Heating of roofs and drains: various schemes of systems. Roof heating: system and installation. Heating of a flat and soft roof.
>
Heating of roofs, gutters and roofs

Raychem - a recognized leader in the field of production heating cables and components for roof heating systems.
- Reliable roof protection from ice damage
- There is no formation of icicles or snow from the roofs
- Provides protection for buildings and people
- Maintenance free
The anti-icing system for heating roofs and roof elements, often called “Icicle-Free Roof” or “Warm Roof”, solves the following particular electrical heating tasks:
|
|
Our cables have been successfully working on the roofs of Moscow and Russia for more than 10 years, causing positive feedback from protection maintenance services. Our systems successfully carry out heating of roofs from icicles and frost on the buildings of the Moscow House of Music, the Grand Kremlin Palace, buildings of hundreds of museums and administrative buildings, more than ten thousand private houses and cottages.



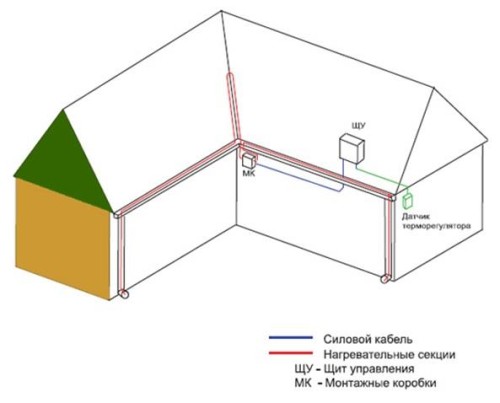
It is very important that the elements cable system heating (KSO) ensured the escort of melt water from the roof to the ground and further into the drainage system. Heating of drainage systems is also solved by cable heating.
Samreg LLC specialists have extensive experience in designing, supplying and installing anti-icing and roof heating systems using the most reliable self-regulating heating cable GM2X And GM2X-C, as well as modern resistive cables specially designed for roof heating.
Snow melters on the roof - the task of creating zones free of snow and ice on a flat serviced roof - is easily solved by a self-regulating cable EM2-XR, EM2-R, with the help of these heating tapes it is possible to create zones with a specific design electric heating power up to 600 W/m, which ensures intensive melting of snow and ice in heated areas.
Usually any anti-icing system for roof heating - Ice Stop system, Gutter gard, Gutter melt, Teploskat, Warm slope, Warm roof, etc. consists of the following elements:
heating part
- heating cable, end and connecting terminations, cable fastening system on the roof and gutters.
Power supply system
- power supply route, its fastening system, boxes and couplings for connecting the route to the heating part.
Control and protection board
.
Temperature controller or weather station with weather sensors
.
Distinctive features of Anti-Ice systems using heaters are as follows:
- reliability and long service life quality of heating cables (this is noticeable even during visual inspection and comparison of heating elements)
- branded components that allow you to mount systems without damage roofing and drains
- availability of a specialized service center of Samreg LLC, which performs a full range of work on the heating cable for the convenience of the Customer or Dealer, including installation, design, training, maintenance and repair of accidental damage to the system, electrical and thermal measurements.
Low energy consumption for roof heating
1. Choosing a self-regulating cable for heating roofs and gutters
2. Calculation of the length of the heating cable for heating the roof and gutters
- The heating cable is installed in the gutter with straight cable sections.
- The length of the heating cable must be adjusted according to the location of the gutters and the geographic location of the roof
- Wide or rectangular gutters and parapets may require multiple runs of heating cable
gutter length
+ downpipe length
+ 1 m per power supply
+ 1 m in soil (max. freezing depth)
__________________________________
= required heating cable length
3. Electrical protection devices for roof heating
- The number and rating of circuit breakers is determined by the total length of the heating cable
- It is necessary to use an RCD (residual current device for earth leakage current) at 30 mA; Max. 500 m of heating cable for RCD
- The power supply to the heating cables must be carried out in accordance with local standards and technical regulations.
- The power supply to the heating cables must be carried out by a certified installer.
- It is necessary to use circuit breakers type "C"
Max. roof heating circuit length based on a minimum start temperature of -10 °C, 230 VAC. current.
| GM-2X | GM-2X-C | 8BTV-2-CT | |
| 6 A | 25 m | 15 m | 25 m |
| 10 A | 40 m | 25 m | 40 m |
| 13 A | 50 m | 35 m | 50 m |
| 16 A | 60 m | 40 m | 60 m |
| 20 A | 80 m | 50 m | 80 m |
Winter and early spring is a special period, which is characterized by icicles hanging from the slopes of the roofs. And they look pretty menacing. They can harm you. Even worse is when the entire gutter freezes over. In most cases, the system will need to change or replace a single element. But so that in winter the drainage system does not freeze, and dangerous icicles do not hang from the slopes, there is a simple solution - a drainage heating system. Thanks to her, icing on the roof and gutters is not scary.
But, why does ice form on overhangs and in the drain? How is the roof heating system arranged? What are its constituent parts? We learn all this from the article.
Why does ice appear
Let's start at the root of the problem. Icicles appear for a reason. This is due to at least two factors. What exactly?

These are the two main reasons for the formation of ice. To solve this problem, you will have to do the heating of the roof and gutters. And this means that they will constantly maintain a positive temperature, so the liquid will not freeze. What are roof and gutter heating systems? Let's find out.
What is the heating of the drainage system and the roof slope
What is the main element that does all the heating work? If we talk about warming the house, then everything is clear, there are pipes and radiators. What insulates gutters? This is a heating cable for gutters and roofs. It is laid around the entire perimeter of the gutters, pipes and overhang so that it maintains their temperature. It is noteworthy that such heating wires are used not only for heating the roof, but also for plumbing, fire safety systems, for fan pipes, etc.

What is the essence of insulation? The heating cable for the roof is mounted in all elements of the drain. It performs heating due to the electrical energy that comes from the outlet. In order for the system to work properly, there are many additional elements, which we will talk about later. They measure the temperature outside, start or stop heating, act as fuses, etc. Electricity flows through the wire, which heats it, giving out the necessary heat. There are two different types cables that can be used to insulate the roof and drain.

Types of heating cables for heating the drainage system
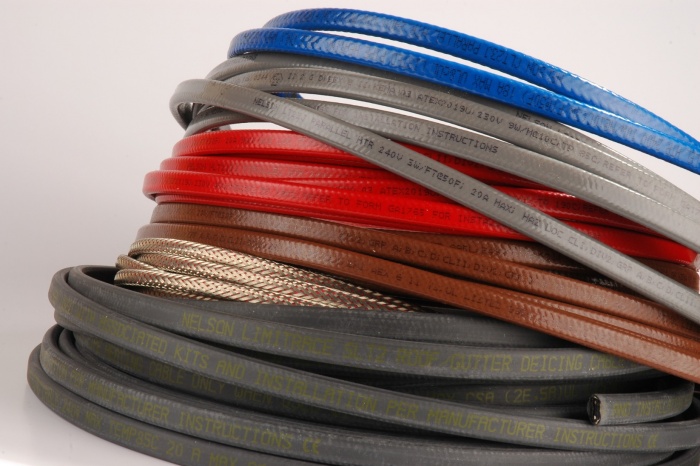
If this is the first time you hear about heating wires, then there are only two types. They are strikingly different from each other, but both the first and the second type successfully do their job. What are these cables?
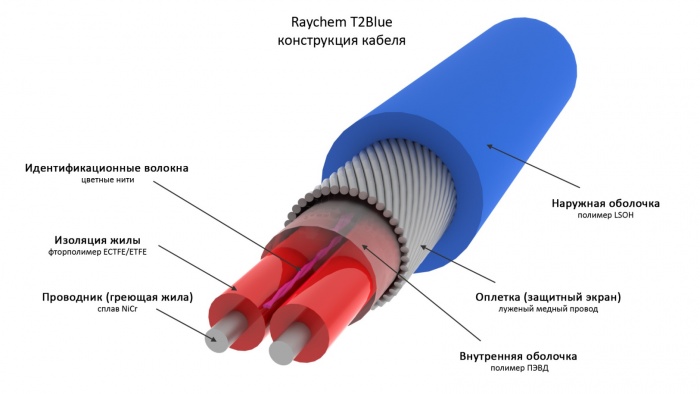
What is the difference between them? Very big. If we talk about the resistive type, then in life it looks like a simple wire that has an inner metal core (conductor) and protective insulation. Its characteristic lies in the fact that it has a constant resistance, the same heating temperature in all areas and an unchanging power. This is both a plus and a big minus. It is heated by means of a closed circuit of electricity.
Note! The wire can be single-core or double-core.
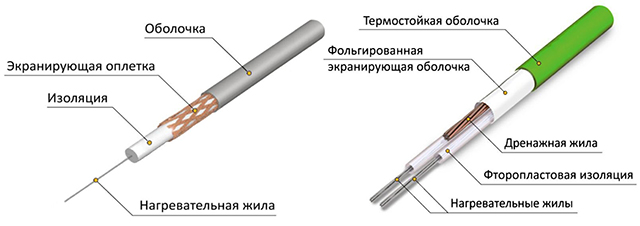
But the self-regulating heating cable works differently. It is not so simple, but rather high-tech. It consists of copper conductors, thermoplastic elastomer insulation, protective braid and basic insulation. But a feature of the heating element is its semi-conductive self-regulating matrix. It interacts with the temperature outside, and, depending on it, changes the resistance of the wire. As a result, the degree of heating in a particular area also changes. But what does it give? What heating cable for a drain to choose?
Resistive or self-regulating
We have looked at two types of cables, but which one is better, how do they differ and what are their advantages? Resistive cable is not exactly economical. The thing is that the temperature is always the same in all areas, which increases energy consumption. It costs much less than a self-regulating cable and has the following advantages:
- Fast heating.
- High heat dissipation.
- Able to provide a constant value of the power of the heating system.
- Has a low price.
- Requires low starting current.

But still, there are also enough shortcomings. And they are quite serious:
- Large consumption of electrical energy.
- Has a short service life.
- In places where there is an overlap, the cable may burn out.
Together, this negatively affects the performance of the cable. Although it is cheaper than self-regulating, it will last less, it can burn out, and the money you spend on heating will be much more. And what about a self-regulating cable for a heating system?
Its main advantage is the ability to control the air temperature outside the house, adjusting its temperature regime. This means that he will not constantly waste thermal energy on unnecessary heating of gutters and roofs. It uses all energy purposefully and economically. The benefits are clear:
- economical energy consumption;
- ease of installation;
- increased resistance to burnout;
- high level of isolation;
- long service life;
- versatility, it can be used for any type of roof with any coating.

As for the shortcomings, there are few of them:
- High price.
- Slow heating.
- Requires high starting current.
Most prefer to use self-regulating cable for heating drains. But in order to save money, you can consider combining one and the other type of cable. But, without additional elements of the heating system, the cables would be useless. What are these elements?
Complete set of drainage heating system
To perform heating of gutters, you need to have a set of components:
- Fasteners.
- Switchboard.
- Distribution network components.
- Temperature controller.
But, that's not all. If we talk about the control panel, then it includes:
- circuit breaker, consisting of three phases;
- a device that forcibly turns off the system (RCD);
- four-pole contactor;
- single-pole circuit breakers for each phase;
- warning lamp.

If we talk about the elements of the distribution network, then there are 4 of them: power cables, from which the heating wires are powered, signal cables used to connect the thermostat sensor to the control panel, mounting boxes, couplings that allow tight connection of cables.

The thermostat is a sensor that regulates the entire heating system. It can control by temperature sensor or weather station. The temperature sensor starts the heating system at the specified temperatures. It measures the air temperature, and if it falls below the programmed value, it turns on the system, and vice versa. But the weather station not only determines the temperature, but also measures precipitation and the process of snow melting on the roof. It's all about the humidity sensor.

If cable heating is carried out by means of a temperature sensor, then the owner will need to start and turn off the heating system himself when there is precipitation, and when there is none. If a weather station is used, then the whole process is fully automated. But if you compare the price, then it is more profitable to start the burning on your own using a temperature sensor. Now you know how roof heating works. Cables in one or two strands are mounted in gutters, pipes and on the roof slope. The system is assembled and everything is put into operation.
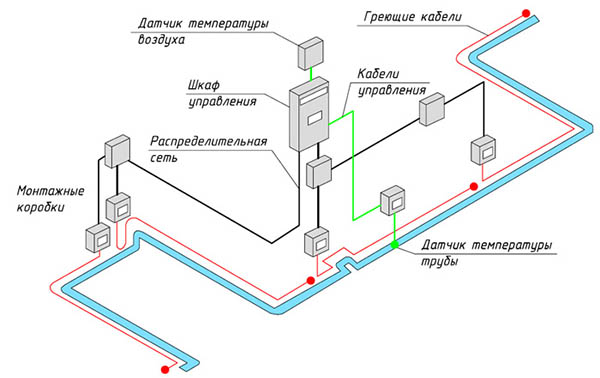
- To save money and increase system efficiency, combine resistive and self-regulating heating elements. For the roof, use the resistive type, and for the gutter system, use the self-adjusting type.
- It is necessary to fix the cable in pipes and gutters with a mounting tape with a maximum thickness. This will ensure good fastening.
- The mounting pitch of the resistive cable is 250 mm, and the self-regulating cable is 500 mm.
- All cables must be connected using heat shrink tubing, as water ingress is unacceptable. Joints must be well insulated.
- The roof cannot be drilled. Fasten the cable on the roof with a sealed mounting tape.
- All sharp objects near the cable must be removed.
- It is better if all the components of the heating system are from the same manufacturer.
Conclusion
If you do not want icicles or frost on the roof to damage both you and your family, as well as the elements of the roof and drain, then the heating device will solve all your problems.
Have you ever noticed how, in the Russian climate, everyone carefully chooses a parking place, bypasses some sidewalks and cautiously walks up the stairs? The reason is that icicles are “too expensive” for people and hundreds of cars and people are affected every year because of them. In addition, ice growths deform the roof itself, the facade of buildings, requiring major repairs in just a few years.
How to ensure the safety of the building in any weather? How to protect people's lives? How to improve the comfort of building operation in winter?
If you walk through the city blocks on a February day and pay attention to the roofs of buildings, you can see an interesting picture: large icicles and snow caps hang menacingly on the eaves and drains of some houses, while on other roofs this is not the case. The reason lies in the fact that the latter have electric heating of the roof.
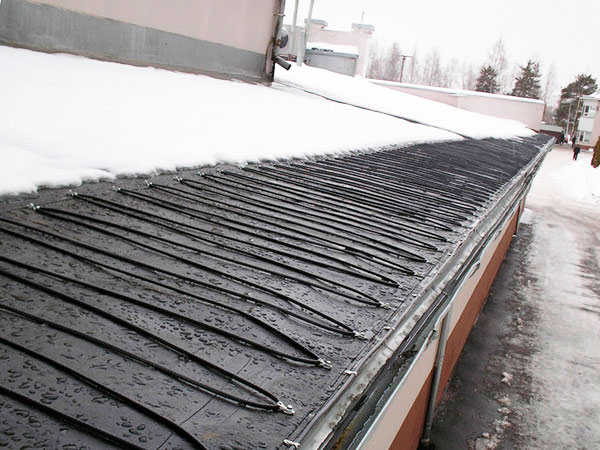 |
In the gutters and pipes of such a roof, and sometimes along the cornices and along the edge of the roof, a heating cable is laid, which allows the melt water to drain through the drainage system.
Thus, pipes and gutters remain free of ice and snow, the risk of their breakage is prevented, as well as the risk of icicles falling from roofs onto pedestrians and vehicles under the house.
BENEFITS OF ROOF HEATING
- Ensuring the safety of life and health of people.
- The facade of the building is not destroyed, the roof does not leak or deteriorate.
- The ability to regulate the cost of electricity due to the choice of various modes of operation of the heating system, as well as the possibility of installing various types heating cables.
- The high efficiency of the system makes it possible to completely remove frost even with a significant level of precipitation.
- The rooftop heating system is truly durable.
- Minimal human intervention in the process of system maintenance (due to the presence of "smart" temperature controllers in the system).
Of course, the installation of a roof heating system requires certain costs, especially since it requires the involvement of a qualified company to install it. But the solution to these problems more than cover the price of heating the roof even for one season.
TYPES OF CABLES USED IN ROOF HEATING SYSTEMS
Two types of cable are used for roof heating systems:
- Resistive cable, which is a metal core covered with a layer of insulation. When current flows through it, the cable heats up uniformly to the specified temperature. The heating level is fixed by sensors connected to the thermostat.
- Self-regulating cable, which is able to change the resistance depending on the ambient temperature in different sections of the circuit. For example, areas of the roof that are in the shade will be heated more intensively than those in the sun.
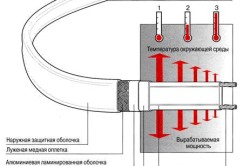
Features of self-regulating cable
The basis of a self-regulating cable is a semiconductor matrix enclosed between two conductive copper conductors. Due to flow through the matrix electric current and its heating, the resistance of the matrix increases. When a “cold” self-regulating cable is turned on, current flows through it, the matrix heats up, the resistance increases, and the current decreases. Thus, at a certain temperature, a balance occurs between cable heating and power consumption.
The colder the environment around the cable, the more power it releases, and vice versa. The same cable in different sections may have different temperatures. This is what self-regulatory effect.
The main advantages of a self-regulating cable:
- Unlike resistive cables, self-regulating cable can be cut to any length.
- Versatility - the cable has a wide range of applications: from heating a freezing water supply pipe to maintaining the temperature of an oil pipeline or a tank with fuel oil. These cables are widely used in anti-icing systems for roofs and drainage systems.
- Simple and quick installation - the cable can be cut anywhere from 20 cm to tens of meters (cutting and coupling with the cold end of the heating section can be done directly on the site), bends easily (minimum bending radius 5 cm); immediately after connecting the cable can be operated.
- Low power consumption - power consumption directly depends on the temperature of the environment in which the cable is located. If the temperature is above zero, then the consumption is automatically reduced by 30 - 80% of the nominal.
- Environmental friendliness and safety - there are no harmful emissions in environment, the sheath of some cable models is resistant to ultraviolet rays; the cable can cross itself, while the risk of its failure is minimal.
- Mobility - it is possible to transfer the cable to another place, lengthen and shorten sections without loss of quality.
- Durability - service life of cables up to 15 years. Even if the cable is damaged, for example, during its installation by unskilled specialists, power loss is possible in certain sections of the cable, while the operability of the entire heating section is maintained.
ROOF HEATING: DESIGN AND INSTALLATION OF HEATING SYSTEMS
The heating cable is not placed on the entire area of the facility, but only in certain areas in places where ice and snow are most likely to accumulate. Proper design allows you to protect the slopes and edges of the roof, downpipes, gutters and flumes and other elements of the spillway. In addition, cable heating of terraces, porches and heating of pedestrian crossings and steps is possible.
The whole process of creating a "roof heating" system can be divided into the following stages:
- communication with the Customer and clarification of his needs and wishes, recommendations of the specialists of the KaskadStroy company for heating a particular area on the roof;
- filling in the questionnaire for the project and agreeing the terms of reference for the performance of work with the Customer;
- execution of a technical and commercial proposal for the Customer
- calculation and design of the heating system (if necessary, a heat-technical calculation of the heating system is performed, justifying the need to use a certain power for a specific heated zone);
- clarification and approval of the cost of the heating system according to the design specification;
- production of system elements in the factory, delivery of the "roof heating" system to the facility;
- assembly of cable sections (in the workshop or directly at the facility), laying and fixing the sections;
- tracing power and control cables, installation of control cabinet and junction boxes;
- commissioning works.
ROOF HEATING INSTALLATION PRICE CAN BE REDUCED!
At correct installation and operation of the system will serve for decades. Of course, every year the cost of operating roof heating will include operating costs - the cost of electricity spent on heating and the cost of routine inspections before and after the winter season. But even these costs do not make the installation of a roof heating system unprofitable.
In addition, if you go for the initial investment and install a system with a full range of sensors and a weather station, then subsequent costs can be significantly reduced. These costs will pay off in one or two seasons.
There is another way to save energy and increase safety in the roof heating system - this is the use of a self-regulating heating cable. Although its price is several times higher than conventional resistive cable, it is increasingly found on the rooftops of our cities due to its obvious benefits.
For the properties of the cable, see the information titled "self-regulating heating cable for roof heating".
Icing of roofs and gutters is a phenomenon that is often observed in winter, especially when there are significant temperature fluctuations. The fallen snow melts at positive temperatures, then the temperature drops, and as a result, the formation of ice blocks in the funnels of drainpipes is observed, and icicles form along the edges of the roof. With a slight increase in air temperature, the process of melting the formed ice cannot be controlled. Water does not flow into the drainpipe, but straight from the roof, falling under the roof slope, onto the walls, and it may flow into various seams. Naturally, this brings tangible damage to the building. Roof heating can remove the consequences of these phenomena.
Heating the roof with a heating cable prevents the accumulation of snow and the formation of icicles in winter time on roof edges and gutters.
To eliminate this phenomenon, it is necessary to install a heating system on the roof and gutter nodes of the building, which in the future will help to avoid the formation of frozen ice. All roof and gutter heating systems operate automatically. The principle of operation is based on the heating of an electric current conductor at certain temperatures, the heating process is controlled by a control unit. As a rule, the system is switched off at +5 degrees of heat and -10 degrees of frost, since it is in this range of temperature changes that ice forms, and heating of the roof and gutters solves this problem.
List of materials and tools for installing a roof heating system
![]()
- pliers equipped with side cutters;
- Screwdriver Set;
- screwdriver;
- pincers for crimping contacts;
- perforator;
- a set of clips for the heating cable and wiring cables;
- dowels;
- hammer;
- adhesive sealant;
- ladder;
- set of safety equipment.
Basic principles of the roof heating system
Heating includes the technology of special placement of a special thermal cable on the roof and in spillways and its connection to control controllers. Thermal cables are used in two types. Their operating principle is different. The first type is a resistive cable. It is a conductor of electric current, coated with a special composition. The conductor during the passage of current heats up due to the calculated resistance. The heat dissipation of the resistive cable will be the same along the entire length of the installed heating system. The second type is a self-regulating cable. The global difference from resistive is that
that such a cable is able to change its resistance depending on the temperature at different places on the roof.
In other words, a self-regulating cable generates more heat when it is in colder places, such as a rooftop covered with snow, windward, and heavy accumulation of melted ice. This approach ultimately leads to both energy savings and an increase in the efficiency of the installed roof and drain heating system.
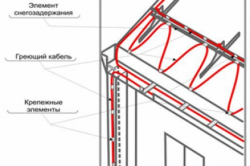
There are certain technological conditions and standards for the installation of heating cables on the roof and in gutters. Cable installation should be in places where there is the greatest contact with ice and snow masses in order to carry out maximum heating. This achieves the highest efficiency. To do this, it is necessary to calculate the places of the roof where the greatest accumulations of ice and snow occur. As often happens in practice, the installation of the heating system is carried out along the perimeter of the roof, while capturing such places as the joints of the drain lines, the entry points of the gutters into the downpipe. In complex geometric roof structures, heating lines are installed not only along the perimeter, but also at the intersection of the planes of the roof slopes and in the so-called valleys.
Installation on different types of roof
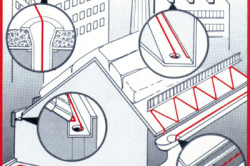
Depending on the type of roof and, accordingly, the places "weak" to icing, the heating cable is laid in different ways.
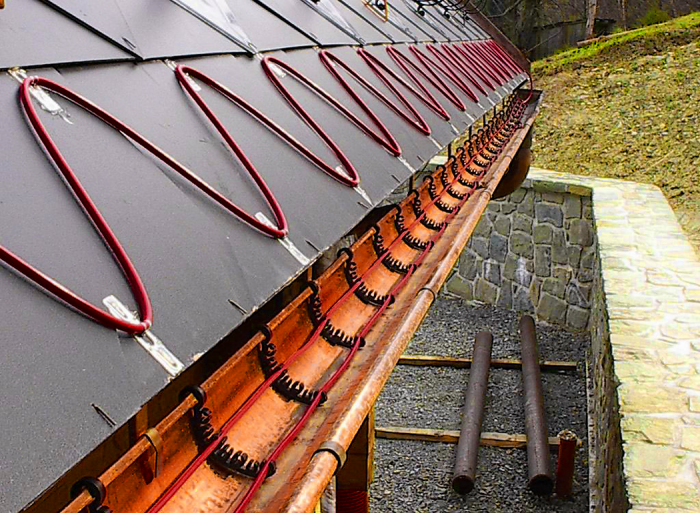
High-quality heating is possible with the correct location of the wire. The cable, as a rule, is laid in a snake, the height of its laying is usually equal to the length of the roof slope to the intersection with the plane of the walls and plus 20 cm. In such places, the most intensive accumulation of melted ice occurs. The cable is laid in increments of 50 or 60 cm. Here you need to proceed from the climatic zone. In places where the temperature changes above or below zero degrees very often, it is necessary to reduce the laying step, in which case the heating will be more efficient. For the free passage of melt water, the cable must be laid in gutters and gutters around the perimeter of the building. This method is applicable for one, gable roof with a soft finish.
For a metal roof, the following method of laying heating elements is typical. The wire is laid on each side of the seam of metal sheets, then passed through the gutters to the second seam and beyond. The cable allowance along the seam is approximately equal to the distance from the roof slope to the intersection with the plane of the walls and plus 30 cm.
The heating of the roof and drains with a flat surface is carried out by placing the wire around the perimeter and in the waste inclined planes. In sloping roof options for buildings where gutters are not provided, the method of loop-like placement of the cable is used with an allowance for the edge of 7 cm.
Ice accumulations also form in valleys, that is, in the inner corners of the intersection of a sloping roof, so they also need heating.
Methods for fastening the heat-producing core are selected depending on the type of roofing material. On soft roofs mechanical way fastening with clips that are nailed to the surface. The joints are treated with sealant. About 50-55 clips will be needed on the side of the roof with a length of about 10 meters, when laying in a "snake" way.
Mounting with glue is also possible. On a metal roof, the installation of the wire is carried out by gluing staples with special glue. 5 staples are required for each seam. With the glue method, it is important to pay attention to the quality of the glue and follow the technology of its use, due to the fact that ice is especially strong on metal roofs and the heating conductor must be securely fixed. Fastening brackets with nails and screws to a metal roof is rarely used, due to the direct impact on the roofing material and the violation of the anti-corrosion coating.

In gutters less than 15 cm wide, the wire is placed without rigid fixation; in wider gutters, it is recommended to place two cores separated by inserts. Directly into the drain or funnel, the core must be lowered by 30-40 cm to prevent ice accumulation, since freezing of drains renders the entire system of melt water runoff unusable.
Features of the choice of control automation
Electrical installation has several types. The choice of a connection scheme through an automatic type humidity and temperature controller is most justified. The system is fully automated thanks to humidity sensors installed in those places on the roof where snow and melted ice most often accumulate. Automatic control unit and self-regulating cables lead to high system efficiency and energy savings. It can be connected via an air sensor or thermostat. Such a system uses only one parameter in its work - air temperature. And the probability of ice formation is no longer taken into account. Manual connection is the cheapest way, but requires constant attention and monitoring of weather conditions.
Roof and gutter heating is a relatively inexpensive and high-quality option for protecting a building in difficult climatic conditions and seasonal weather changes.
Roof without icicles
One of the priorities of the company Antiled Group is the development of systems called "roof without icicles". This is a special set of technical means to get rid of the occurrence of ice. Already now it has established itself as the most effective, and therefore it turned out to be extremely popular in the construction and private sectors (due to the peculiarities of our climate).
Roof icing problem.
 In Russian realities, the need to protect the roof from ice and snow is quite obvious. The problem is especially acute in connection with climate change, when in winter middle lane Russia often began to experience a sharp change in weather: from frosty to thaw and back. In such weather, the snow lying on the roof begins to thaw, and melt water begins to fill the drainage system, as well as drip from the edge of the roof. When the temperature drops below zero, for example at night, the melt water begins to freeze, forming ice plugs in the gutters and pipes, and ice stalactites, or icicles, grow on the edge of the roof. Also, a melted snow mass can move to the edge of the roof, forming a so-called snow cap, which over time can either break off and fall down, or cause icicles to form on the edge of the roof. All these phenomena create certain problems for the safety of people and their property. The roof itself also suffers from this, since ice frozen in the drainpipe can cause the pipe to burst or break from its fasteners and collapse down. The same is true for suspended gutters. If there are valleys on the roof, frozen ice in them can also cause water to leak into the interior during thawing. Roofing is also damaged when ice is knocked off the edge with ice crowbars.
In Russian realities, the need to protect the roof from ice and snow is quite obvious. The problem is especially acute in connection with climate change, when in winter middle lane Russia often began to experience a sharp change in weather: from frosty to thaw and back. In such weather, the snow lying on the roof begins to thaw, and melt water begins to fill the drainage system, as well as drip from the edge of the roof. When the temperature drops below zero, for example at night, the melt water begins to freeze, forming ice plugs in the gutters and pipes, and ice stalactites, or icicles, grow on the edge of the roof. Also, a melted snow mass can move to the edge of the roof, forming a so-called snow cap, which over time can either break off and fall down, or cause icicles to form on the edge of the roof. All these phenomena create certain problems for the safety of people and their property. The roof itself also suffers from this, since ice frozen in the drainpipe can cause the pipe to burst or break from its fasteners and collapse down. The same is true for suspended gutters. If there are valleys on the roof, frozen ice in them can also cause water to leak into the interior during thawing. Roofing is also damaged when ice is knocked off the edge with ice crowbars.
Solution
 To combat the problems of icing roofs in Lately systems such as electric roof heating system, roof heating system, anti-icing system, “Roof without icicles” are gaining popularity. All these are variations of the names of the same system - a cable heating system for the roof. The roof heating system consists of the main element - a heating cable, as well as supply electrical cables, a control panel and junction boxes for connecting the heating cable to the power supply system. Electric heating system controltakes place by controlling the outdoor temperature air (thermostat) or weather station (measures the temperature air and humidity) to switch on / off in a given temperature range to save electricity.
To combat the problems of icing roofs in Lately systems such as electric roof heating system, roof heating system, anti-icing system, “Roof without icicles” are gaining popularity. All these are variations of the names of the same system - a cable heating system for the roof. The roof heating system consists of the main element - a heating cable, as well as supply electrical cables, a control panel and junction boxes for connecting the heating cable to the power supply system. Electric heating system controltakes place by controlling the outdoor temperature air (thermostat) or weather station (measures the temperature air and humidity) to switch on / off in a given temperature range to save electricity.
The principle of operation of the roof heating system 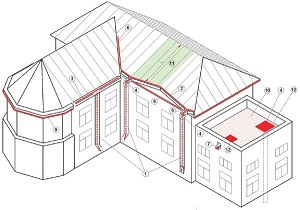 The principle of operation of the electric roof heating system is that the heating cable, mounted in the roof drainage system, heats up under the influence of current, releasing energy in the form of heat into the external environment. Thus, it heats a certain area around itself, preventing the freezing of water in the drainage system and melting the falling snow, preventing it from accumulating on the heated surface. Melt water is discharged from the roof through the drainage system into the drain. This ensures the protection of the drainage system and the roof itself from the above problems.
The principle of operation of the electric roof heating system is that the heating cable, mounted in the roof drainage system, heats up under the influence of current, releasing energy in the form of heat into the external environment. Thus, it heats a certain area around itself, preventing the freezing of water in the drainage system and melting the falling snow, preventing it from accumulating on the heated surface. Melt water is discharged from the roof through the drainage system into the drain. This ensures the protection of the drainage system and the roof itself from the above problems.
Due to the great variety design features roofs and the roofing materials themselves, the design of roof heating systems should be carried out on an individual basis. Such elements of the roof as a valley, pediment, drip, canopy, skylights, etc. should be taken into account. It is also necessary to take into account whether the object has a snow retention system.
Therefore, with independent design, in the absence of experience, you can make a mistake in which the roof heating system will only aggravate the situation at the facility.
With vast and successful experience in design and installation a large number a wide variety of electrical heating systems, knowing all the subtleties of their business, our specialists can accurately calculate the roof heating system, based on all the experience accumulated by our company, taking into account all the nuances that are specific to your specific case.
In the examples below, simple cases are considered when calculating an electric roof heating system.
Flat roof.  The main problem for flat roofs in winter is the freezing of drain funnels. As a rule, the freezing depth of the pipe passing inside the building is up to 1.5 m. This leads to flooding of the roof surface when the snow melts, since the ice in the pipe will thaw in last turn. Constantly rising water accumulates on the roof surface and then flows through any defects in the coating to the lower floors, causing significant material damage. The ice that appeared during the next drop in temperature will rapidly break existing cracks, as well as create new ones. There is also a high probability of a pipe rupture due to the freezing of water, which, when turning into a solid state, increases its volume. In the spring, this will result in a pipe leak and flooding of the interior. Worse, in the zone of negative temperatures of the insulation, ice also forms, under the pressure of which the waterproofing carpet of the roof is broken. Melt and storm water get free access to the slabs and beams (trusses) of the building, causing corrosion in them. To avoid this, it is enough to protect the drain and funnel from freezing. How to do this, we will analyze in the following example.
The main problem for flat roofs in winter is the freezing of drain funnels. As a rule, the freezing depth of the pipe passing inside the building is up to 1.5 m. This leads to flooding of the roof surface when the snow melts, since the ice in the pipe will thaw in last turn. Constantly rising water accumulates on the roof surface and then flows through any defects in the coating to the lower floors, causing significant material damage. The ice that appeared during the next drop in temperature will rapidly break existing cracks, as well as create new ones. There is also a high probability of a pipe rupture due to the freezing of water, which, when turning into a solid state, increases its volume. In the spring, this will result in a pipe leak and flooding of the interior. Worse, in the zone of negative temperatures of the insulation, ice also forms, under the pressure of which the waterproofing carpet of the roof is broken. Melt and storm water get free access to the slabs and beams (trusses) of the building, causing corrosion in them. To avoid this, it is enough to protect the drain and funnel from freezing. How to do this, we will analyze in the following example.
EXAMPLE: roof with one internal drain. Funnel diameter 100 mm. The drainpipe runs inside the building, it has a positive temperature along its entire length.
TASK: heat the funnel
To warm up 1 square meter the roof around the drain funnel, it is necessary to provide the power of the electric heating system of the order of 250 watts per square meter. This will ensure the complete absence of snow in this area and prevent the melt water from freezing. When using a self-regulating heating cable with a power of 40 W per linear meter, the total amount of cable is 7 meters in 30 cm increments, as shown in fig. 1. Plus, it is necessary to lower the cable into the drain funnel to a depth of about 1.5 m to prevent freezing of the drain pipe in its upper part, while the edge of the funnel before lowering the heating cable inside is heated in a circle with one loop. This will take another 2 meters of heating cable. It is recommended to take a margin of 10% for cable cutting and termination. In total we get:
| Heating cable power(W/m) | Funnels (pcs) | Boxes(pcs) | Reinforcing mesh(m2) | Heating cable(m) | Sets of RGS(pcs) |
| 40 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 1 |
Table 1 indicates the required volume of material for heating two funnels on a flat roof (without taking into account the safety factor).
Pitched roof with hanging gutter.
 With such roofs, the main problem is, as a rule, icing of downpipes and hanging gutters. It is also possible to form a snow cap on the edge of the roof, which over time, under the influence of temperature changes, can turn into ice growth and icicles. This is typical for roofs with poor thermal insulation and with gutters suspended at a distance of 10 cm and below from the edge of the roof. Therefore, the heating of gutters should be complex. Cable installation in such a system is carried out immediately along the edge of the roof, in downpipes, and a hanging gutter. With a diameter of 100 mm for gutters and downpipes, a self-regulating heating cable with a power of 40 W/m is sufficient, with a diameter of 150 mm, a power of 40 W/m may no longer be enough. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a cable already with a power of 60 W / m, or lay a heating cable of 40 W / m in two parallel lines. For gutters and pipes with a diameter of 200 mm, the heating cable is laid in two lines, and for guaranteed protection of the drainage system from ice inside the pipes and gutters, the cable is selected with a power higher than 40 W / m. The edge of the roof is heated by a heating cable laid in a wave to a depth of 60 cm from the edge of the roof. Such a roof heating system should provide, as well as when heating a funnel on a flat roof, a power of at least 250 W per square meter. meter of heated surface. Also, on such roofs, a system of tubular snow retention is often installed. To prevent the formation of excess mass of snow accumulating on it, a roof heating system is also used. The heating cable is mounted before snow retention, in the place of snow accumulation. The characteristics of the heating system in this case fully correspond to the characteristics of the heating system for the edge of the roof.
With such roofs, the main problem is, as a rule, icing of downpipes and hanging gutters. It is also possible to form a snow cap on the edge of the roof, which over time, under the influence of temperature changes, can turn into ice growth and icicles. This is typical for roofs with poor thermal insulation and with gutters suspended at a distance of 10 cm and below from the edge of the roof. Therefore, the heating of gutters should be complex. Cable installation in such a system is carried out immediately along the edge of the roof, in downpipes, and a hanging gutter. With a diameter of 100 mm for gutters and downpipes, a self-regulating heating cable with a power of 40 W/m is sufficient, with a diameter of 150 mm, a power of 40 W/m may no longer be enough. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a cable already with a power of 60 W / m, or lay a heating cable of 40 W / m in two parallel lines. For gutters and pipes with a diameter of 200 mm, the heating cable is laid in two lines, and for guaranteed protection of the drainage system from ice inside the pipes and gutters, the cable is selected with a power higher than 40 W / m. The edge of the roof is heated by a heating cable laid in a wave to a depth of 60 cm from the edge of the roof. Such a roof heating system should provide, as well as when heating a funnel on a flat roof, a power of at least 250 W per square meter. meter of heated surface. Also, on such roofs, a system of tubular snow retention is often installed. To prevent the formation of excess mass of snow accumulating on it, a roof heating system is also used. The heating cable is mounted before snow retention, in the place of snow accumulation. The characteristics of the heating system in this case fully correspond to the characteristics of the heating system for the edge of the roof.
EXAMPLE: the roof is pitched, with hanging gutters, 2 drainpipes with a diameter of 100 mm. The height of the building is 7 m. The perimeter of the roof is 40 meters. There is no snow retention.
TASK: protect the roof from ice and icicles, ensure the outflow of melt water into the drain.
Pipes: if the height of the building is 7 meters, then not only the height of the building itself is taken into account when determining the length of the downpipe, but also the elbow, if any, as well as the margin required to connect the heating cable (10% or 1.1). We assume that the pipes have one 45O elbow 0.5 m long. In this case, the length of the heating cable for 2 pipes is calculated as follows: (7 m + 0.5 m) × 1.1 × 2 = 16.5 m. Let's round this number up to 17 m.
Hanging gutter: roof perimeter 40 meters, usually hanging gutter is equal to the roof perimeter. From here, the calculation of the cable length is calculated as: 40 m + 10% = 44 m.
Roof edge: for cable installation in a wave, it must be taken into account that in this case, in order to achieve required power at 250 watts per sq. meter of roof requires 3.5 m of heating cable. Thus, the edge of the roof with a width of 60 cm is heated, with a heating cable laying step of 30 cm. the amount of heating cable used to heat the edge of the roof along the entire perimeter will be calculated using the following formula: (40 m × 3.5) = 140 m.
As a result, the total length of the heating cable will be 201 m. Round up to 200 m.
Next, it is necessary to take into account how many junction boxes, couplings and electrical cable are required to provide power to the system (this is determined on site, or taken with a small margin) and the power of the electric heating control cabinet is determined.
Pitched roof with wall gutters. Cable heating of the roof in this case is organized somewhat differently. After all, the main problem here is the formation of ice and icicles on the edges of the roofs. Therefore, the installation of the cable is carried out immediately along the entire length of the gutter. It is better for reliability and protection from the “snow cap” to run two wiring strands at once. After that, the cable gets into all possible downpipes, as well as into the stormwater system. A dropper is mounted on the very edge of the roof, which is attached to the very edge of the roof. The cable will be laid in the existing groove (as shown in Figure 1). The use of a drip is guaranteed to provide reliable heating of gutters and roofs, as well as protection of the edge of the roof from ice.
Cable heating of the roof in this case is organized somewhat differently. After all, the main problem here is the formation of ice and icicles on the edges of the roofs. Therefore, the installation of the cable is carried out immediately along the entire length of the gutter. It is better for reliability and protection from the “snow cap” to run two wiring strands at once. After that, the cable gets into all possible downpipes, as well as into the stormwater system. A dropper is mounted on the very edge of the roof, which is attached to the very edge of the roof. The cable will be laid in the existing groove (as shown in Figure 1). The use of a drip is guaranteed to provide reliable heating of gutters and roofs, as well as protection of the edge of the roof from ice.
FIG.1![]() EXAMPLE: Four-pitched roof with wall gutters 10 meters high, 4 drainpipes with a diameter of 100 mm. The roof perimeter is 50 meters. There are no endows.
EXAMPLE: Four-pitched roof with wall gutters 10 meters high, 4 drainpipes with a diameter of 100 mm. The roof perimeter is 50 meters. There are no endows.
TASK :
protect the roof from frost and icicles.
The calculation of the cable is carried out in parts.
Pipes: if the pipes are 10 meters long, then it is necessary to take into account not only their bends, but also the distance for connecting the cable to the junction boxes, in this example, the length for all pipes is calculated as follows (10 m + 2 m + 10%) × 4 = 53 m.
Wall gutter: Roof perimeter 50 meters, usually wall gutter is 10% longer. From here, the calculation of the cable length is calculated as: (55 m × 2) + 10% = 121 m.
Drip: The length of the drip usually corresponds to the perimeter of the roof. The cable in the drip is placed in one thread, so in this example the cable footage along the edge of the roof is 50 m + 10% = 55 m
The total cable length for the entire roof is 229 m.



