The thickness of the monolithic wall of a residential building. Monolithic concrete walls
During the construction of structures and buildings, hollow walls are often made of reinforced concrete. However, few people know what kind of walls they are and what their characteristics are. Therefore, before using these structures for construction, it is worth studying all their features.
Types of reinforced concrete slabs
Depending on the composition and type of structure, there are the following types:
- Reinforced concrete slabs with solid construction. These products are available in different sizes. Their length varies between 1790-6260 mm, width 1200-4500 mm, and thickness 120 mm, 170 mm, 210 mm. This type of product has a large mass. Their weight depends on the size of the slab itself and ranges from 0.625 tons to 3.7 tons. The height dimension reaches 220 mm. These products are used to cover walls in residential and
- Plates with round voids. These are also quite large structures. Plates with a width of 100 mm have a length of 240-1200 mm, with a width of 120 mm - 170-890 mm, with a width of 150 mm - 240-890 mm. Their height reaches a maximum of 220 mm. But unlike a solid floor slab, reinforced concrete hollow core slabs have good sound and heat insulation. These indicators are provided due to the presence of voids in the inner part of the plate.
- Plates for special purposes. These designs are suitable only for balconies, loggias, bay windows and overlapping plumbing units. Their difference lies in the fact that the design has special holes for laying pipes. The height of these structures is 200 mm.
- Plates with ribbed structure. They are used to cover brick residential and public buildings, are also very often used for arranging the supporting base of the roof. They are very large. Their length can reach up to 18 meters, width - 3 meters, and height - from 600 mm to 800 mm.
- Spacer floor slabs. They are installed between the columns of buildings. The length of these plates reaches 1.5 meters.
- Heavy concrete slabs. These structures are installed between the columns on the ground floor.

Features of walls made of hollow core slabs
Currently, hollow core slabs are used in the construction of the walls of many buildings, including residential buildings. This is understandable, because hollow walls made of reinforced concrete have the most good performance and qualities.
It is worth paying special attention to the following features of these structures:
- Due to the fact that the panels have voids, they are very easy to install and the load on the walls is significantly reduced.
- The voids provide good thermal insulation, and therefore the walls do not need to be additionally insulated.
- Another one nice feature is soundproofing. Despite the fact that reinforced concrete does not change, the sound insulation is very high. External sounds and noise practically do not penetrate through the walls.

Criteria for choosing slabs for hollow core walls
It is especially important to choose the right structures for the construction of hollow walls. Therefore, before you start making hollow walls from reinforced concrete, you should pay attention to the properties of the slabs.
Many people think that they differ only in parameters and sizes, but this is not entirely true. Hollow core panels also have distinctive characteristics that are useful in the construction of houses and public buildings.

Distinguishing criteria for hollow core panels
- The first distinguishing characteristic is the method of reinforcement. Depending on the type of slab, reinforcement can be either prestressed or non-prestressed. Especially often in construction, panels with prestressed reinforcement are used.
- Another one important feature- this is the number of sides of the support of the entire structure. Basically, all hollow structures allow support only on two short sides. But sometimes there are structures with supports on three or four sides.
- It is worth paying attention to the way the plates are made. Basically, hollow reinforced concrete slabs are produced with two markings PC or PB. Depending on this, the method of manufacturing the design of these products is different.
Differences between hollow core panels PB and PC
Panels under the PB brand are made by casting continuous formwork. They have a flat and smooth surface, and they almost do not crack. These structures are used. Reinforced concrete slabs of this type can be easily cut lengthwise or into separate pieces, and they can also be made oblique at an angle of 30 to 90 degrees. At the same time, their Basic structure is not violated. These properties make it much easier to work on the construction site.
Plates under the brand name PC are cast in the formwork. With a length of up to 4.2 meters, they can be produced without prestressed reinforcement. In addition, they have free deflection.

Features of the installation of plates during the construction of hollow walls
Of course, in order for reinforced concrete hollow walls to be strong and strong, it is necessary to install the panels correctly.
Installation of hollow walls consists of the following steps:
- Since hollow core slabs grade PB there are no mounting loops for mounting, loading and unloading of these structures should be carried out using soft chocks or a special traverse.
- In order to pull the chalk out from under the panel, it is necessary to leave a small gap to the next panel during laying. Next, the already installed plate should be moved with a crowbar to the adjacent panel.
- It is necessary to observe the value of the minimum depth of support of the structure. These figures depend on the type of wall. For example, for brick walls, the minimum depth should be 8 cm, and the largest 16 cm, for reinforced concrete wall, respectively, 7 cm and 12, for gas and foam concrete blocks - from 10 to 15, for steel structures - 7 cm.
- Before starting the installation of panels, it is necessary to hammer the ends of the holes with voids. Voids can be sealed with pieces of wood or fragments of bricks. This is done to prevent water from entering the structure. Due to this, the service life of hollow walls increases, they do not crack, do not crumble.
- After the slabs are fully installed, it is necessary to anchor and fill the cracks with cement. For PC marking plates, the anchor is hooked onto the mounting eye, and the void is filled with cement.
Also, before proceeding with the installation of hollow structures, a crane should be ordered. It is important to take into account the size of the access ways, the maximum possible outreach of the truck crane and the possibility of the permissible weight of the crane.

The cost of hollow structures made of reinforced concrete
Few people know how much hollow-core reinforced concrete costs, the price of this product is different everywhere. Of course, it all depends on the quality and design of this product.
A PC brand stove costs from 2 to 12 thousand rubles. And panels of the PB brand cost from 1500 to 15 thousand rubles. The cost of these products depends on the size of the structure, quality and composition. The higher the quality and the larger the plate, the higher the price of the product, respectively.
erection monolithic walls : we'll talk about this in this article on the site site. Monolithic walls from lightweight concrete compared to bricks are just as strong, but less thermally conductive and more economical. For this reason construction of monolithic walls today is gaining considerable popularity. Due to this circumstance, we have created this article. In it, we outlined all the technology in detail. construction of monolithic walls with your own hands.
There are two technologies for erecting concrete monolithic walls. Their difference lies in the use of different formwork structures. In the first option, a removable (the structure is removed after the concrete has hardened) is used, and in the second, a fixed (dismantling is not provided) formwork.
Construction of monolithic walls with removable formwork
Used in the construction of monolithic walls removable formwork It is made most often of metal or wood and is a team. metal formwork has the form of assembled (as a designer) shields. More popular wooden, it is knocked together from boards and plywood right at the construction site. This type of formwork can be reused.
During installation, the formwork is set to a height determined by the thickness of the concrete layer, which is planned to be poured at a time. This value can be veiled from 20 to 200 cm, and sometimes even more. The width of the formwork structure, and hence the wall itself, is calculated based on the thermal conductivity of the concrete and the region of construction.
Inner surface formwork (in contact with concrete) should be as smooth as possible. For this purpose, plastic or laminated chipboard is used.
Do-it-yourself construction (erection) of monolithic walls made of concrete (reinforced concrete):
- Assembly and installation of formwork. From boards 30-50 mm thick and bars of "ribs" nailed to their outer side, shields are assembled. Panels (connected shields) are set opposite to each other. The distance between them is set by temporary struts (horizontal bars between the shields). If the width of the walls exceeds 500 mm, then to strengthen the structure, the "ribs" are connected by "battles" - a horizontal bar. Opposite panels are connected with tie bolts or wire twist. At the end, with a step of 1-1.5 m, spacer slope racks are installed.
- Reinforcement of monolithic walls. A reinforcing mesh (plastic or steel) is installed in the formwork, or, which is more important, a frame made of reinforcement.
- Filling the walls with concrete. The concrete mixture is laid in layers (no more than 50 cm). The filling of each subsequent layer takes place after the "seizure" of the previous one. The poured mixture is compacted with a deep vibrator. After the concrete has hardened, the formwork is moved to a higher level, followed by concreting.
It will take 4-5 weeks for concrete to acquire maximum strength. After this period, you can start warming and finishing.
A wall reinforced with reinforcement, the diameter of which is 8 mm or more, will be quite cold. The reason for this is the "cold bridges" that create the metal parts of the frame.
In case when monolithic walls houses are built using, instead of conventional concrete can be used mixtures with much lower thermal conductivity. These include: expanded clay concrete, slag concrete, perlite concrete, sawdust concrete, wood concrete, etc. Walls made of such materials will be warmer, but at the same time less resistant to increased loads.
Construction of monolithic walls with fixed formwork
The fixed formwork used in the construction of monolithic walls of the house is blocks or panels made of various materials. They are mounted in a formwork structure, which is reinforced and poured with concrete. After the concrete has set this formwork is not removed, it becomes a functional part of the wall.
The most common type of fixed formwork is blocks (thermoblocks) made of expanded polystyrene with voids. These are plates (usually 50 mm thick) located at an average distance of 150 mm from each other and interconnected by removable or non-removable jumpers.
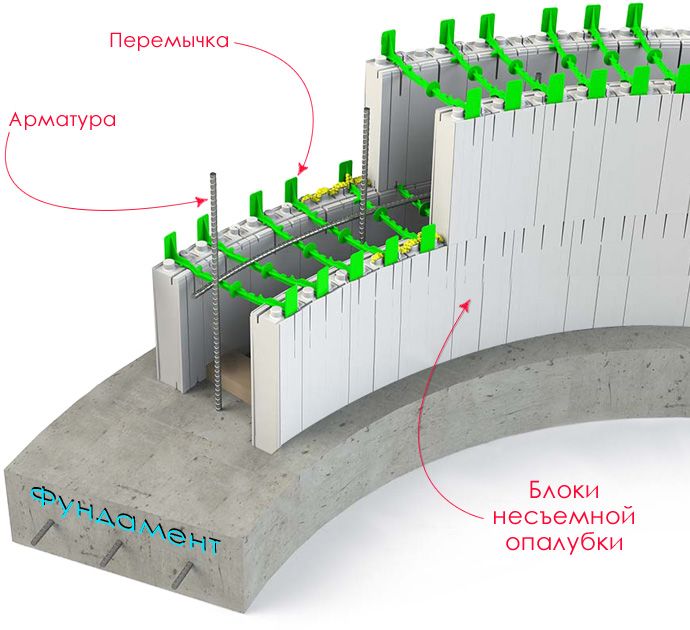
Do-it-yourself construction of monolithic concrete walls:
- Formwork installation: fixed formwork elements are laid out on the prepared foundation surface. Blocks are fastened to each other with the help of connecting "locks". They give the structure the required level of tightness and exclude the possibility of concrete leakage. The formwork is erected to a height of up to 50 cm. After pouring the concrete, the next “batch” of blocks is laid out. During this time, the concrete has time to dry. Thus, the work is practically uninterrupted.
- Reinforcement of fixed formwork: horizontal reinforcement rods are laid in special grooves of the blocks. Next, vertical reinforcement is installed. The rods are connected with a knitting wire.
- Formwork pouring concrete: the concrete mixture is laid in a layer of 50 cm (to the height of the formwork: point 1) and compacted with a vibrator.
- Wall decoration of the house. By result construction works walls are obtained in the form of a “sandwich”, where reinforced concrete is located between two plates of expanded polystyrene. Such a design needs protection from mechanical damage, as well as a fireproof coating. To do this, the walls of the house, both from the front and from the inside, are finished with non-combustible material (a layer of at least 30 mm): drywall, plaster.
Formwork blocks are supplied standard sizes, therefore, they have to be adjusted on the spot by cutting.
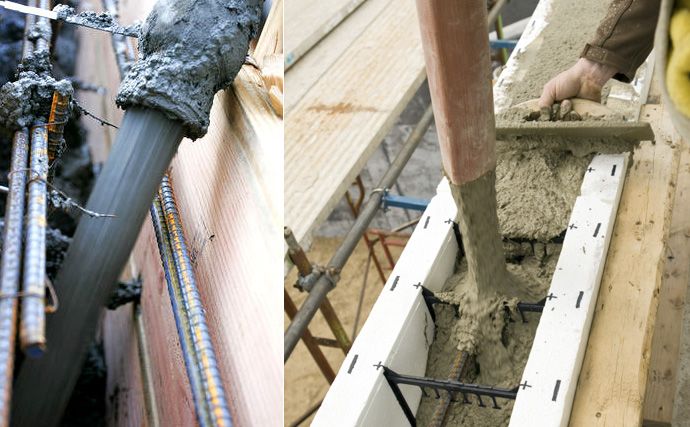


For pouring fixed formwork, only concrete should be used. The use of warm mixtures is prohibited. The reason is that the vapor permeability of expanded polystyrene is lower than that of warm mixtures - 0.05 Mg/(m*h*Pa) on the 0.09 Mg/(m*h*Pa). Consequently, in warm concrete compressed between polystyrene foam, condensate will inevitably accumulate. And this will inevitably lead to the formation of mold and mildew.
Types of concrete solutions for monolithic construction
Monolithic construction allows the use of mortars with different thermal conductivity and vapor permeability:
- Concrete - a cottage with such walls needs to be insulated. The reason for this is the high thermal conductivity of the material 1.51 W / (m * C) with a vapor permeability of 0.03 Mg / (m * h * Pa);
- Reinforced concrete is even colder than concrete, since the armored frame acts as a "cold bridge";
- Expanded clay concrete - with such walls the house will be warm enough. The thermal conductivity of expanded clay concrete is 0.66 - 0.14 W / (m * C) with a vapor permeability of 0.09 - 0.3 Mg / (m * h * Pa). These indicators may vary depending on the density of the mixture (the larger the porosity of expanded clay concrete, the warmer the walls will be);
- Slag concrete - concrete from slag. The same expanded clay concrete is only less durable;
- Sawdust concrete - a mixture of cement, sand, sawdust(needles) and water. Such walls will be warm, durable, fire-resistant and environmentally friendly. But there is one thing, such material must be necessarily covered with a waterproofing layer;
- Arbolite (wood concrete) - a combination of wood chips with cement. Compared with sawdust concrete, the material is more durable and warm;
- - cellular concrete, obtained by hardening a mixture of cement, sand, water and a foaming agent. The material has a thermal conductivity of 0.29 - 0.08 W / (m * C), together with a vapor permeability of 0.11 - 0.26 Mg / (m * h * Pa).
For the erection of walls of low-rise buildings that do not require increased strength, lightweight concretes, both monolithic and small-block, are widely used. With relative cheapness and simplicity of construction, such walls have good performance properties.
As aggregates in the manufacture of lightweight concrete, slag, expanded clay, brick batt, sawdust reeds and other local materials are used. Binders are cement, lime, clay, gypsum.
The most common is slag concrete based on fuel or metallurgical slag. To increase the strength, 10-20% sand is added to it (from the volume of slag).
The slag must be clean and free from foreign impurities: earth, clay, ash, unburned coal and debris. To reduce the content of unbaked clay particles and harmful salts, fresh slag is kept for a year in dumps in the open air, ensuring free drainage of rain and flood waters during its storage.
The strength and heat-shielding qualities of slag concrete largely depend on its granulometric composition, that is, on the ratio of large (5-40 mm) and small (0.2-5 mm) parts of the slag filler. With coarse slag, concrete is lighter and less durable, with fine slag, it is more dense and heat-conducting. For external walls, the optimal ratio of fine and coarse slag is from 3:7 to 4:6, for internal load-bearing walls, where the main advantage is strength, this ratio changes in favor of fine slag, and lumpy slag larger than 10 mm in the composition of cinder concrete in this case is not included at all.
Cement with additives of lime or clay is used as a binder. Additives reduce cement consumption and make cinder concrete more plastic.
Approximate composition of cinder concrete.
To prepare cinder concrete, cement, sand and slag are mixed (large pieces are pre-moistened), then lime and clay dough, water are added and everything is thoroughly mixed again. The finished mixture is used for 1.5-2 hours.
Monolithic cinder-block walls are erected in adjustable formwork 40-60 cm high, knocked down from four centimeter boards. The inner surface of the shields is covered with a film or pergalin. Formwork panels are usually attached to fixed posts with a diameter of 10-15 cm, installed on both sides of the future wall through 1-1.5 m along the front to the full height. Temporary spacers are inserted inside the shields, and wedges are inserted between the posts and shields.
The thickness of the walls of monolithic slag concrete is 55-60 cm, when using expanded clay, pumice as a filler, the thickness can be less - 45-50 cm, the walls for garden houses can be reduced to 35-40 cm.
Slag concrete is laid in layers of 15-20 cm with uniform compaction and bayonet. After two or three days, and in warm weather after a day, the formwork is rearranged. The laid slag concrete is shaded from direct sunlight for seven to ten days, and in dry weather it is periodically moistened.
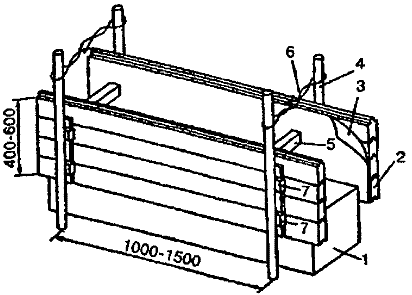
: 1 - slag concrete; 2 - formwork shield, 3 - glassine; 4 - racks, 5 - spacer; 6 - wire twist; 7 - wedges.
Monolithic walls can be built with internal voids. This improves the heat-shielding qualities of the walls and reduces the consumption of slag concrete. Inserts made of lighter concrete, foam plastic, old newspapers and cardboard, milk bags, etc. can be used as void formers. However, it should be borne in mind that voids weaken bearing capacity walls, so the strength of cinder concrete in this case must be increased. It is possible to trim (plaster) monolithic walls no earlier than three to four weeks after their erection, when the cinder concrete is completely dry and gains the necessary strength.
From the outside, the walls made of blocks are plastered with cement-sand mortar, from the inside they are lined with sheets of dry plaster. A good technological solution is obtained by installing monolithic cinder-concrete walls with external brick cladding, which gives the wall a more solid appearance, does not require subsequent finishing (with brickwork with jointing), and in the process of concreting it acts as an external formwork.
Lintels over door and window openings on 6 lightweight concrete walls are arranged, as a rule, dove, that is, along the course of masonry from a monolithic reinforced concrete belt 30-40 mm thick, laid on wooden formwork, or from wooden bars 1/20 span high. The length of the supporting parts of the jumpers is 40-50 cm on each side of the opening.



