Stuffed piles. Stuffed Piling Methods
Device stuffed piles exists in many variants. There are types of piles according to the material of manufacture and construction: concrete, reinforced concrete, metal, asbestos-cement and synthetic shells.
According to the location on the construction site, the piles can be single, installed in strips or in a pile field or bush. Supports are installed both vertically and obliquely. Just like other types of supports, stuffed piles can be hanging, uprights and anchor supports. Wells for stuffed supports are formed by several types: mechanical and vibromechanical drilling, drilling under clay mortar and blasting.

Such piles, today, are one of the most popular foundation supports. Work on their device is unpretentious and quite affordable for an individual developer. Despite the fact that these designs are intended for weak water-saturated bases, they are also successfully used on denser soils. The attractiveness of their use lies in the availability and cost-effectiveness of work on their device.
AT industrial construction stuffed piles look like pipes of large diameter. Massive pipes are lowered to a great depth using special equipment.
Stuffed piles in their history of application have proven to be one of the most reliable foundation foundations.
Stuffed Piling Methods
The technology for the installation of stuffed piles differs from the installation of driven supports, and consists of several stages of work:
- First, a well is drilled in the ground. If the well rests on loose soil, then a sand cushion is created at its bottom.
- The underlying layer is prepared by mixing sand and gravel in equal proportions. The thickness of the compacted cushion must be at least 150 mm. As a rule, as a waterproofing, a layer of roofing material is laid on the surface of the pillow.
- In the case of installing a pile in watered soil, additional strengthening of the borehole walls will be required to prevent the collapse of the side surface of the wellbore.
- Saturated clay solution is supplied to the well walls under pressure by a special device. This creates a waterproof layer. The formed "bark" reliably protects the side surface of the well from collapse.
Casing applications

Casing pipes are used in the weakest soils. Pipe segments are immersed into the finished drilled well using hydraulic jacks. The interior of the casing pipe is cleaned of foreign objects and debris.
A reinforcing cage is placed inside the pipe. Concrete is poured through a special sleeve. It is very important to observe the layer-by-layer compaction of the concrete mixture with internal vibrators. Each layer is rammed with a thickness of 200 mm.
Bored pile with wide heel
The device of piles with a broadened heel is carried out in three ways:
Reinforced compaction
Concrete is poured into the base of the well with a layer of 200 - 300 mm thick. Concrete preparation is heavily rammed. Under pressure, the concrete pushes back the surrounding soil, thereby forming a widened heel of the pile base.
Mechanical soil removal
Mechanical removal of soil at the base of the well is carried out using a special knife. A folding knife fixed on the drill column opens at the design depth. As a result of the rotation of the knife, the base of the well is widened up to 3 meters. The knife is remotely controlled by a hydraulic mechanism.
The resulting cavity is filled with concrete. A reinforced frame is installed on the frozen concrete pad.
explosive way
The cavity under the broadened heel is obtained by means of a directed explosion. After installing the casing, explosives with an electric fuse are lowered to the bottom of the well. Then the casing pipe is lifted up by 500 mm. With the help of remote control produce an explosion.
The result is a recess in the ground of a spherical shape. The cavity is filled with concrete mix. Under the influence of the force of the explosion, the soil is strongly compacted, which significantly increases the bearing capacity of the supporting structure.
After installing the reinforcement, the casing pipe is filled with concrete with layer-by-layer compaction.
Installation of stuffed piles pneumatically
The pneumatic method is used in flooded soils. Compressed air is constantly supplied to the laid concrete mixture inside the pipe by a compressor. Concrete is poured in layers. To do this, use a special pneumatic injection unit.
Stuffing piles with soil
Works on the device of soil-filled piles are carried out with special drilling equipment. The unit has a drill rod, a mixing drill with special blades. The blades cut the soil and mix it with the concrete mixture at the same time.
A cement slurry is fed into the drilled well through a rod under pressure. Together with the reverse rotation, the drill with the rod is lifted up. The soil is mixed with concrete and compacted at the same time. As a result of such work, a soil-filled pile is formed, which does not require excavation of soil from the support shaft.
It is advisable to use stuffed piles of this design on sandy, weakly bearing bases.
Drilled supports
Sometimes, for fear of causing undesirable movements in the soil base from nearby buildings, driving operations cannot be carried out. Excavation during drilling operations can also adversely affect the bearing capacity of the subgrade.
Do-it-yourself installation of stuffed piles
Consider an independent installation of stuffed piles by a developer for a small housing construction. Refusing to carry out driving work on its plots, the developer decides on the construction of the foundation of a new building from stuffed piles.
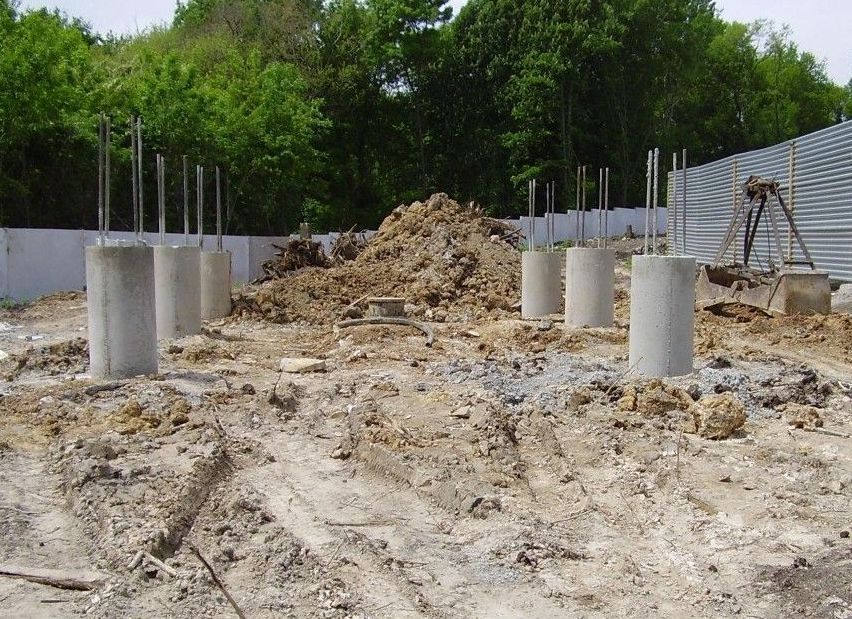
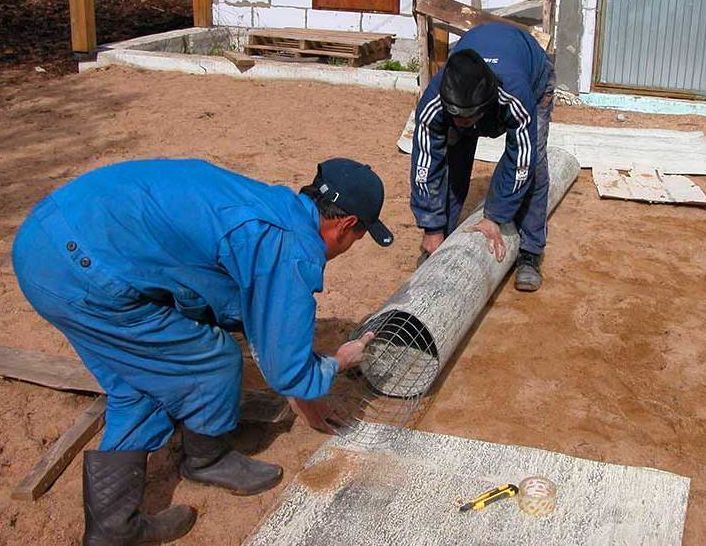
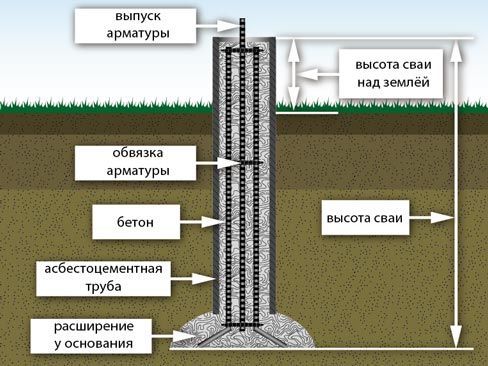
Wells are drilled at the points established by markings. In wells all over pile field insert metal or asbestos-cement pipes. The standard distance between the supports is considered to be from 1.5 to 2 meters.
If a pipe with a diameter of 200 mm is immersed in the ground by 1.5-2 meters, then the upper part should protrude 300-400 mm above the ground. The pipes are filled with concrete one third of the length.
A reinforced frame is placed in the pipes, consisting of two or three vertical rods fastened with transverse smooth reinforcement. Gaskets from improvised material regulate the verticality of the frame. Work on pouring concrete is carried out with layer-by-layer compaction. Concrete is poured from the outside into the sinuses between the pipes and the soil. With the help of a grinder, the upper parts of the supports are leveled to one level with an abrasive wheel.
Supports are installed under load-bearing walls, in the corners of the building and in places of concentration of loads.
In the upper part of the reinforcement, a threaded stud is attached at the end or a metal plate is welded. The design of the end cap of the reinforced frame depends on the type of grillage.
Work on the installation of a grillage from a wooden beam begins by fastening with nuts the studs threaded through the holes in the beam. If the grillage is made of a metal profile, then welding is carried out to fasten the channel or corner to the embedded parts of the upper part of the supports.
Compliance with safety regulations
Safety regulations in the production of pile work must be strictly followed by all participants in the production process.
It is necessary to constantly monitor the operation of the drilling rig. In the event of any malfunction, work must be stopped.
All participants performing work on the installation of stuffed supports must be familiar with the safety regulations, which they sign in the log. In the winter season, the construction site must be cleared of snow and ice, and sprinkled with sand.
The fundamental aspect of housing construction is the construction of a reliable foundation for the building. The strength of the construction object, its service life depends on the perfection of the foundation. These criteria are fully met by the foundations, which are based on bored piles, which have proven themselves as an efficient, durable and modern structure used in the construction of various objects.
The production of bored elements is carried out by drilling a well, strengthening it with a steel reinforcing cage and subsequent concreting. Distinctive feature the design of these supports is a high bearing capacity. It allows you to use it as a base for high-rise buildings, bridges and other heavily loaded structures, critical structures.
The idea of a bored base is very simple: where it is impossible to dig down to dense soil at minimal cost, long posts can be used.
Regulations
The design, installation of these products, which perceive the entire load of the facility under construction, is subject to a set of serious requirements regulated by regulatory documents. There is no single GOST, the scope of which applies to bored piles.
The requirements for them are united by the following building codes and rules:
- 02.03, approved in 1985, which are called "Pile Foundations";
- 02.01, developed in 1987, referred to as "Earth structures, foundations and foundations";
- 03.01 issue of 1984 under the name "Reinforced concrete and concrete structures".
Despite the fact that these regulatory documents were developed and approved a long time ago, their requirements are relevant at the present time. What parameters should pile foundations meet? Why are these rules fundamental? Let us consider in detail what requirements bored structures must meet.
In the presented material, construction specialists and design engineers will find a lot of useful information. After all, they are united by the main task - ensuring the reliability of the building, compliance with all the requirements established by the standards!
Definition Table bearing capacity 1 m / n bored pile-rack
Pile classification
In accordance with SNiP, pile driving used in construction is carried out by various methods. According to the method of deepening, piles are divided into the following types:
- Concrete-reinforced piles of the driving principle of immersion, which are pressed into the ground using vibration or hammers.
- Reinforced concrete supports-shells, the formation of which is carried out with excavation and filling in whole or in part with mortar.
- Concrete, providing for the possibility of reinforcement, stuffed piles, during the arrangement of which a concrete solution is poured into a well obtained by displacing soil.
- Reinforced concrete, obtained by drilling the soil, in which steel reinforcement is placed in the wells and the concrete mixture is poured.
- Screw piles, which are a steel pipe with a screw part, the immersion of which is carried out by screwing.
Let us consider in more detail bored structures, as the most widely used, in demand in construction. According to the method of construction, they are divided into drilled and stuffed piles.
Pile foundations should be designed based on the results of engineering and geodetic, engineering and geological, engineering and hydrometeorological surveys of the construction site
Stuffed supports
Their arrangement is carried out in the following ways:
- by immersion in the ground of special pipes with a temporarily closed end, which are gradually removed as the concrete solution is poured;
- the method of vibrating compaction of the concrete solution, which is filled with a pre-prepared well;
- by filling with concrete a cone-shaped or pyramidal well, previously stamped in the ground.
Drilling support elements
The designs of bored piles differ in the way they are formed, which provides for:
- Concreting of wells made in various types of soils located both above the level ground water without strengthening the walls, and below, with fixing the walls with a clay solution or casing pipes.
- Use of a prefabricated vibrating core for compacting round concrete supports.
- Compaction of crushed stone fed into the face.
- Formation in the supporting part of the cavity obtained by the method of explosion, followed by filling with a concrete mixture.
- Injection injection of a cement-sand composition or concrete mortar into a pre-drilled cavity with a diameter of 15–25 cm.
Drilling a well for bored piles
Preparatory activities
According to the provisions of SNiP, before installing bored piles, engineering surveys should be carried out to determine the design forces that the foundation will take. Pile foundations are developed based on the results of the following types of surveys carried out at the building site:
- geological;
- hydrometeorological;
- geodetic.
The features of the construction object, the forces acting on the foundation, the features of the operation of the structure are also taken into account. Only after that, according to SNiP, the type of stuffed foundation, the dimensions of the supports, and the method of their arrangement are determined. The design organization is responsible for the reliability of the survey results.
Drilling and ramming operations are preceded by the planning of the construction zone at a given level. Then marking is carried out, coordinates are fixed in the conditions of the construction site.
The locations of bored supports are documented by a special act containing information on tying piles to elevations.
The exact value of the bearing capacity of a bored pile is calculated using a formula that takes into account several parameters
Influence of climatic factors
According to the recommendation of SNiP, pile driving in wet soils is carried out if the temperature environment not colder than -10 degrees Celsius. When the temperature changes down from the specified value, it is necessary to take a set of measures aimed at protecting the fresh composition from freezing, as well as ensuring the possibility of uninterrupted operation of the drilling equipment. Special requirements for the implementation of construction activities must be indicated by the design organization in a special project.
Reinforcement specifics
According to the requirements of building codes and regulations, when equipping pile foundations, it is necessary to ensure their reinforcement by reinforcement. For this, strong steel reinforcement is used, united by a single frame by welding.
The spatial structure consists of reinforcement bars, located at equal intervals along the perimeter of the circle. With a rod diameter of more than 1.8 cm, the frame must include more than six longitudinal rods, the distance between which should not be less than 400 millimeters. It is preferable to use AIII reinforcing steel for longitudinal bars.
Reinforcement of piles is performed with vertical rods of a periodic profile (diameter 12-14 mm)
Protection of the steel reinforcement cage from the damaging effects of corrosion is achieved by maintaining a protective concrete layer. Ensuring the immobility of the reinforcement frame is provided by plastic tubes, the dimensions of which are:
- diameter - 9 cm;
- length - 7 cm.
Work area requirements
Before starting bored activities, it is necessary to perform a set of works aimed at preparing the construction site:
- Install fences in the work area in accordance with the construction master plan.
- Disable, transfer from the event area all communications above and below the zero mark.
- Free the place of work from temporary structures, unnecessary buildings.
- Remove and lay down the vegetative surface of the soil in certain places.
- In accordance with the marks indicated in the project, the flatness of the base should be ensured.
- Carry out drainage or water reduction.
- Cover the surface of the site with a crushed stone pillow, on top of which it is necessary to lay the slabs.
- The area of the construction zone should allow the placement of the kit technological devices(drilling rig, concrete pump, concrete delivery and unloading equipment) and have convenient access roads.
Calculations of the structures of piles of all types should be made for the impact of loads transferred to them from a building or structure
Bored activities are carried out after controlling the coordinates of the prepared site and checking the location of the axes of the supports of the future foundation.
Building codes and regulations provide for the use of automobile concrete mixers and self-propelled equipment for its transportation. It is allowed to deliver pre-mixed dry components to the work area, adding water before starting concreting.
Technology features
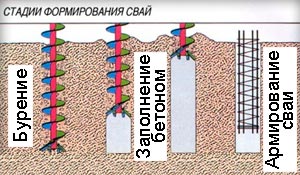
How, according to GOST, are bored supports arranged? What are the steps in the manufacturing process? In general, the implementation of the support involves two main stages:
- directly drilling in the soil of the cavity;
- filling the resulting well with concrete mortar with preliminary installation of the reinforcement frame.
There is a feature provided by building codes. The well and mud have a limited period of use. Over time, their quality decreases. The cavity together with the solution becomes unsuitable for further work. Therefore, GOST regulates a period limited to 8 hours between the completion of drilling and concreting.
All calculations of piles, pile foundations and their foundations should be performed using the calculated values of the characteristics of materials and soils
The supporting structures are pre-drilled, according to the project, wells with a reinforcing cage installed. Before pouring the concrete solution, the cavity is compacted, sealed with a clay solution that prevents soil collapses, and then the volume is filled with concrete. It is allowed to use casing pipes or pour concrete directly into the well.
The manufacture and installation of supports are carried out according to the algorithm provided for by the standards:
- First, the impact rig or drilling machine is installed on the drilling site.
- Drilling activities are carried out that form a well with certain dimensions (diameter, depth). The expansion at the bottom of the base of the structure allows you to increase the bearing capacity of the future support.
- A clay solution is introduced, which acts hydrostatically on the walls, eliminating the spalling of the well surface.
- Drilling products are carried away by the fluid flow and are extracted to the zero mark.
- Using lifting equipment, a reinforcement frame is placed in the prepared well, which can be placed along the entire height of the pile or near the surface. It all depends on the project effort.
- The reinforcing cage is fixed with non-metallic stops that provide a protective layer.
- The cavity is filled with concrete mortar delivered by an auto-concrete mixer. The concreting process, according to SNiP, should not exceed three hours.
- A special installation removes the casing elements.
- The drilling and crane equipment moves to the next point of work in accordance with the scheme given in the standard.
Quality control
All materials delivered to the work area are subject to incoming control. This applies to casing pipes, reinforcing reinforcement cages and other raw materials. Visual control is carried out, as well as the information specified in the accompanying documentation, passports, certificates. The concrete mixture delivered from the manufacturer is controlled visually and according to the documents of the concrete plant.
When performing bored activities, acceptance and operational control is carried out at all stages. Future pile foundations are checked for compliance with the coordinates of the alignment axes. After completion of drilling activities, the actual dimensions are compared with the parameters provided for by the project.
The material of the article covers the general provisions of building codes and regulations, the strict observance of which guarantees the quality of work. Guided by SNiP, pile driving will be carried out at a high technical level.
On weak soils (peat, marshland), as well as in cities, beaten piles are used for the construction of foundations. Their use is due to the specifics of the soil: the construction of other foundations is either technically impossible or economically impractical.
Bored piles are a method of driving piles, which consists of drilling a well and pouring it with concrete. Concreting is carried out using metal reinforcement. In private suburban construction, depending on the soil, formwork may or may not be installed (on stable soils, where there is no risk of shedding inside the walls of the well, formwork is not needed). In larger construction, casing pipes are used for the same purpose.
Where applicable
- In urban areas where other piling methods may have a dynamic effect on surrounding structures.
- In heavily wetlands or other types of soft soils where the incompressible layer is too deep
- When building houses on steep terrain.
- For building heavy industrial buildings and objects.
- It is not economically feasible to erect such a foundation as a support for light frame or wooden buildings.
Classification and design of bored piles
The most complete classification bored piles contains the Code of Rules under the designation SP 50-102-2003. He describes the design different types foundations based on piles.
Stuffed piles by manufacturing method are divided into:
- arranged by immersion of inventory pipes, at the end of which there is a metal "shoe" or a pointed plug made of concrete, which remain in the well, and the pipe is removed when the internal space of the pipes is gradually filled with concrete;
- arranged by vibro-stamping in the well of the laid concrete, which is compacted with a pipe pointed at the end with a vibrator;
- a conical or pyramidal well is stamped in the ground and filled with concrete mortar.

Fig.1 Bored pile
By device boreholes are divided into:
- uniform section and with expansion from below;
- round section using a vibrocore of several sections;
- with compaction of the face with a rammer of large crushed stone;
- with a camouflage heel (expansion at the bottom), obtained by an explosion of a charge at the bottom of the well and filled with mortar from above - the cavity after the explosion is filled with concrete mortar pouring from the well;
- borehole with a camouflage heel - an ordinary reinforced concrete pile is immersed into a well with a camouflage cavity filled with non-hardened concrete;
- borehole injection (injection) - a concrete fine-grained mortar based on cement and stone screenings is injected into a small-diameter well;
![]()
Rice. 2 Driving of bored piles
- borehole injection - after drilling a well, a concrete solution is fed under pressure through a hollow auger and the auger is gradually removed;
- injection piles of the RIT type - the soil is compacted using the technology of pulsed discharges;
- pillar piles - they drill wells with or without widening and alternately lay a mortar of cement and sand and concrete prismatic or cylindrical elements.
Technology of the device of bored piles
For the manufacture of many designs of bored piles, only a few methods are used:
- with the help of a continuous screw (CPS), which has a cavity inside for supplying a concrete solution to the lowest point of the well;
- with wall protection by a casing pipe, loaded and retrieved by a vibrator;
- with protection against sprinkling of walls by creating counterpressure with bentonite mortar;
- using a casing pipe submerged by a "dreytailer".
The NPSh method is used in "durable", non-crumbling soils, for example, in clayey ones. A well is drilled along it with an auger having a pipe along its entire length and a soil-removing spiral welded to this pipe. The internal cavity is closed at the end with a plug, which has the function of a check valve and prevents the drilled soil from entering the cavity.
When rotating, the auger crushes the soil with its working drilling part and delivers it to the surface along the auger spiral.
At the desired depth, a concrete solution is fed into the internal cavity under pressure, which opens the plug and begins to fill the well. As it is filled, the screw is raised to the surface, rotating it or pulling it out without rotation. The well filled with mortar is left for temporary exposure for concrete to gain strength.
Rice. 3Stages of pile formation
If the pile is reinforced concrete, then a reinforcing cage is immersed into the well with concrete using a vibrator.
Casing Technology used in flooded soils, and this pipe protects the well:
- from the collapse of the walls during drilling;
- from the pressure of the soil layers around the well;
- from the collapse of the reinforcing cage during its introduction.
The casing pipe is immersed in separate sections and also removed section by section. Immersion is carried out either by mechanical indentation, or by indentation with vibration, or by "dreytail", i.e. by indentation with rotation.
The choice of one of these methods is determined by the characteristics of the soils traversed during drilling of the well and economic characteristics. pile foundation. In most cases, casing pipes are not left in the well. Regulations allowed to leave them only in exceptional cases. For example, with landslide soils on slopes or with a speed of movement of underground flows of more than 200 m per day. In each case, a technical justification must be drawn up for this.
Technology of the device of bored piles with casing pipe
In loose, flooded, landslide and unstable soils, the well is protected by a casing pipe. The drill makes the well equal to the diameter of the casing. The casing pipe under its own weight, or by rotation in the direction opposite to the auger, or by mechanical indentation is immersed into the well to the design depth, the drill and the remaining soil are removed.
Stuffed piles are arranged directly at the construction site, at the site of the future building or structure.
Depending on the method of arranging wells and laying concrete in them, there are two types of stuffed piles:
a) piles for which wells are formed by drilling; In this case, there can be two ways of laying concrete:
b) piles for which holes in the ground are formed by plunging a closed-end steel pipe and the concrete is compacted by frequent tamping using hammer blows on the pipe (often tamped piles) or using vibration from a vibratory driver.
Wall mounting can be done:
1. using a casing pipe (dry method) extracted from the well as concrete is placed, and
Dry way applicable in stable soils; its technology is as follows (Fig. VI.10). Rotary drilling in the ground drills a well of the required diameter and to a given depth. After the well bottom reaches the design mark, if necessary, the lower part of the well is widened with special expanders. After the well is accepted, according to the act, a reinforcing cage is mounted in it and concreted using the vertically moving pipe (VPT) method. As the concrete is laid, the concrete pipe is removed from the well. The concrete mixture is compacted with the help of vibrators mounted on the receiving funnel of the concrete pipe.
2. no casing (wet method) when concrete is laid using a slurry (called bentonite);
Without casing it is also possible to arrange bored piles (Fig. VI. 11). Here, as a formwork that prevents the collapse of the walls of the well, a clay solution is used, which enters the well through a hollow drill rod. Due to the hydrostatic pressure exerted by this solution, the density of which is 1.2 ... 1.3 g / cm 3, piles are arranged without casing pipes. The clay solution is prepared at the work site mainly from bentonite clays, and as it is drilled, it is injected into the well. Rising along the well along its walls, the clay solution enters the sump, from where it is returned by the pump to the drill rod for further circulation. Then a reinforcing cage is installed in the well. The concrete mixture is fed using a vibrobunker with a concrete pipe, which is lowered into the well. The vibrated concrete mixture, entering the well, displaces the clay solution. As the well is filled with concrete mix, the concrete conduit is removed.

The considered method of fastening the walls of wells is the simplest. However, it is not reliable enough and is very laborious in the production of work in winter.
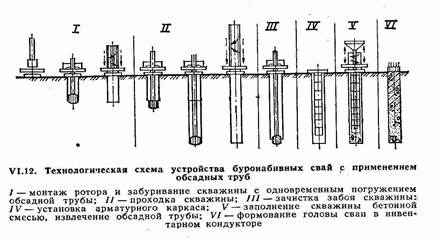
The device of bored piles with fastening of the walls of wells with casing pipes(Fig. VI. 12) is possible in any geological and hydrogeological conditions. Casing pipes can be left in the ground or removed from wells during the pile making process (inventory pipes). Sections of casing pipes are usually connected by joints of a special design or by welding. Casing pipes are immersed in the process of drilling a well with hydraulic jacks, as well as by driving a pipe into the ground or by vibration immersion. Wells are drilled in a rotary or percussive way with special installations.
At shock drilling, the casing pipe is immersed in the ground as the well is developed. At the same time, individual sections of casing pipes are increased as necessary.
At rotational In the drilling method, a leader well is first drilled to the length of the casing pipe section, after which the casing pipe is lowered into the well. Then the next section of the well is drilled, after which the next section of the casing pipe is built up and lowered into the well. These operations are repeated until the well is drilled to the design level.
After cleaning the bottomhole and installing a reinforcing cage in the well, the well is concreted using the VPT method. As the well is filled with concrete mixture, the inventory casing is removed. At the same time, a special system of jacks mounted on the unit imparts a reciprocating and rotational movement to the casing pipe, additionally compacting the concrete mixture. Upon completion of concreting, the pile head is molded in a special inventory jig.
Stuffed piles are often made with a broadened lower part - the fifth. The widening is done with special drills, as well as by exploding an explosive (camouflage piles). The widening is done to increase the bearing capacity of the pile.
Camouflage piles are made as follows (Fig. VI. 13). First, a well is drilled, a casing pipe is lowered into it. An explosive is placed at the bottom of the well, which is covered from above with a layer of 0.7 ... 1 m of cast concrete. The resulting concrete plug is needed so that the energy of the explosion is directed to the formation of a cavity in the ground. The cavity is then filled with concrete and the pile is concreted in the usual way.
Often-tamped piles are arranged by driving casing pipes resting on a metal tip. Then, in the cavity formed by the casing, a reinforced (or non-reinforced) pile is arranged.
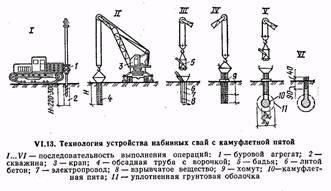
Often-tamped piles (Fig. VI. 14) are arranged using a special pile driver. A hammer and a casing are lifted onto the headframe with a winch, which has a head in the upper part. A metal shoe with a resin rope is placed on the lower end of the casing pipe to prevent water from entering the pipe. Under the action of hammer blows, the casing pipe is immersed to the design mark. While plunging, the pipe pushes the soil particles apart and compacts it. Then the hammer is raised and the reinforcing cage is lowered into the pipe cavity (if the piles are reinforced). Concrete mixture with a cone draft of 8...10 cm is fed from the vibratory tub through a funnel into the cavity of the casing pipe.
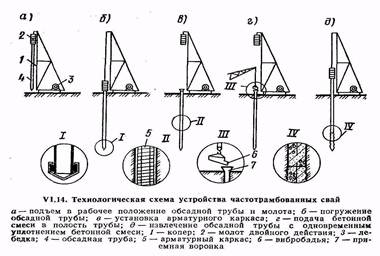
In parallel with the laying of the mixture, the casing pipe is removed (pulled out) by a small amount and again upset with a hammer to compact the concrete, while the metal shoe remains at the base of the pile.
AT last years began to arrange soil-concrete piles, for which they use crane-drilling machines with a hollow drill rod, which has a mixing drill with cutting and mixing blades at the end. A water-cement slurry produced in a mortar mixer is injected through the rods with a mortar pump. The mixing drill, during reverse rotation and extraction, compacts the soil saturated with water-cement emulsion in layers. As a result, a soil-concrete pile is formed, made on site without excavation. On fig. U1.15 shows a schematic diagram of the arrangement of soil-filled piles.




