Relative air humidity, % | Air speed, m/s |
| Cold | Ia | 20 – 25 | 15 – 75 | 0,1 |
| Ib | 19 – 24 | 15 – 75 | 0,1 – 0,2 | |
| IIa | 17 – 23 | 15 – 75 | 0,1 – 0,3 | |
| IIb | 15 – 22 | 15 – 75 | 0,2 – 0,4 | |
| III | 13 – 21 | 15 – 75 | 0,2 – 0,4 | |
| Warm | Ia | 21 – 28 | 15 – 75 | 0,1 – 0,2 |
| Ib | 20 – 28 | 15 – 75 | 0,1 – 0,3 | |
| IIa | 18 – 27 | 15 – 75 | 0,1 – 0,4 | |
| IIb | 16 – 27 | 15 – 75 | 0,2 – 0,5 | |
| III | 15 – 26 | 15 – 75 | 0,2 – 0,5 |
Normative values of microclimate indicators for working premises with a heating microclimate, with a cooling microclimate, for open areas and unheated premises, taking into account climatic zoning, as well as the distribution of working conditions by the “microclimate” factor by class, are given in Guideline R 2.2.2006-05.
If the measured parameters meet the requirements Sanitary regulations and norms SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96 "Hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises", then working conditions in terms of microclimate indicators are characterized as optimal (grade 1) or admissible (grade 2) . In case of discrepancy, the working conditions are classified as harmful and the degree of harmfulness is established, which characterizes the level of overheating or cooling of the human body.
Measurement technique
Measurements of microclimate parameters should be carried out twice a year - in the cold and in the warm period of the year. Measurements should be carried out at all workplaces at least three times per shift (at the beginning, in the middle and at the end of the shift).
If within work shift the employee is located in several working areas, measurements are taken in each of them.
During work performed while sitting, the temperature and air velocity are measured at a height of 0.1 and 1.0 m, relative humidity– at a height of 1.0 m from the floor or work surface; for work performed while standing - the values \u200b\u200bof 0.1, 1.5 and 1.5 m, respectively.
Where sources of radiant heat are available, thermal exposure is measured from each source.
When assessing the microclimate in an open area and in unheated premises, it is necessary to determine the climatic region.
Climatic regions (belts) (Fig. 1) are characterized by the following indicators:
air temperature (average of winter months) and wind speed (average of the most probable values in winter months) and are divided into:
Ia (special) - 25 ° C and 6.8 m / s;
I6 (IV) - 41 °С and 1, m/s;
II (Sh) - 18.0 °C and 3.6 m/s;
III(II) - 9.7 °С and 5.6 m/s; IV(I) - 1.0 °С and 2.7 m/s.
Location of climatic regions Russian Federation shown in Figure 1.
Picture 1– Climatic regions of Russia
When assessing the microclimate in an open area or in unheated premises, it is also necessary to assess the presence or absence of regulated breaks for heating.
Measuring instruments
Instruments for measuring microclimate parameters are shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2– Instruments for measuring microclimate parameters
Measures to eliminate the harmful effects of the microclimate
to improvement measures industrial microclimate include:
- rational organization of the heating and ventilation system (air shower, air conditioning;
- improvement of the technological process and mechanization of heavy work;
- protection from sources of thermal radiation (protective screens) in a heating microclimate;
- elimination of large cold surfaces, insulation of doors, windows, installation of a thermal air curtain and installation of heat guns in a cooling microclimate;
- rationalization of the regime of work and rest (introduction of regulated breaks, equipment of a rest room);
- use of personal protective equipment.
A rare person will begin to study the microclimate in his home if everything is fine in his life. But when the children suddenly began to get sick often, their mother “got out” of an allergy, it’s not clear what, and the head of the family himself often went to the doctors, then you involuntarily think about it. There must be a reason for all this trouble. And often the reason is the unfavorable microclimate in the living room.
What is the microclimate of the room, what does it consist of
The term "microclimate" is used to characterize the meteorological conditions in a certain relatively small space. In our case, such a space is a living space (apartment, room, house) in which the child and his parents are located. Adults can and must create an optimal microclimate in the home, create favorable weather conditions for family living.
Components of the microclimate in a residential area:
- air temperature;
- relative humidity;
- air exchange and air velocity;
- concentration of light air ions in the air;
- the content of particulate matter in the air.

All these factors together form the microclimate of the room. But it is not always comfortable and safe for a person. We notice that in a rainy autumn, when the heating has not yet been turned on, the damp interior doors and there is mold in the corners of the bathroom. But, when the heating radiators come to life and begin to “spit” so that it is impossible to touch them with your hand, the dry laminate moves around, and the doors to the room swing open on their own. And the reason for this is the unstable microclimate: sometimes hot and dry, sometimes cold and damp. And first of all, the human body, and especially the body of a child, reacts to this instability.
The optimal microclimate of the room where the child is
In order to understand which component of the microclimate has left the "green zone", you need to know the numerical values of some parameters that are optimal for a dwelling.
So, the humidity in the room where the child is located should not be less than 50% and more than 60%. The air temperature at which the human body is in a state of complete calm can range from +18 °C to +22 °C. It is desirable that in the hot summer the temperature difference between the street and the house does not exceed 5 ° C. As for the speed of air movement in the room, it can only be assessed subjectively: whether it blows through the windows or not, whether there is a draft or not.
 It is not possible to determine the content of dust and air ions in the ambient air, since devices capable of measuring these indicators have so far been designed only for industrial and military use. Therefore, it is believed that repeated ventilation and wet cleaning twice a day are sufficient to maintain these indicators at an acceptable level. The amount of fresh air entering the room, which should not be less than 30 cubic meters per hour, is also problematic to fix.
It is not possible to determine the content of dust and air ions in the ambient air, since devices capable of measuring these indicators have so far been designed only for industrial and military use. Therefore, it is believed that repeated ventilation and wet cleaning twice a day are sufficient to maintain these indicators at an acceptable level. The amount of fresh air entering the room, which should not be less than 30 cubic meters per hour, is also problematic to fix.
Important:if you are serious concerned about the microclimate of your home and decided to correct it, first of all, purchase a room thermometer and a household hygrometer or a compact weather station for home use.
How microclimate affects human health
Air temperature
Let's start with air temperature. If the room is very hot, the first to suffer skin and mucous membranes. They dry up and, as a result, do not fully fulfill the protective functions assigned to them. The skin peels off, cracks form on it, diaper rash and prickly heat appear in children. If a child has a tendency to allergies, then often it is manifested by symptoms. Pathogenic microbes easily penetrate skin microcracks, causing pustular diseases.
The secretory function of the cells of the mucous membranes deteriorates sharply. Therefore, allergens, microbes, dust particles that have fallen on a parched mucosa are not washed out, but settle on it. Microorganisms easily enter the bloodstream and cause infectious diseases. Allergens, if the body has hypersensitivity to them, trigger an allergic reaction.
Dry mucous membranes are favorable soil for the reproduction of fungi, for example, candida, causing. The mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract also suffer from the heat: they produce less mucus, which is necessary for proper digestion. In children, this can be manifested by abdominal pain (colic), stool disorders and other dyspeptic disorders.
Due to the imperfection of the thermoregulation system, if the room is hot, the child may overheat. This is often facilitated by the mother herself, who incorrectly dresses the baby. With an increase in body temperature, the child sweats more, therefore, heat transfer increases. But since it is also not perfect, you need to be wary of hypothermia.
In a cold room, the body is always in tension, trying to warm up, which adversely affects the immune system. The child begins to get sick often with colds.
Air humidity
It's even worse when heat air is combined with its low humidity. , dying in damp rooms, in this case "lives and thrives", posing a threat to both children and adults. Due to the excessive dryness of the surrounding air, the child develops crusts in the nasal passages, making it difficult to breathe through the nose. The kid is naughty, sleeps restlessly during the day, wakes up at night, eats poorly.
High humidity in a warm room is what you need for the growth and reproduction of fungi. Fungi are mold, and mold in a home is inevitably a respiratory disease.
Air pollution
In addition to various gases, the indoor air contains microorganisms, dust, decay products of automobile fuel that have fallen from the street, mites, pet hair, plant pollen, etc. Inhalation of such air provokes the development of both allergic diseases and intoxication of the body, and infectious diseases. In such a microclimate, a growing child's body is the most vulnerable target.
Air exchange and air velocity
These parameters depend on how well ventilation is established in the living room, how often it is ventilated. In the indoor air, the concentration gradually increases carbon dioxide and the person is deficient in oxygen.

The content of carbon monoxide increases, which, when combined with blood hemoglobin, causes hypoxia. The number of air ions decreases. All this causes a deterioration in general well-being, fatigue, insomnia or drowsiness, headaches. In deaf rooms, the air is saturated with harmful substances that emit Construction Materials, furniture, household chemicals. All of them, to a greater or lesser extent, adversely affect human health.
 AT atmospheric air air ions (gas ions) are formed under the influence of cosmic radiation, lightning discharges, radiation, ultraviolet rays, and when water is sprayed. Therefore, their high content in the air is recorded in mountainous areas, forests, near large reservoirs. And in settlements, and even more so in enclosed spaces, their concentration in the air is extremely low.
AT atmospheric air air ions (gas ions) are formed under the influence of cosmic radiation, lightning discharges, radiation, ultraviolet rays, and when water is sprayed. Therefore, their high content in the air is recorded in mountainous areas, forests, near large reservoirs. And in settlements, and even more so in enclosed spaces, their concentration in the air is extremely low.
Scientists and doctors do not stop discussing the beneficial and harmful effects of air ions on the human body. But for a long time there have been numerous practical confirmations of the beneficial effect of light negative air ions on all systems of the human body. Inhalation of ionized air normalizes metabolism, increases the body's resistance to infections, and improves performance. In addition, air ions purify the air, attracting solid particles suspended in it, and prevent the formation of mold.
How to create the optimal microclimate in a residential area
The creation of an optimal microclimate implies the constant conduct of a whole range of activities in a residential area, namely:
- ensuring sufficient air exchange;
- maintaining a comfortable air temperature (18–22°C);
- creation optimal humidity air (50–60%);
- fight against air pollution.
note: you should always start with ensuring good ventilation of the room! And only then you can clean, humidify, heat or cool the air in it.
Important:do not forget about the good old methods and means of creating a healthy microclimate that do not require special material investments: regular airing, wet cleaning twice a day, landscaping the living space by breeding indoor plants.
This video review provides a description of plants that can purify the air in residential premises:
Climate technology for the home
Unfortunately, a universal device has not yet been created that would lead to optimal values all the microclimate parameters. Therefore, in order to create an optimal microclimate in the room, you will have to purchase several units.
 In order for the air conditioner not to become the cause of frequent colds, it must be properly installed and properly operated. Air conditioners cool or heat the air in the room, but at the same time dry it. The built-in cleaning filter requires regular cleaning and disinfection, as the microorganisms that settle inside the unit multiply and enter the living room with the air current. In expensive models of air conditioners, there are additional options: air humidification, oxygen enrichment, fresh air supply.
In order for the air conditioner not to become the cause of frequent colds, it must be properly installed and properly operated. Air conditioners cool or heat the air in the room, but at the same time dry it. The built-in cleaning filter requires regular cleaning and disinfection, as the microorganisms that settle inside the unit multiply and enter the living room with the air current. In expensive models of air conditioners, there are additional options: air humidification, oxygen enrichment, fresh air supply.
Breezers
Breezer is a device for providing supply ventilation indoors. It supplies the room with neutralized and oxygen-enriched street air.
 Heaters
Heaters
 For the room where the child is, you should not take an oil heater or fan heater, as they burn oxygen and dust that has settled on their surface. The best option– modern electric convector. It is safe, efficient, economical and silent.
For the room where the child is, you should not take an oil heater or fan heater, as they burn oxygen and dust that has settled on their surface. The best option– modern electric convector. It is safe, efficient, economical and silent.
 Steam and ultrasonic humidifiers cope with only one task: increase the humidity of the air in the room.
Steam and ultrasonic humidifiers cope with only one task: increase the humidity of the air in the room.
Air washing- this is the same humidifier, but only improved. The sink purifies and humidifies the air, and (with the correct selection of the device for a given room) all the air in the room passes through the unit twice an hour.
Compact electrical multifunctional devices are climatic complexes. They saturate the air with moisture, purify it from house dust, harmful chemical compounds, plant pollen, animal hair, and also eliminate unpleasant odors. There are models with the functions of ionization, aromatization, dehumidification.
Air ionizers
These devices are suppliers of aeroins, which are so lacking in the air of city apartments and even country houses. But before purchasing an ionizer, it is still better to consult with your treating doctors: a pediatrician, a therapist, narrow specialists, if you are being observed by them. There are a number of conditions and diseases in which the inhalation of ionized air is contraindicated.
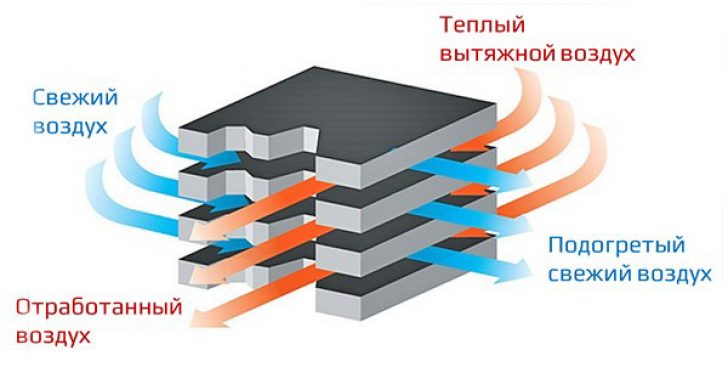
Air recuperators
These are devices designed for ventilation of rooms. The exhausted warm air from the room, going outside through the heat exchanger, gives off its heat to the fresh air coming from outside. The air temperature in the room does not decrease with such ventilation.
 Important:when buying any climatic device, be sure to read the accompanying documents for it, check for a certificate of compliance with established standards. Specify the warranty obligations of the manufacturer and seller.
Important:when buying any climatic device, be sure to read the accompanying documents for it, check for a certificate of compliance with established standards. Specify the warranty obligations of the manufacturer and seller.
Observe the following rules:
- follow all recommendations for the safe operation of the unit;
- if the ecological situation outside the window allows, ventilate the room hourly;
- if it is impossible to open the windows (smog, flowering season, etc.), ventilate the dwelling with a breather;
- in hot weather, use air conditioning to cool the air;
- in winter, but not in summer time use a humidifier;
- if there are allergies in the family, an air purifier will help;
Important: not forget to pay attention to the indicators of the weather station, control the microclimate you create. (79 voice., middle: 4,63 out of 5)



