What electrodes to use for the inverter. How to choose a welding electrode?
Instruction
Understand the electrode device. It consists of high quality welding wire and a coating in the form of a mixture of various powders. The coating is attached to the base with an adhesive mass. Electrodes to perform special types welds may or may not be coated. In total, several hundred varieties of electrodes are known, which allows you to satisfy almost any need that arises during welding, including work with steel, non-ferrous metals and complex alloys.
Choose electrodes, focusing on the upcoming type of welding work. For example, for joining low-alloy steels and alloys, you will need mixed-coated stainless electrodes.
Opt for rutile electrodes if you need to weld rusty parts. Rutile electrodes are somewhat more expensive than conventional ones, but when using them, it is possible to reduce metal spatter, stabilize combustion and increase the strength of the weld. Slag after working with such electrodes is very easily removed.
Use ilmenite electrodes to increase the elasticity of the seam. The seam treated with an ilmenite-coated electrode tolerates temperature changes well environment. The disadvantage of such electrodes is that they are not very reliable when welding rusty parts.
If you need to connect non-ferrous metals together, use electrodes with a high melting point. The composition of such an electrode includes tungsten and special additives with high resistance to thermal effects.
Pay attention to color coding. Electrodes marked green are suitable for welding magnesium and aluminium. Blue marking indicates that the electrode is made of tungsten with the addition of lanthanum oxide. Most often, the latter type of electrodes is used to work with copper or alloy steels.
When choosing electrodes, take an interest in the conditions in which they were stored. The fact is that the electrodes have a certain shelf life. If this period is violated, the electrode will not be able to guarantee high quality seam. Do not purchase welding electrodes that have been stored in high humidity conditions. It is highly undesirable to buy such products from the hands, since in this case it will be almost impossible to determine the expiration date.
Transformers are long gone. Now they are being replaced by welding inverters. They allow you to quickly and efficiently weld metal parts and structures. Typically, inverters are used as power sources for welding machines in fusion arc welding. The use of this type of apparatus is famous for the fact that, due to the constant characteristic welding current and its stability, excellent seam quality is achieved, which guarantees a strong and reliable metal connection.
What is inverter welding? Strictly speaking, it is a process using a circuit, a system, or some device that creates AC voltage when connected to a DC source. To be more specific, this type of welding is an inverter-assisted process, traditionally it is manual arc welding.
The general scheme of such welding consists of a mains filter, a mains rectifier, a frequency converter, a high-frequency transformer, a power rectifier and a control system.
Of course, for the implementation of metal welding, one device is not enough, you also need accessories - a mask, holders and, of course, electrodes. Without them, no work is possible. There are three types of electrodes for inverter welding - carbon, alloy and high alloy.
The main advantages of welding with an inverter machine are:
Easy and fast ignition, stable arc burning, good elasticity;
- high-quality welding seam;
- energy saving;
- high efficiency;
- supply voltage fluctuations do not affect the welding parameters;
- lightness and mobility.
Of course, inverter welding also has disadvantages: the devices used during operation, like any other electronics, really do not like water, dust and frost. Therefore, you need to store inverter welding in a dry and fairly warm room. It is also important to regularly open the case and blow out the machine components with compressed air.
Related videos
Sources:
- electrodes for inverter welding
Related videos
In the welding trade, the ability to choose the right electrodes depending on the type of joints and steel grade is a very important professional skill. In this article, we will tell you about the main varieties of MMA welding electrodes and explain how to use them for their intended purpose.
How they work and how they differ
An electrode is a simple metal rod that melts in an ignited electric arc and fills the seam between two parts, simultaneously heating their edges. The electrode coating, when burned, ionizes the medium and maintains continuous arcing. In addition, during combustion, the composition releases gases that displace oxygen from the weld pool and forms slag that floats to the surface of the molten metal and covers it, protecting it from corrosion, cracking and other negative effects at the time of cooling.

Understanding the essence of the operation of electrodes is very important for explaining such a huge number of their varieties. They differ not only in the strength characteristics of the seam, but also in its position and the type of welding current used.
The difference between the electrodes by the location of the seam
Let us briefly recall how the orientation of the weld pool in space can change and how this affects the welding technique. The most convenient is the lower position of the horizontal seam, which can be flat and angular. In this case, the melt effectively fills the seam and chamfer, and a uniform slag crust forms on top, which is easily separated. Almost all brands of electrodes, with the exception of special ones, can be welded in the lower horizontal position.

Vertical seams are more difficult to weld. Typically, a pull-off welding technique from bottom to top is used. Accordingly, the coating of the electrode should allow for quick and short-term ignition of the arc and efficient guidance of the molten metal. Also, vertical seams can be welded without tearing, but for this the coating must have a thickness greater than usual, so that a semicircular hole forms at the point of contact on the electrode.

The upper (ceiling) location of the horizontal seam is considered the most difficult in MMA welding. It is practically impossible to weld such seams without separation; more often they are welded by the spot method with an overlap of 3/4 of the previous weld. The coating of electrodes for ceiling joints contributes to the rapid melting of small portions of metal and the same rapid cooling. Slag from electrodes also behaves differently. For the most part, it flies off to the side (the electrode is held at an angle) and covers the previous sticking point. Electrodes for ceiling welding are most sensitive to current mode and polarity.

Type and polarity of welding current
As you know, inverters have an alternating or direct current at the output, the latter has a direct and reverse polarity connection. Most electrode welding tasks are solved by reverse polarity, in which the electrode is connected to the positive "+" contact, and the workpiece to the negative "-". The peculiarity of reverse polarity is that the electrons, continuously moving from the negative to the positive pole, heat the electrode and its coating, and the metal of the part is heated only by indirect radiation.
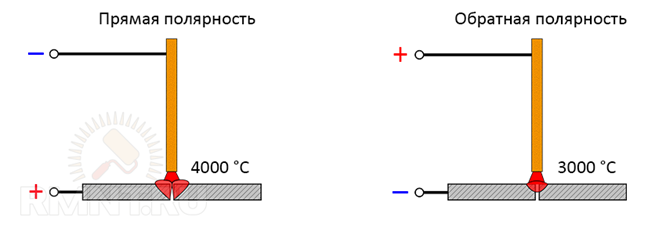
With direct polarity, the flow of electrodes is directed from the electrode to the part and heats it directly. The electrode burns more slowly by adding small portions of molten metal to the bath. It is useless to expect that such welding will effectively fill a joint with a wide gap, direct polarity is used to connect well-fitted parts with a uniform weld thickness. For example, in this way it is good to weld sheets of metal, the seam is minimally noticeable. Thanks to more high temperature weld pool with direct polarity, it is optimal to weld massive parts that require the maximum depth of heating.
Welding alternating current usually characterized by strong spattering of molten metal. The coating of electrodes for AC welding has additives to stabilize the arc and special alloying impurities that make the melt more viscous. The quality of the weld when working with electrodes on alternating current is considered the highest for RDS.
Explanation of symbols
There are two main specifications according to which electrodes are marked: the domestic GOST 9466 and the European standard ISO 2560. Each of them uses its own naming convention.

GOST
Top line - Т11-XXX-Y-ZN:
· T - type of electrodes, "E" for MMA welding;
· 11 - metal yield strength in MPa;
· ХXX - brand of electrodes;
· Y is the electrode diameter;
· Z - purpose of the electrode (U - low-alloyed and carbon up to 60 kgf / mm, L - alloyed over 60 kgf / mm);
· N is the coating thickness.
Bottom line - E-AAA-B-C-D:
· E-AAA - type and regulatory index defining strength characteristics seam;
B - type of coating;
· C - seam position;
· D - current characteristics.
ISO
T XX Y SS 01:
· T - designation of the type of electrodes, "E" - for MMA welding;
· XX - metal yield strength in MPa;
· Y - impact fracture resistance index in MPA;
· SS - electrode coating type;
· 0 - performance index of surfacing, type of current and polarity;
· 1 - seam position index.
Types of coatings
The acidic coating (A) strongly melts the weld pool, which is why the metal is prone to cracking during solidification. Currently replaced by rutile acid.
The main (B, B) coating provides a high viscosity of the metal in the bath and uniform heating of the part. Such electrodes are designed for welding loaded structures, however, they should be annealed before use to avoid the formation of pores in the metal.

Cellulose (C, C) coating burns out in an arc almost completely, almost without forming slag. This type of electrode is one of the few that can weld vertical seams from top to bottom.

The basis of the rutile (P, R) coating is titanium dioxide. The electrodes are optimal for welding with a gap: they ignite and hold the arc well, and evenly deposit metal. Rutile coating provides full control over the welding process and allows you to vary the length of the arc in a wide range.

Rutile-cellulose (RC, RC) coatings inherit the positive qualities of both types. It is these electrodes that are used for installation in cramped conditions, they leave an aesthetic facial seam that does not require further processing.
Most Popular Brands
The lower the complexity of the seam, the more convenient the electrodes are, some literally cook themselves. These, first of all, include the famous E46 of the MONOLITH trademark, they are also ANO-36, popularly called "school" electrodes. Cooking with them is really simple: the rutile-cellulose coating holds the arc well even at very low currents, the metal is transferred in small and medium drops, filling the bath well. However, one should not approach critical structures with such electrodes: due to the increased silicon content, the seam loses its plasticity and impact strength.

Units and connections operated outdoors, including metal frame structures with hinged cladding, are recommended to be welded with electrodes, the coating of which contains alloying additives. Such seams have a much higher yield strength, and they are subjected to corrosion to a much lesser extent due to the low hydrogen index. An example of such a brand is OK-48. They have a basic coating and melt the metal to a viscous-liquid state, setting the optimal degree of heating, suitable for welding in any position. If a penetration of 12 mm or more is needed, it is recommended to pre-weld the seam with electrodes with an organic coating of the ANO-7 and ANO-8 types.

Electrodes OK 61.35 are used for welding structures with oscillatory types of loads and containers under pressure. Their coating is basic, the metal is very viscous during melting, the seam is practically insensitive to intercrystalline corrosion.
http://www. rmnt . ru/ - RMNT website. en
In order for electric welding using an inverter to give the desired result, and the resulting weld to have high reliability and strength, it is necessary to choose the right electrodes for inverter welding. It is very easy to get confused in the huge variety of similar products presented on the modern market.
They differ in the material of manufacture, their type, diameter, composition of the coating, as well as a number of other significant characteristics. What electrodes can be used for welding with an inverter, as well as how to choose them correctly, we want to talk in this article.
Criteria for choosing electrodes
First of all, it should be borne in mind that the electrodes can be of consumable and non-consumable type. The former are made of a metal rod, on the surface of which a special coating is applied, which contributes to the protection of the welding zone and increases the stability of the arc. They are used to perform manual arc welding. Products of the second category - non-consumable - are used for welding in a shielding gas (argon) environment, their varieties and features of use will be discussed in a separate article.
When choosing electrodes for welding using an inverter, it should be taken into account that the material of manufacture of the parts to be joined will also affect the quality characteristics of the formed seam. Accordingly, in order to cook different materials, are used different types. So, for example:
- to connect products made of, choose carbon electrodes;
- to connect products made of alloyed steels, electrodes of the corresponding grades are used: OZS-4, MP-3 (GOST 9466-75), MP-3, ANO-21, UONI 13/45 (GOST 9467-75);
- if it is necessary to perform welding work with surfacing or other types of steel, then choose electrodes with a core of high-alloy metal - TsL-11 (GOST 9466-75);
- in order to cook cast iron, it is also necessary to select electrodes of the appropriate brand - OZCH-2 (GOST 9466-75).
![]()
To date, the following rating of electrodes used for welding using an inverter has been formed.
- ANO. Welding electrodes of this brand ignite well, they do not need to be additionally ignited. Both novice welders and professionals can work equally well with them.
- MP-3 is a universal type, they can even be used to join uncleaned surfaces.
- MR-3S. Electrodes of this brand should be chosen if increased requirements are imposed on the characteristics of the seam.
- UONI 13/55 is used for the installation of critical structures that require high quality welds. It will be difficult for a novice welder to work with them: their use requires certain experience and high qualifications.
Benefits of Popular Electrode Brands
Many modern types of electrodes for welding using an inverter have the following advantages.
- Ease of welding. Difficulties when welding with such electrodes can arise if you incorrectly selected them according to the composition of the core material.
- High quality seam. This parameter is the most important in welding work, and the electrodes of these brands make it possible to provide it. Using such electrodes for the inverter, it is possible to obtain high-quality internal and external connections, convex and concave welds.
- Easy separability of slag. The slag obtained during welding using such electrodes is easily separated, which makes it possible to immediately see what kind of weld quality they provide.
- Corroded parts can be welded. Of course, products covered with a layer of rust are welded very infrequently, but these electrodes make it possible to obtain a high-quality and reliable seam even in this case.
- The welding process is safe for the welder in terms of sanitary and hygienic standards.

Differences in electrodes by brand and diameter
Among experienced welders, there is an opinion that when using an inverter, you can weld with any electrodes. As a rule, such an opinion is based only on personal experience such specialists involved in the performance of work of a certain type (welding of structures made of profile pipes or corners). When performing work using an inverter, the connection does not impose serious requirements for its tightness, therefore, electrodes with a diameter of 0.5–2 mm can be used without problems.
The choice of the diameter and brand of the electrode should be based on how thick the metal must be connected with them. Details of large thickness require long-term welding, respectively, and the electrode for their welding must be selected with a larger diameter. Small-diameter welding electrodes still need to learn how to work, they burn out very quickly. Usually tacks are made with such products.
Which electrodes are better to choose is also influenced by the type of work for which they are planned to be used. So, to perform complex route work, it is necessary to select electrodes of large diameter, and the installation of structures from profile elements can be performed with products with a diameter of up to 2 mm. It is these electrodes that are used, in particular, in the installation of sectional doors and the manufacture of various enclosing structures from profile pipes and corrugated board.
Classification of welding electrodes
First of all, welding electrodes are divided into separate types according to their main purpose. So, it is customary to distinguish the following types:
- those with which carbon and low alloy steels are welded;
- for connecting structures made of high-strength heat-resistant steels;
- to work with (they are often called);
- those with which they perform, as well as its alloys;
- designed for welding copper and its alloys;
- for joining parts made of cast iron;
- those with which to produce surfacing and perform various repairs;
- designed for joining parts made of steels of indeterminate composition and hard-to-weld steels.
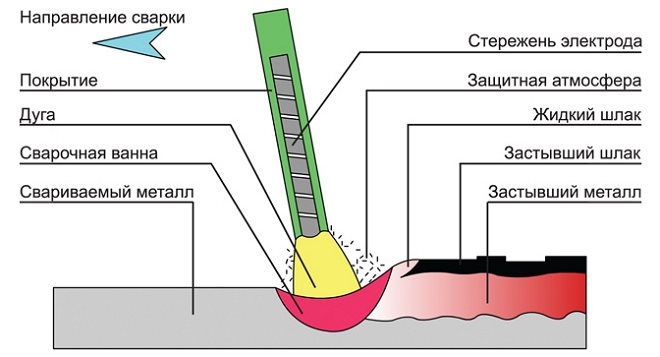
Various coatings can be applied to welding electrodes. According to the type of coverage, they are divided into 4 categories. The most common are electrodes with coatings of two types.
Products with a basic coating, which are called the main ones. The most popular products are UONI 13/55. It is worth choosing them if you need to obtain welds that correspond to high quality, which are distinguished by exceptional impact strength, ductility and mechanical strength. In addition, welds obtained when working with such electrodes are highly resistant to crystallization cracks. They are also not prone to natural aging. Their choice is worth making if you need to install critical structures that are planned to be operated in harsh conditions.

They also have a drawback: if their coating is moistened or there is rust, traces of oil or scale on the edges of the parts that are connected, then pores form in the weld. Pores in the seam can also form when welding is performed on a long arc. The disadvantage of using such electrodes is that they are allowed to work only on direct current and reverse polarity.
The second type is rutile-type coated electrodes. Products with such a coating, the most popular brand of which is MP-3, are successfully used for joining parts, the material of which is low-carbon steel. Welding electrodes of this brand are distinguished by the following technological advantages:
- stable arc burning during operation both on direct and alternating current;
- minimal spattering of material during welding with an inverter;
- the ability to obtain high-quality welds of any spatial position;
- easy separability of slag;
- welded seams have excellent decorative characteristics;
- suitable for welding surfaces covered with rust or dirt.
Selection of products according to other parameters
The type of current, as well as the polarity of its connection, are the most important parameters of welding operations. predominantly generate direct current, which can be connected to the workpiece and the electrode in two ways.
- Direct polarity. With this scheme, the plus is connected to the ground, and the minus is connected to the welding electrode.
- Reverse polarity. Such a scheme involves connecting the minus to the mass, and the plus, respectively, to the holder with the electrode.
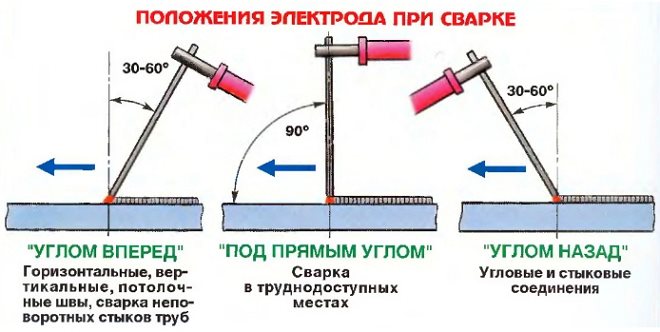
When deciding which electrodes to choose for welding structures of a certain thickness, you can be guided by the following criteria:
- for parts with a thickness of 2 mm, electrodes Ø 2.5 mm are best suited;
- when connecting parts with a thickness of 3 mm, electrodes Ø 2.5–3 mm should be selected;
- if the thickness of the parts to be welded is 4–5 mm, then electrodes Ø 3.2–4 mm are suitable;
- parts with a thickness of 6–12 mm are best welded with electrodes Ø 4–5 mm;
- when the thickness exceeds 13 mm, then the choice of electrodes Ø 5 mm will be optimal.
It is very important to choose the right electrode diameter, since when this parameter is exceeded, the welding current density decreases. This will lead to the fact that the welding arc will become unstable, the penetration of parts will deteriorate, and the width of the weld will increase. Many manufacturers indicate on the packaging information about which amperage values are best to use.

If such information is not contained on the package, then the following recommendations can be followed:
- for welding with electrodes Ø 2 mm, a welding current should be set, the strength of which is 55–65A;
- for products Ø 2.5 mm use a current of 65–80A;
- electrodes Ø 3 mm - current 70–130A;
- for electrodes Ø 4 mm, a welding current of 130–160 A is selected;
- products Ø 5 mm - current 180–210 A;
- It is better to cook with 6 mm electrodes at a current of 210–240 A.
As it becomes clear from the foregoing, for high-quality welding with an inverter, it is important right choice electrodes according to their diameter. You should also set the optimal strength of the welding current. If, for example, you are going to weld thin metal with an inverter using large-diameter electrodes, or the welding current exceeds the permissible values, then pores may form in the finished seam, which will significantly reduce its quality characteristics.
Electrodes of foreign manufacturers
Electrodes of the ESAB trademark have gained great popularity in the domestic market. A characteristic feature of the electrodes from the Swedish manufacturer is that their marking begins with the designation "OK", followed by 4 digits. Among the wide variety of models of electrodes of this brand, the following ones are most widely used.
- OK 46.00. According to their characteristics, they are very similar to domestic MP-3 products. Using an inverter, they can cook carbon, low alloy steels using direct as well as alternating current. When used, the high quality of the resulting connection is ensured.
- OK 48.00. They can work exclusively on direct current, they are used for the installation of particularly critical structures.
- OK 53.70. They belong to a specialized type, with their help they perform welding of root passes, joints of pipes.
- OK 61.30 and 63.20. They are used for inverter welding of stainless steel parts, but before purchasing them, it is important to clarify whether they are suitable for working with the grade of metal you are interested in.
- OK 68.81. With the help of products of this brand, inverter welding of parts from undefined steel grades, as well as from hard-to-weld grades, is performed.
- OK 96.20. They work on cast iron, and also connect cast iron parts with steel.
- OK 92.60. Are intended for welding of products from aluminum, its alloys with use of the inverter.
By the way, in the range of electrodes of this brand there are also products that can be used to weld copper and its alloys.
What to be guided by when choosing electrodes
Summarizing all of the above, a number of basic parameters can be distinguished, on the basis of which electrodes for inverter welding should be selected. First of all, you need to consider the type of materials that you are going to cook. If installation of a responsible structure is required, then it is better to choose electrodes from a well-established manufacturer for this. For example, ESAB products manufactured by a well-known Swedish manufacturer are well suited for such purposes.
If the surface of the carbon steel parts that you are going to weld with the inverter is rusty or wet, then it is better to choose electrodes with a rutile type coating.
Products with a basic coating are used in cases where it is necessary to perform inverter welding of particularly critical structures. The quality of welding with such electrodes also depends on how carefully you prepared the surfaces to be joined. To understand how such preparation is performed, you can watch a training video that is easy to find on the Internet.
A review of the best electrodes for manual welding of carbon and corrosion-resistant steels is compiled using publications from the journals Welding and Diagnostics, Metallurgical Bulletin and other specialized sources. The article summarizes online reviews of professional welders about products from different manufacturers.
Selection criteria
Unfortunately, Russian electrodes lose to many foreign counterparts in most parameters. However, "breakthroughs" in this area have already been outlined. Russian electrode products, manufactured at a few joint ventures so far, are no longer inferior to many venerable brands in terms of quality stability. Some factories of domestic subordination began to "pull up" to them. However, in cases where it is required to confidently ensure high quality of the seam, professionals still prefer to use more expensive, but also better foreign-made electrodes. For welding inverters any type of electrode is suitable, not all types are suitable for AC welding machines.
When choosing the best electrodes for review, we were guided by the following criteria:
- production volumes;
- product quality;
- getting the manufacturer into the reviews on the electrode industry;
- professional reviews.
For the correctness of the price comparison, we have included in the review only the most commonly used electrodes with a diameter of 3 mm.
The main parameter of any welding electrode, which determines most of its properties - from the ease of ignition to the quality of the seam - is the composition of its coating. The most common today are the following types of coatings:
- Rutile electrodes(and electrodes with a mixed coating on this basis - rutile-cellulose, and so on) have become one of the most popular due to the ease of ignition, including repeated, reduced (within reasonable limits) sensitivity to dampness. They can be used both on alternating and direct current in all directions of the seam, but when choosing a rutile electrode, you need to be careful - you can buy both a good electrode and a polluting seam with a huge amount of slag pits, suitable only for tacks.
- Basic coated electrodes are most often used when welding with direct current in especially critical places. When burning the coating in in large numbers stands out carbon dioxide, which reliably protects the weld pool from oxygen exposure. The seam itself is more ductile than when welding with common types of rutile electrodes. The other side of the coin is hypersensitivity to humidity and difficult ignition: it is much more difficult to cook with such electrodes.
Welding is today a demanded process both in the work of professional craftsmen and home specialists. With its help, you can repair metal products, as well as create new ones if necessary. For the quality of the seams to be worthy, a minimum experience with welding machine. Not the last role is played by correctly selected consumables.
Therefore, many novice welders are interested in the question of which electrodes to choose for. This process should be taken responsibly. The advice of experienced craftsmen will help you understand the difference between the material presented and choose best option for every type of work.
Characteristics of inverter welding
Before choosing electrodes for it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the features of this process. It involves the use of special equipment. The inverter is a welding machine that uses the fusion method in the arc welding action.
The advantages of such a technique in comparison with transformer varieties have long been appreciated by professional craftsmen. Inverters today are used much more often than other types of equipment. This is due to their stable welding current performance. At the same time, it turns out to be very durable and of high quality.
An inverter unit equipped with a rectifier is capable of generating direct and alternating voltage when turned on. If there is no mains filter, only a constant voltage is obtained at the output. This feature must be taken into account when carrying out work.
Welding scheme
Using the inverter in your work, you need to familiarize yourself with its scheme of action. Electrodes are the main consumable material of this equipment. They are made in the form of a metal rod through which current flows to the working surface. When studying which electrodes are best for inverters, you should delve into the scheme of equipment operation and the process.
When operating the inverter, other devices are also involved. These include the control system (or rectifier), the transformer, and the frequency converter. This allows the device to work with different materials. Even the same instance of the installation involves the use of different brands of electrodes when welding various materials. Therefore, their choice must be given special attention.
The essence of the electrodes
When studying the question of which electrodes are best to choose for welding with an inverter, you should familiarize yourself with the design of this consumable. As mentioned above, the same model of the device is used in different conditions. Therefore, the electrodes have to be selected according to the working process.

Modern production produces the predominant part of its products in the form of consumables for inverters. This tool is made of metal wire. This rod is pressed with a layer of a special coating. It is designed to ensure combustion stability, as well as protect the weld pool from exposure to atmospheric air. Materials for the production of such products are used very different. Production norms electrodes is regulated by GOST 2246, approved back in 1970.
Varieties
When deciding how and which electrodes to choose for welding with an inverter, you must refer to the above GOST. He says that there are three types of consumables suitable for such work. The electrodes can be carbon, alloyed and highly alloyed. They are made from different types wire.

A beginner who is going to make inverter welding at home does not have to delve into such varieties at all. It should only be noted that all electrodes are divided into two large groups. The first category includes materials intended for critical structures, and the second - for ordinary ones.
If welding is not involved in the process of creating load-bearing metal structures, which will be subjected to significant pressure, then simple varieties of products should be preferred. When using an inverter for household needs, this will be quite enough.
Overview of household electrodes

The first type of electrodes do not cause problems during operation. They are easy to ignite without requiring pre-ignition. For a novice welder, ANO is the best option. MP-3 is considered a universal consumable. It allows you to weld even on rusty, dirty surfaces, as well as in wet conditions.
Overview of professional electrodes
When studying which electrodes to choose for welding with an inverter, for critical types of structures, it is necessary to choose brands such as MP-3C, as well as UONI-13/55. They belong to the group of consumables used to create critical structures.
With increased requirements for the quality of the finished seam, it is better to give preference to the MP-3C brand. Such electrodes are used in metal processing with direct, alternating current of reverse polarity.
For particularly demanding work in welding load-bearing structures you should choose consumables brand UONI. However, only a professional master can work with them. For a beginner, the capricious nature of such an electrode will be too tough. But, having learned how to handle SSSI, you can create the most durable seams with high density (and even at low temperatures).
Type of metal
When studying which electrodes to choose for welding with an inverter, you need to pay attention to the type of working material. Each metal has its own types of welding rods.

For cast iron, it is necessary to give preference to electrodes of the OZCH-2 type. Their production is regulated by GOST 9466 of 1975. If it is necessary to carry out work with it, it is better to purchase ANO-4 products with a rutile top layer or ANO-6, which have an ilmenite type of coating.
Ordinary carbon steels require the use of electrodes OZS-4, MP-3S, MP-3, UONI13/45, ANO-21, etc. Stainless and high-alloy steels require the use of consumables for inverter welding under the TsL-11 brand.
How to choose an electrode
Having considered which electrodes are better to choose for inverter welding, it is worth saying a few words about the features of their purchase. First of all, it is necessary to pay attention to the composition of the coating applied to the product. This information can be found in the instructions for use. This will allow you to choose the right variety in accordance with the type of material.

Also, do not purchase products that do not have the appropriate quality certificates. This may not be safe. The quality of the seams when using dubious materials can be very different from the desired result. Therefore, the selection and purchase process must be taken responsibly.
Having considered which electrodes to choose for welding with an inverter, even a novice master will be able to acquire the right variety. The work will be done quickly and safely. The result will be good even for a beginner.