Types of particle boards. Pressed plywood: material description, production technology and price.
The use of waste from the woodworking industry as a raw material for the manufacture of various sheet materials has long been put on an industrial basis.
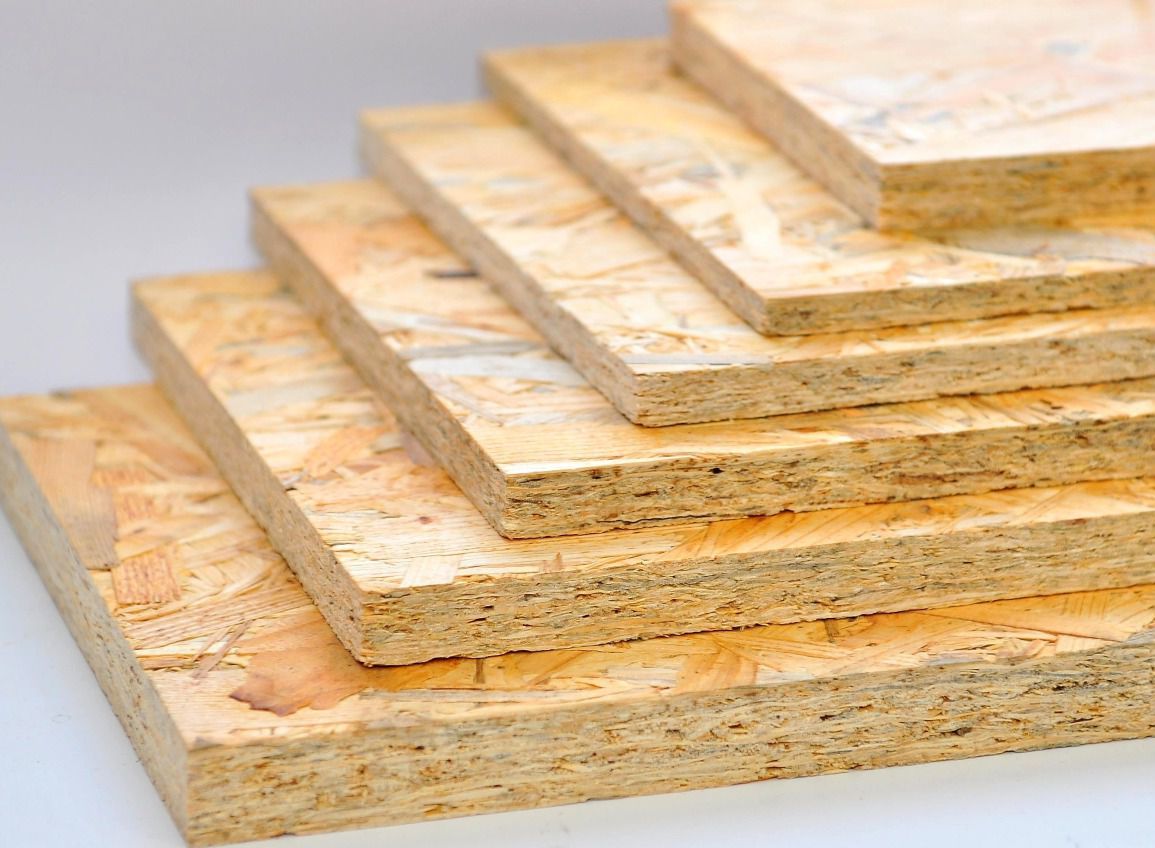
OSB boards, like plywood, are sheet material made from flat wood shavings of coniferous species by hot pressing with the use of phenol-urea-formaldehyde waterproof resin as a binder.
For the manufacture of such wood slabs, chips of certain sizes are used, up to 180 mm long and 6 to 40 mm wide. Each layer of wood shavings is laid in a strictly defined order: the inner layer is located in the transverse, the outer layers - in the longitudinal direction of the sheet. Most often, OSB boards are made four-layer. Such a layered cross OSB structure plate creates additional rigidity of the finished sheet, reduces its plasticity and possible deformations during laying, equating specifications OSB boards made of wood to plywood parameters. To increase the protective properties of the boards, synthetic wax and a salt of boric acid are added to the resin, and only then, under the influence of high temperature and pressure, the process of hot pressing wood chips into boards takes place.
Types of OSB boards
Depending on the indicators of mechanical strength and moisture resistance, OSB boards are divided into four types:
- OSB-1. It has low moisture resistance and low mechanical strength. Use a plate of this type only for the manufacture of furniture and as a packaging material.
- OSB-2. With high mechanical strength, this type of plate has low moisture resistance, so it can only be used in dry rooms. OSB-2 is widely used for the manufacture load-bearing structures floor beams.
- OSB-3. Possessing good moisture resistance and strength, plates of this type are used for the manufacture of load-bearing structures that can be used in conditions of high humidity.
- OSB-4. Very high mechanical strength and moisture resistance make it possible to use boards of this type in the most difficult conditions.
OSB boards are also divided into several types depending on the features:
- varnished OSB boards, one side of which is varnished
- laminated boards used as reusable formwork when constructing monolithic reinforced concrete floors
- tongue-and-groove plates having tongue-and-groove connecting spikes at the ends.
The thickness of the OSB board is from 6 to 38mm. The most common sheet size is 1250mm*2500mm. The advantages of OSB boards over other sheet materials based on woodworking products include good fire resistance, the absence of structural defects in the form of knots and voids inherent in solid wood, resistance to mechanical stress and moisture, good heat and sound insulation, as well as low material cost. The disadvantages inherent in the OSB board are the strength indicators (lower than that of plywood), as well as the need to finish the surface of the boards when used indoors.

Scope of OSB boards
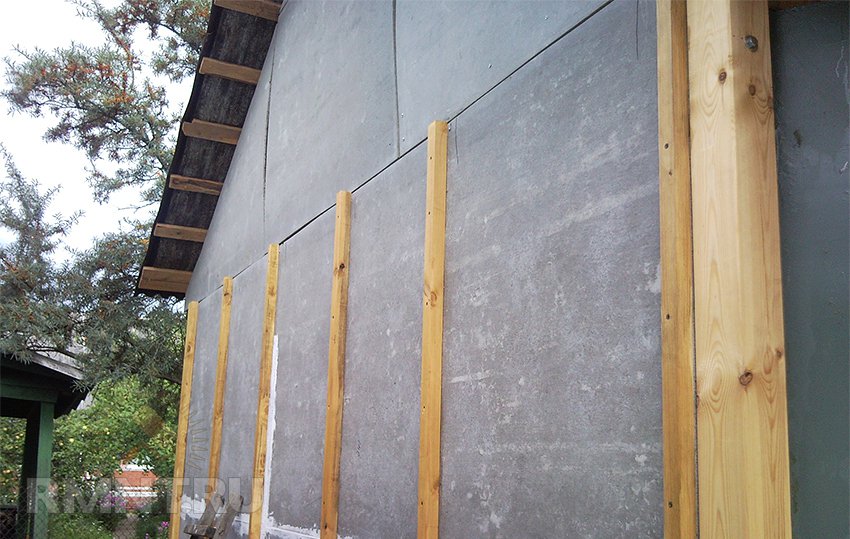
The technical characteristics of the OSB board allow it to be used in many areas, primarily as a wall material. Slabs of this type can serve as a rough deck. OSB boards are fastened to a wooden frame using self-tapping screws. Widely applied OSB plate in the construction of small architectural forms, temporary buildings and structures, as well as in the conversion of the attic space of the house for living quarters. Plates of this type are also used for the manufacture of wall and ceiling sandwich panels. When creating a roof from bituminous tiles, the OSB plate is used for the construction of a continuous flooring, on which the shingles of the tiles are fixed.
There are two ways to fix OSB boards:
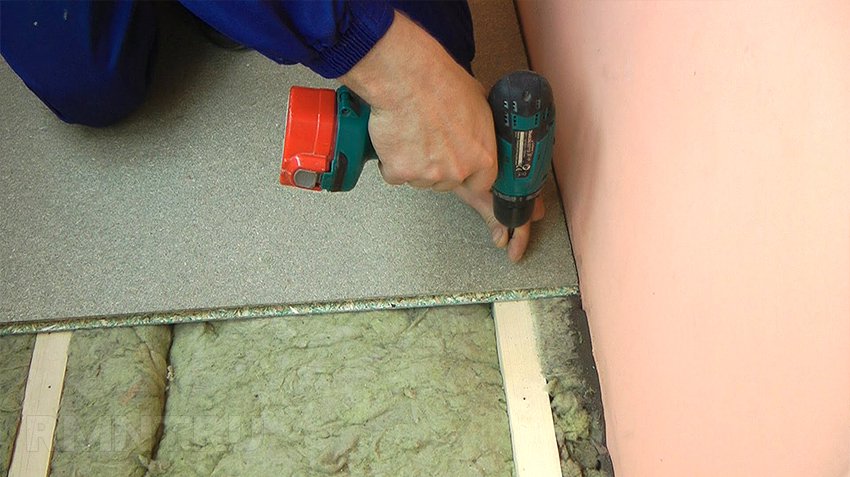
- directly to the rafters, the pitch of which should not exceed 600 mm when mounting the sheet perpendicular to the direction of the rafters,
- to the crate from the rail. The minimum distance between the laths of the lathing with a section of 50 × 30 mm with a plate thickness of 12 mm should be no more than 400 mm. A prerequisite for laying slabs is the displacement of vertical joints. When fixing the plates to the crate between the mineral insulation, which is placed in the space between the rafters in case the attic space is residential, and the OSB flooring of the plate, a ventilation gap remains through which water vapor will be removed.
The use of OSB boards in the manufacture of I-beams wooden beams allows you to get a light and durable overlap with good bearing capacity. Beams of the same type are used as load-bearing elements for panel formwork when constructing monolithic reinforced concrete floors. OSB laminated boards 22 mm thick are used as formwork panels. OSB board is also widely used in flooring as a rough base, on which laminate, linoleum or carpet is then laid.
In construction, as well as in repair work, wood-based panels are often used. There are quite a few types of such plates, they are all made according to various technologies and have certain characteristics. In this article, we will take a closer look at different types wood-based panels, we will talk about their features and applications.
Natural wood is the main raw material for the production of such material, and therefore the boards have all the positive qualities inherent in it. For example, like the tree itself, the plates have good thermal insulation properties and are highly environmentally friendly. During the manufacturing process, special components are added to them, which help to minimize the disadvantages inherent in natural wood.
The advantage of boards is that they are produced in various formats and are easier to work with than logs and boards. It is impossible not to take into account the price of such material, because it is much lower than the cost of natural wood.
Types of wood boards
Plywood
Plywood is a building and finishing material that has a sheet format and is produced by joining thin layers of wood veneer. Veneer sheets are glued together so that the fibers of each subsequent layer are perpendicular to the fibers of the previous one. The number of layers of veneer varies from 3 to 23, which determines the thickness and strength of plywood. In addition, plywood is divided into 2 types: equal-layer and unequal-layer. In the first case, all layers of the material have the same thickness, in the second, the middle layers are somewhat thicker than the outer ones.
The manufacturing technology of wood-based panels of this type is different, depending on this, several types of plywood are distinguished:
- Peeled plywood is made by cutting thin sheets of wood from a rotating log.
- Sawn plywood is made by sawing wood into thin strips, the thickness of which does not exceed 5 mm.
- Sliced plywood is made from planed layers, the thickness of which is 3.5 mm.
Such material is also classified according to the type of raw material used. Depending on the type of wood that is part of the sheets, plywood is divided into the following types:
- Hardwood material - it is made from hardwood trees, such as maple, alder, poplar, aspen or birch. Birch is considered the most popular raw material because it is quite durable and has an attractive texture. Plywood of this type is used as a finishing material, to create furniture and cars, as well as in construction.
- Coniferous plywood is made from conifers: pine, fir, larch and Siberian cedar. The last two types of wood are most often used for the production of decorative plywood for interior decoration. Since the feedstock in this case has a high resin content, the material is durable and moisture resistant.
- Combined plywood incorporates the raw materials of the two types listed above. Her distinctive features are strength and moisture resistance. The scope of the material is quite wide, but most often it is used for the manufacture of furniture.
In addition to the above features, plywood is also classified by grade:
- FSF - this abbreviation refers to plywood with increased water-repellent characteristics. Its component composition includes phenol-formaldehyde resins - they make the material waterproof, and also protect it from fungi and mold. Due to its resistance to high humidity, such plywood can be used in outdoor decoration.
- FC is plywood with average moisture resistance. Layers of such material are interconnected using carbamide glue. This substance makes plywood durable, but does not give it waterproof properties. In addition, plywood of this brand does not tolerate temperature fluctuations well and is not resistant to mold development. Such sheets are not suitable for outdoor use, but are widely used in interior decoration, as well as in furniture production.
- Bakelite plywood is abbreviated FB. Such material is produced by gluing veneer sheets with bakelite varnish and synthetic resins. The final product is moisture-resistant, refractory, wear-resistant and very durable. Plywood of this type is well tolerated by temperature fluctuations and prolonged exposure to moisture, which makes it possible to use it in exterior decoration, as well as in the field of ship and automotive industries.
- FBA is plywood, the layers of which are interconnected using albumin-casein glue. This glue is of natural origin, so the material is environmentally friendly. But plywood of this type does not have high moisture resistance, so it is used only for interior work or in the manufacture of furniture.
- Aviation plywood grade BS is produced by gluing veneer sheets with bakelite alcohol-soluble glue. This glue makes plywood extremely durable and waterproof. The positive qualities of such a material should also include its flexibility and elasticity, biological stability, and the ability to withstand the influence of aggressive chemicals. Plywood of this type is used in shipbuilding and aircraft construction. Due to the high price, the material is rarely used in the construction of buildings.
- BV is plywood, the layers of which are glued together with water-soluble bakelite glue. According to its characteristics, it almost does not differ from the previous version, but is inferior to aviation plywood in terms of its moisture resistance.
- Laminated plywood has a special coating on both sides, which is distinguished by increased strength and decorative effect. Such a coating is resistant to physical influences, tolerates moisture and direct contact with water well, and prevents the destruction of the inner layers of plywood. Most often, such material is used for decorative interior decoration premises or for the manufacture of furniture.
As you can see, different types of plywood have their own distinctive properties and have a specific scope. But all these types can be combined with common positive qualities:
- All plywood is highly durable and wear resistant. This feature is due to the structure of the material, namely, the fact that different layers of veneer have a perpendicular arrangement of fibers.
- Plywood is easy to work with, its sheets are easily cut into fragments, and its light weight facilitates the installation process.
- The cost of plywood is relatively small, much lower than that of solid wood. And the reason is that wood waste is often used to make the material.
- Plywood can be bent, thanks to which it is given different shapes. This allows you to make original curly furniture and other interesting details.
- Such material has excellent thermal insulation.
Along with the advantages, plywood also has certain disadvantages:
- Many brands of this material do not tolerate prolonged exposure to moisture and water.
- In the production of plywood, especially high-strength and moisture-resistant, substances with a certain degree of toxicity are used.

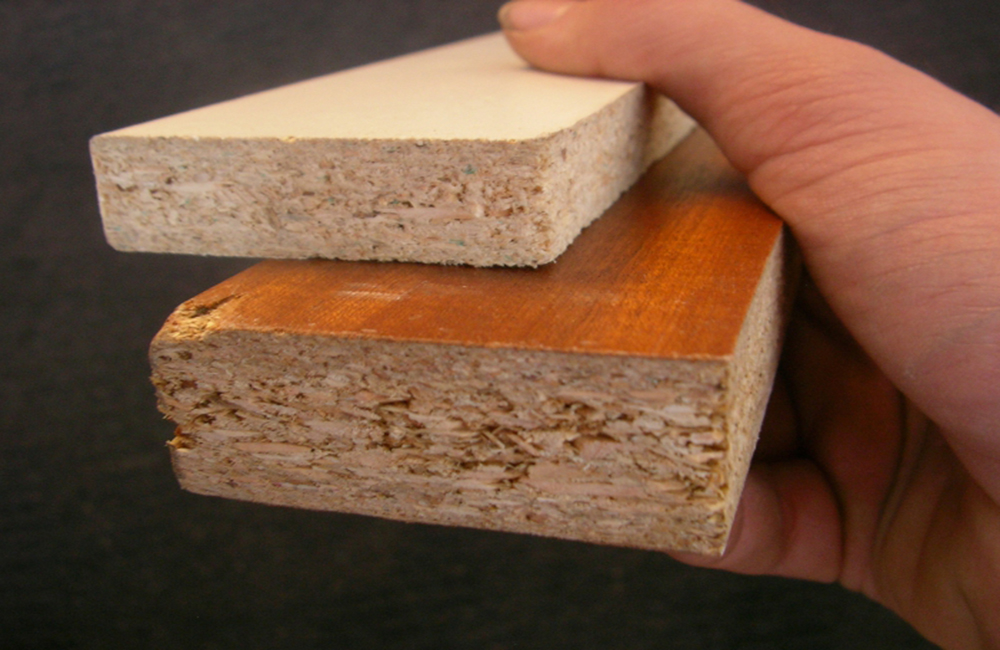
Chipboards
Chipboard is a combination of sawdust and a binder, which are joined together under high temperature and pressed into boards. These slabs are subsequently cut into individual sheets. As a rule, the binder is urea-formaldehyde or phenol-formaldehyde resins. Due to the fact that the constituent parts of the material are reliably and firmly interconnected, chipboard boards are different thickness, while the density and uniformity of the finished product does not suffer.
Chipboards are classified according to different criteria:
- Depending on the appearance material, it is divided into two grades, there are also plates that do not have a grade at all. The first variety differs most high quality: uniform structure, beautiful texture, no defects. The second grade has slightly worse characteristics, and chipboard without a grade is considered the lowest quality material.
- Depending on the number of layers, chipboard is divided into single-layer, double-layer and multi-layer boards.
- Chipboard is also classified according to the type of surface treatment. So, material of polished and unpolished types is distinguished, in addition, there is a separate variety - laminated chipboard. The sides of this material are covered with a melamine film, which is glued to the boards under high pressure. There is also laminated chipboard, the outer coating of which is highly decorative.
- Depending on the amount of formaldehyde, chipboard comes in two classes. Class E1 contains no more than 10 mg of formaldehyde per 100 g of sawdust. Class E2 contains from 10 to 30 mg of the substance per 100 g of dry sawdust.
- Chipboard is also classified according to the criteria of strength, water resistance, hardness. In total there are 2 types of plates: P-A and P-B. The first option has higher rates in comparison with the second one.
- The production process of such material can also be different. Pressing technology can be flat or extrusion types.
- Depending on the density of chipboard, there are 3 types. Plates low density have an indicator of 550 kg / m 3, for medium density chipboard this value is from 550 to 570 kg / m 3, and high-density boards have an indicator exceeding 750 kg / m 3.
- The surface texture of particle boards also varies. Depending on this indicator, coarse-grained and fine-grained plates are distinguished.
The general positive qualities of chipboard can be presented in the form of a list:
- Such material has higher strength characteristics compared to ordinary wood.
- Chipboards are moisture resistant because they contain a large number of artificial resins.
- The price of chipboard is much lower than that of natural wood.
- The process of working with the material is not difficult.
Like any other construction material, chipboard has a number of disadvantages. The most significant of them is the presence of toxic formaldehyde in the composition of the material. In addition, such plates are fragile and cannot be used in the manufacture of small parts. Self-tapping screws and screws in chipboard boards loosen over time, and it is no longer possible to re-tighten them in the same place.
Chipboards are used in a variety of areas: in interior decoration, in the arrangement of roofs, walls and floors of buildings, in furniture production, in the creation of warehouse racks and various collapsible structures.
Cement particle boards
Another type of wood-based panels is cement chipboard. It is a large-format sheet made by mixing sawdust, Portland cement and various chemical additives. The components of the larger fraction are located in the central part of the plates, the smaller particles are outside. Thanks to this structure, the material is not only durable, but also smooth.
Cement particle boards are of several types:
- Fiberboard is a material made from long-fibred wood shavings. The density of such plates is small and is approximately 300–500 kg / m 3, while the thickness reaches from 3 to 15 cm. Fibrolit has softness and low weight, its main scope is the insulation of walls and ceilings, filling frame structures. Plates of this type are very easy to use, and also have good resistance to various microorganisms.
- Arbolit is made from small sawdust and has a higher density than its above-mentioned counterpart. Like fibrolite, arbolite has good thermal insulation qualities, due to which it is used as a wall insulation. The material is also used to create panels, wall blocks and reinforced floors.
- Xylolite is a combination of components such as sawdust, concrete and magnesia binder. Depending on the production technology, xylolite can be cast and slab. Distinctive properties of such material are high strength, resistance to mechanical damage, good shockproof qualities. During the manufacturing process, xylolite can be dyed to desired shades by adding special powder pigments. Most often, such material is used for arranging the floor, because in terms of its strength it is not inferior to concrete, but it has much better thermal insulation characteristics.
The positive properties of cement particle boards include the following qualities:
- good strength characteristics, which are achieved due to the multilayer structure of the material;
- relatively low price, especially in comparison with the cost of natural wood;
- resistance to water, fire, low temperatures;
- environmental friendliness and safety for health;
- excellent soundproof qualities;
- high biological stability, thanks to which the material is reliably protected from attacks by insects and harmful microorganisms;
- ease of work;
- durability - the average service life of cement particle boards is at least 50 years;
- the possibility of finishing plates with almost any facing materials.
There are not so many disadvantages of cement-bonded particle boards. These include a large weight, which makes the installation process more difficult, as well as a small bending strength, due to which the plates can break if mishandled.

Oriented strand board
In the modern construction market, OSB boards have become quite a popular product designed for external and internal construction works. OSB boards are created by mixing shredded wood with waterproof synthetic resins. The chips are pressed with a binder under high temperature conditions. The final product is a durable multi-layer material, the individual layers of which have different grain directions. OSB boards come in several types:
- OSB-1 is the cheapest and least durable material that does not have high moisture resistance. Such plates are most often used in furniture production or in interior decoration of rooms. This material is not suitable for outdoor work.
- OSB-2 is also not considered moisture resistant, but it has higher strength characteristics than the previous type. Plates of this type are used to create ceilings, partitions, load-bearing structures. For exterior finish such material is also not used.
- Moisture-resistant OSB-3 wood boards can be used in outdoor decoration, because along with water-repellent properties, they also have good strength.
- OSB-4 boards are considered the most durable and durable. They are completely unaffected by high humidity, so they can often be found in the construction of roofs, walls and load-bearing elements.
A separate type of material is laminated oriented strand boards, which are convenient to use for creating reusable formwork. And the plates, equipped with a groove-comb system on the end sides, are used as a finishing material.
The positive properties of oriented strand boards include:
- Good strength characteristics, because during the production of the material, the layers of wood are superimposed on each other in such a way that the fibers have a different direction.
- Durability. The service life of OSB boards is at least 50 years.
- Relative ease of use. OSB sheets are easy to cut into pieces, and their low weight facilitates their installation. Among other things, the structure of the material is strong enough, so that when sawing and drilling, chips and cracks do not form.
- Acceptable cost.
- High heat-saving and soundproof qualities. Oriented particle board for walls will provide coziness and comfort in the room.
- Resistant to moisture and fungus.
- Convenient format, thanks to which the finished surface will have a minimum of joints.
Oriented strand boards also have disadvantages, these include:
- Toxic substances that are one of the components of the material. If the plates are supposed to be used in interior decoration, when buying, you should pay attention to their environmental class.
- Flammability is another disadvantage of OSB boards.
- Such material requires additional insulation, as it tends to absorb water, swell and deform.

fibreboard
Boards of this type are made from wood or other plant fibers, which are glued together with artificial resins. The component composition of the material also includes various additives and fillers. There are 2 ways to produce fiberboard boards. The first method is called dry and involves the use of synthetic resin. In the wet method, chemical binders are not added to the composition of the material.
There are 4 main types of fibreboard:
- Superhard - these are plates whose density exceeds 1100 kg / m 3. Such a material has high strength and can be used to create outdoor structures and furniture parts, as well as for flooring. This type of fiberboard, in turn, is divided into 2 varieties: ST and ST-S plates. The first option has high strength, but does not differ in decorative effect. The second variety has a refined outer side.
- Solid fiberboards have a density of about 850 kg/m 3 . This material is also highly durable and can be used both in interior decoration and in the creation of exterior structures, for example, balcony doors. Solid fiberboards have several brands that differ in their appearance. Among them, both unennobled types of material are distinguished, as well as more decorative ones, the outer side of which consists of a finely dispersed mass and can be painted in various shades. The surface of fiberboard can be matte and glossy. In the first case, the plates are painted with polyvinyl acetate water-based compositions, in the second - with enamels containing artificial resins. There are also plates with a decorative texture that imitates various surfaces. This texture is achieved thanks to a special paper covered with a synthetic film on top.
- Semi-hard fiberboards are also called MDF boards. Such material is more environmentally friendly than its counterparts. The positive qualities of MDF include moisture resistance, as well as resistance to fire and damage by microorganisms. MDF has a sufficiently high strength and is used in the manufacture of furniture, in the decoration of walls and floors of premises. The structure of such plates is solid and homogeneous, so the material can be processed in various ways, without fear of cracks and chips.
- Soft fiberboards are not used in outdoor decoration, because they do not have sufficient strength and moisture resistance. This material has found its application in interior decoration, where it performs decorative and heat-insulating functions.
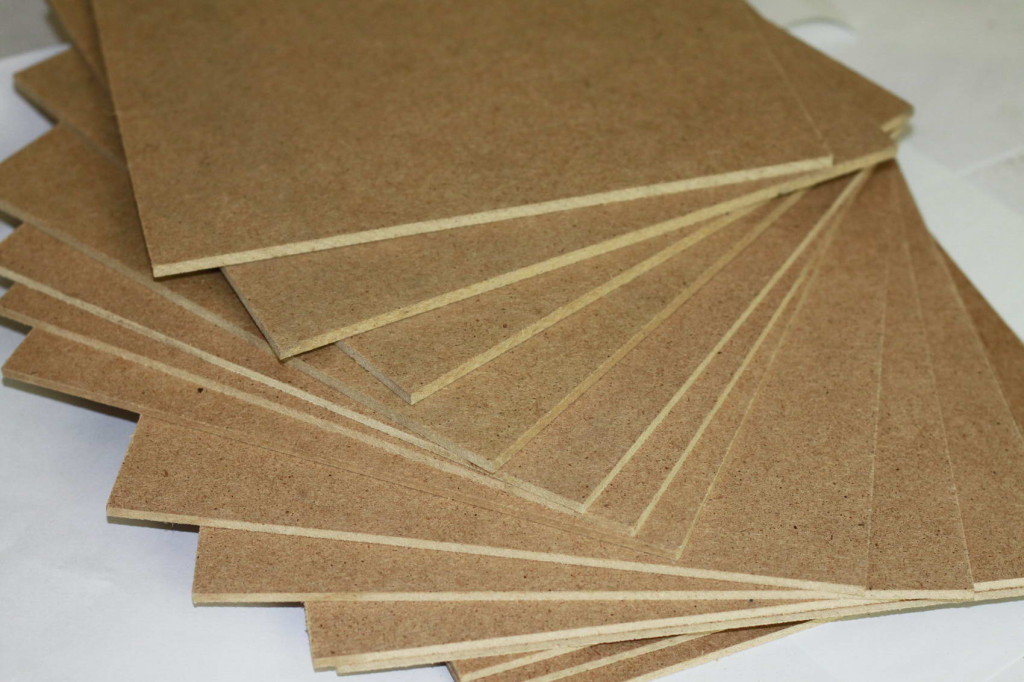

Wood boards, photo:
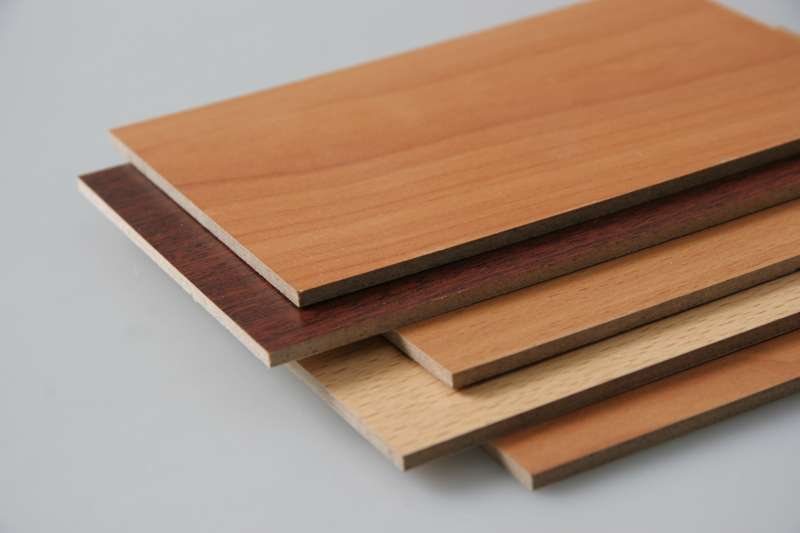
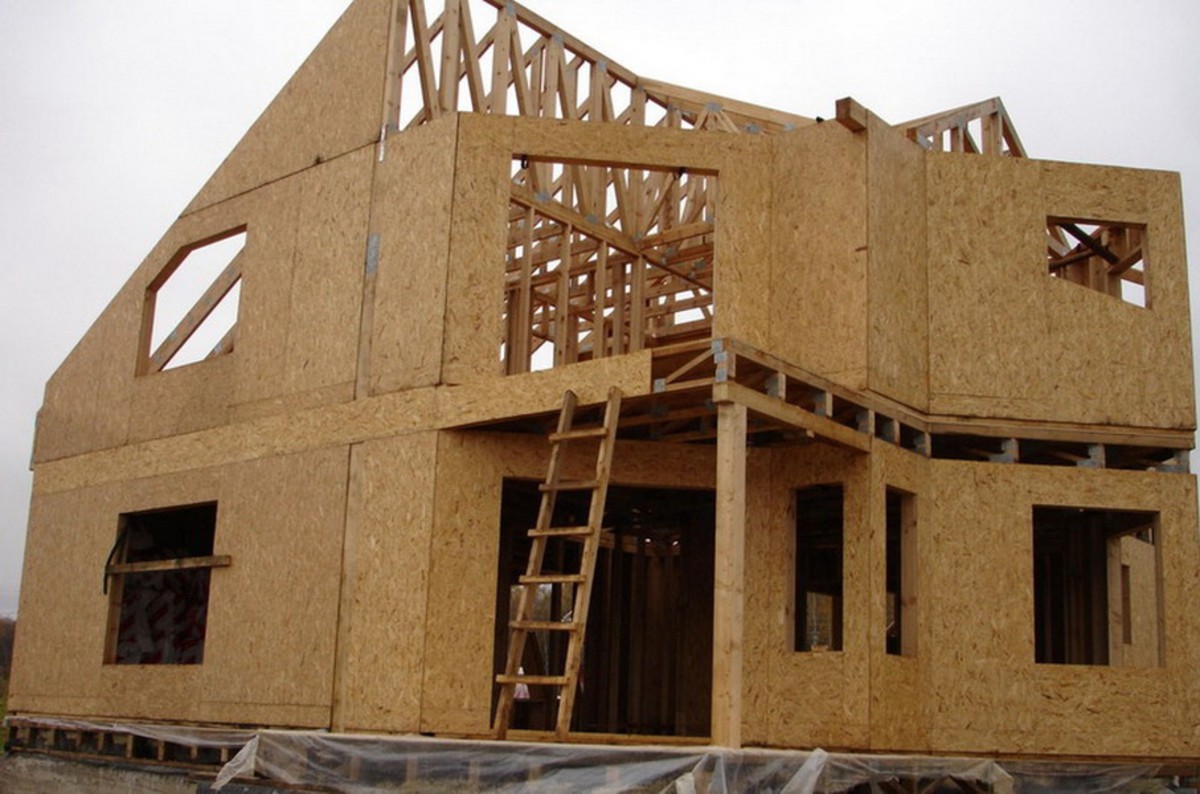
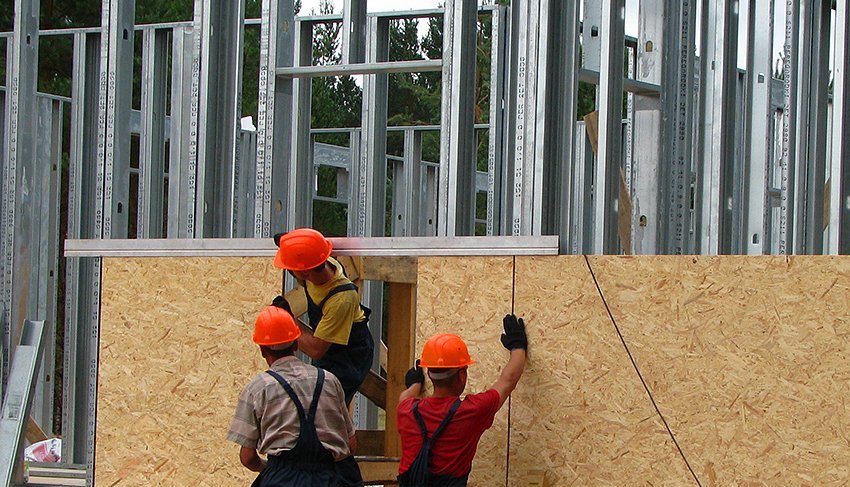





The use of wood-based panels in practice. Video
The ability to retain heat and create coziness in the house, wood retains even in small fragments pressed into slabs. Various types of chipboard and fiberboard have found application in leveling walls using dry plaster technology, creating partitions. Outside, they are used for insulation, cladding and decoration of the facade, they create platbands for windows and doors. In the furniture industry, the front of the furniture and the back walls of their pressed sawdust are made from laminated sheets. The material is easy to work with.
Building materials from production waste are much cheaper

In the woodworking industry, including all its types, less than half of the volume of wood is used. Even after removing the branches and removing the bark, the uniform pattern of the boards is spoiled by knots and sapwood. Now panels and plates are made from:
- chips;
- sawdust;
- shavings;
- scraps, loosened into fibers.
The material has characteristics close to natural wood. The strength and ability to resist water without warping is higher. The cost of such finishing is much lower. You can make insulation and budget repairs with your own hands.

To give a decorative look, the surface of the plate is treated in various ways. Apply:
- grinding;
- lamination;
- lining;
- staining.
Inside buildings, chipboard and fiber boards are used to make partitions and doors with good thermal insulation and noise dampening. Thin sheets are used for wall decoration, creating niches, shelves and other interior elements. Trimmings made from pressed sawdust decorate windows and doors inside and outside houses. Knowing simple rules material processing, you can make repairs with your own hands.
Characteristics of wood fiber materials

Wood fiber is located in the slabs longitudinally or perpendicularly. The outer layers are dense and there is a looser layer between them. This division can be seen from the end of the plate. The main types of fiberboard:
- hardboard - lined with fiberboard;
- biostable;
- with the addition of bitumen;
- slow-burning.
Wood fiber boards have different hardness and dimensions. They are used for finishing and insulating facades, creating sound-absorbing partitions. Fiber cloth serves as an excellent material from which you can make soundproof doors and architraves for interiors with your own hands and buy ready-made ones. For the interior, it is better to use bioresistant boards with a minimum release of harmful substances.
Wood fiber materials are better glued to the wall than fastened with self-tapping screws to the frame. The screws do not hold well in loose material and fall out over time. For decoration, hanging shelves and decor, you can use dowels, hammering them into the solid wall masonry material.
Pressed particle boards in interior design

Wall cladding with chipboard
Chipboards are made from chips by pressing with a binder composition of synthetic resins. Loose middle layer obtained from larger fragments. External dense and polished. Three main types are distinguished by density and hardness. They are presented in the table.
After grinding on a part of the product, a decorative chipboard surface finish is performed. Applicable:
- lamination;
- laminating.
The first method is high pressure paper coating with wax and resins. The decorative surface becomes part of the slab.
Laminating does not require special equipment. You can stick the film to the surface with your own hands. Lack of weak grip at corners and edges.
For interior decoration, chipboard with the E-1 marking is better suited, containing the least amount of formaldehyde. This type of chipboard is allowed to create children's furniture. Craftsmen can make it with their own hands and use sheets for residential premises, make and install trim on interior doors.
A large selection of chipboard finishes imitates the veneer of various tree species. This allows you to give the panels and walls of the interior of the house the appearance of sheathing with natural boards or clapboard. Make lamination - glue the film, you can complete the installation of particle boards or after cutting for finishing with your own hands. Platbands are constantly exposed to friction and shock, so it is better to buy them laminated ready-made.
Internal architectural elements made of chipboard

When building a house with your own hands, solid chipboards can replace natural wood when creating many elements of interior architecture:
- steps of stairs;
- partitions,
- base for flooring;
- ceiling lining;
- wall alignment;
- platbands;
- arch design;
- niches and built-in cabinets hiding pipes and counters.
For wall decoration, especially in summer cottages and in wooden houses, Chipboard is one of the best budget options. The multidirectional arrangement of chips eliminates warping when water enters and temperature changes. In buildings with seasonal residence, moisture-resistant options for interior decoration can be used. They have a greenish tint from impregnation with antipyrine.
Manufacturers began to produce tongue-and-groove chipboard, including moisture resistant ones. The decorative film on them can be easily glued with your own hands after finishing. During the construction of a house, they are used as formwork, wall and floor cladding.
Facade decor from fiberboard and chipboard

Lamination makes the chipboard surface resistant to moisture on the surface of the walls. When working with such panels, it is important not to forget to carefully isolate the ends and cut points with a self-adhesive film or primer. When finishing the facade, moisture-resistant sheets are also used, followed by puttying and painting.
Hard material does not lend itself well to fine workmanship. When creating carved platbands for windows, you have to use special cutters. Then the surface is polished and after deep impregnation with a primer it is painted.
Ready-made platbands of a simple configuration are sold in stores with a laminated moisture-resistant coating for various types of wood.
Chipboard of high hardness is used to create the walls of summer cottages, followed by varnishing. Sawdust materials are great for warming wooden houses. At the same time, decorative elements of the facades are created and attached to the walls with glue and self-tapping screws. Be sure to need a lining that protects against direct contact with water, UV rays. You can make a wet facade and ventilated.
In the furniture industry, fiber and particle boards are widely used.

Chipboard is widely used in the furniture industry. Laminated sheets go to the front and sides. For the manufacture of the rear wall, unlined materials from small chips or sawdust are used. It is much cheaper than natural solid wood products.
When making cabinet furniture with your own hands, you must remember that the base must be made of wooden beams or a metal profile. Holes are drilled for screws. Elements are additionally planted on a special glue. For fixing accessories for self-tapping screws, it is advisable to use adhesive putty. It will keep the material from destruction and the screw will hold on for a long time.
Wood boards retain all the advantages of natural wood and at the same time are practically devoid of its shortcomings. Consider the main types of material and its varieties. Let's get acquainted with their advantages, disadvantages, cost and scope.
Why Choose Wood Boards
Wood boards are materials made on the basis of natural wood with various additives: mineral binders, synthetic resins, etc. The result is products with high performance characteristics, specially designed to solve certain technological problems. The appearance of wood-based panels on the construction market was due to the desire to obtain a material that retains all the many advantages of natural wood, but at the same time devoid of most of its shortcomings.
Wood is known to change size and shape under the influence of changes in temperature and humidity. environment. Uneven removal of moisture leads to stress and cracking of the wood. It is also susceptible to fire, insect damage and decay. In addition, a natural material is anisotropic, that is, a change in its mechanical characteristics for a number of reasons: depending on the direction of the fibers, the breed, the zone of growth, the presence and location of defects, etc.
Almost all of these shortcomings are deprived of wood-based panels, however, they nevertheless retain the performance characteristics of natural wood. Technological features of production make it possible to produce them in different sizes, including in the form of large sheets, which makes it possible to get rid of another unpleasant feature of wood - not always a convenient "format" of the material. Wood boards are more affordable, including at a cost. They are widely used in construction, being considered indispensable for some work. Let's take a closer look at each type of material.
Plywood is a wood-shaving material in the form of sheets consisting of pressed wood veneer sheets tightly fastened together. They are glued together so that the fibers of adjacent layers are mutually perpendicular. The minimum number of veneer sheets is 3, the maximum is 23 pieces. There are equal-layer plywood, where the thickness of the veneer plates is the same, and uneven-layer plywood, which has wider middle layers.
![]()
Depending on the manufacturing technology, plywood is distinguished:
- Shelled. During the production process, wood is cut from a rotating block of wood.
- sawn. Raw materials sawn into thin, about 5 mm thick, strips are used.
- planed. Sliced veneer up to 3.5 mm thick is used.
Depending on the type of wood used for the production of boards, plywood is distinguished:
- Deciduous. Alder, aspen, poplar, maple are used for its manufacture, but most often birch, which is characterized by increased strength and beautiful texture. Hardwood plywood is used in construction, decoration, furniture, automotive, etc.
- Coniferous. Made from coniferous trees. Raw materials, naturally saturated with resins, provide better moisture resistance of the material. In addition, coniferous wood-based panels have an attractive texture, are light and quite durable. Widely used in construction and furniture manufacturing.
- Combined. It is made from wood of both types, combines strength and moisture resistance, while maintaining an affordable cost. It is used in construction and furniture manufacturing.

There is another classification of plywood that divides the material into several grades:
- FSF or plywood of increased moisture resistance. Produced using phenol-formaldehyde adhesive resins, which give the material a special moisture resistance and biostability. The size of the boards is slightly inferior to other brands of plywood. The material has class D4, which allows it to be used for outdoor work. It is also used for interior decoration of buildings, car interiors, street fences, concrete formwork, etc.
- FC or plywood of medium moisture resistance. In the process of gluing veneer, carbamide adhesives are used, which give the finished board a high strength that exceeds the strength of the original wood. However, the moisture resistance of such materials is low, the class does not exceed D3, therefore, it cannot be used for outdoor work. The biostability of FK plywood is also insufficient; with prolonged moisture, fungi can begin to develop in it. The material also reacts to sudden changes in temperature. Used for interior decoration and furniture production.
- FB or plywood baked. Veneer plates are glued with bakelite varnish and synthetic resins, which allows the material to be used in fairly harsh weather conditions. The wood board is durable, has increased moisture resistance, fire resistance and wear resistance. Easily withstands sudden temperature changes. It is used in construction, including for outdoor work, shipbuilding and automotive industry.
- FBA. Material glued with natural albumin-casein glue. Such impregnation makes plywood non-moisture resistant, which significantly limits the scope of its application. The main advantage of the FBA brand is absolute environmental friendliness, since only natural ingredients are used in its production.
- BS or aviation plywood. The veneer is impregnated with an alcohol-soluble bakelite adhesive, which gives the boards special properties. The material is characterized by super-strength, flexibility, high elasticity, resistance to aggressive environments, micro-organisms and water resistance. Initially, it was used exclusively in aircraft and shipbuilding. Today it is also used in construction, but is not very common due to the rather high cost.
- BV. In its manufacture, water-soluble bakelite glue is used. It has the same properties as BS, except for moisture resistance.
- Laminated. Lined on one or both sides with a special paper-resin coating. It is resistant to destruction and corrosion, is resistant to abrasion and prevents moisture from entering the material. In addition, the decorative coating can imitate any materials and textures. Used for interior decoration, furniture production, etc.
All plywood according to existing standards is divided into five grades, denoted by the letter E or numbers from one to four. The criterion in this classification is the general appearance, the presence of acceptable processing defects and defects. Grade E or the elite is completely devoid of them, all the rest allow a certain number of flaws. The grade of plywood is most often indicated by two characters put through a dividing line. The first indicates the grade of the front layer, and the second - the back.

Despite the variety of types of plywood, they all have common advantages:
- Wear resistance and strength. Design features suggest high wear resistance and material strength due to the different direction of the fibers in the veneer layers that make up the board.
- Ease of use. Light weight facilitates installation. In addition, the material is easy to process. The structure of plywood allows it to be cut in any direction and in any place, which distinguishes the board from wood.
- Cheapness of production. Solid wood is not necessarily used as raw material for plywood, waste is minimal. All this significantly reduces the cost of the material.
- Flexibility and dimensional stability. The plates are easily bent and take various shapes without cracks and deformations.
- Holds heat well.
Among the significant disadvantages of plywood, it should be noted:
- Insufficient resistance to adverse environmental conditions, especially to high humidity. Stamps intended for outdoor use are more resistant.
- Structural flaws. The structural features of the material make it vulnerable to moisture. Layers of wood easily absorb liquid and "conduct" it deep into the plywood, which weakens the adhesive joints and destroys the tree.
- The use of moderately toxic materials in the production of boards. This is true for moisture resistant brands of plywood. The share of harmful substances is about 5% of the dry residue and decreases with time to almost zero.
The cost of the material varies greatly depending on the type of plywood, thickness, brand, etc. For example, the price of a 4 mm thick sheet of the second grade of the FK brand starts at 310 rubles, while a board with the same characteristics, but of the FSF brand, will cost from 670 rubles .
Chipboards
Particleboard is a composite sheet material that uses a mixture of sawdust and a binder to produce it. Wood chips are combined with urea-formaldehyde and phenol-formaldehyde resins, thoroughly mixed and processed under high temperature and pressure. The binding components activated under such conditions reliably connect the sawdust, which makes it possible to produce boards of various thicknesses. High pressure makes chipboard more homogeneous and denser.
![]()
There are several classifications of chipboard:
- By varieties. The main criterion for separation is the appearance of the plate. The presence or absence of chips, cracks, spots, depressions and protrusions is taken into account. Grade 1 material has a minimum number of defects, grade 2 allows large flaws on the surface, and products without grade have even more significant damage.
- By the number of layers. One, three and multilayer plates are issued.
- The degree of surface treatment. Unsanded and sanded wood boards are produced. In addition, allocate laminated chipboard, on which, under conditions of high temperature and high blood pressure a melamine film is applied, and a laminated board with a decorative coating glued under high pressure.
- According to the level of formaldehyde emission. They stand out: class E1 material, which contains less than 10 mg of substance per 100 g of dry board, and class E2 boards, in which the formaldehyde content is in the range from 10 to 30 mg.
- By brands. The division criteria are indicators of water resistance, flexural strength, susceptibility to deformation and warping. Two brands stand out: P-A, different the best performance, and P-B.
- Pressing method. A distinction is made between extruded and flat pressed boards.
- By density. Low-density chipboard is produced, which is less than 550 kg / m 3, medium density, the value of which varies from 550-750 kg / m 3 and high, which is more than 750 kg / m 3.
- Type of outer layer. Slabs are produced with a coarse-grained surface, fine-grained, which allow facing with polymeric materials, and ordinary, with a possible veneer coating.
The main advantages of chipboard are:
- High strength, superior to that of natural wood.
- Good water resistance due to the presence of synthetic resins in the composition of the material.
- Ease of processing. Plates are easy to cut, paint and glue.
- Affordable cost.

The most noticeable disadvantage of chipboard is the presence of formaldehyde in its composition, a very toxic substance. When choosing boards, special attention should be paid to the formaldehyde emission class. In addition, the material is quite brittle, which does not allow for fine processing of parts, and does not hold screws and nails well, especially when twisting again.
The scope of chipboard is very wide. They are used for the construction of fences and collapsible structures, sheathing and arranging roofs and walls, making a substrate for floor coverings, floors, wall panels, finishes and decorations, removable formwork, as well as in the production of furniture, packaging, racks, etc. The cost of plates starts from 650 rubles. for a standard sheet.
Cement particle boards
Cement particle board is a relatively new large-format sheet building material, which includes fine wood shavings, Portland cement and special chemical additives. During the production process, the components are mixed, after which the structure of the plate is formed from them. Larger fractions are placed inside, and small fractions are placed outside. This layering provides the material with special strength. The cement chip mass is pressed, resulting in a smooth multi-layered slab.
![]()
The types of CSPs include:
- Fiberboard. For the manufacture of boards, long-fiber shavings, the so-called wood wool, are used. The material is molded in the form of heat-insulating plates with a height of 3-15 cm and a density of 300-500 kg/m 3 . This is a fairly soft coating, easy to process, and has a high biostability. It is used for internal insulation of brick and stone ceilings and walls, as well as for filling panel and frame structures.
- Arbolit. In its production, small chips and sawdust are used. The density of the material is 400-850 kg/m 3 . Plates have good heat-saving characteristics. They are used as thermal insulation, as well as structural materials: panels, wall blocks, reinforced slabs of coatings and ceilings, etc. Arbolite slabs, used as a material for external walls, must be covered with a protective finishing layer.
- Xylolite. It is made up of lightweight concrete sawdust on magnesium binder. There is a cast and slab variety of material. Differs in high resistance to attrition, durability and resistance to shock loadings. To obtain the desired color, alkali-resistant powder pigments are introduced into its composition. It is used as a material for the manufacture of floors, which are not inferior to stone in their characteristics, but far exceed them in terms of thermal insulation.
Cement particle boards have a number of advantages:
- High strength due to the multilayer structure of the material.
- Low cost.
- Good frost resistance, water-repellent and fire-resistant properties.
- Environmentally friendly, since the composition of the material does not contain toxic substances.
- High soundproof characteristics.
- Ease of processing, the plates can be sawn with a hand tool.
- Usability various types finishes: wallpapering, painting, plastering or ceramic tiling.
- Resistance to microorganisms and insects.
- Long service life, which is more than 50 years.

The disadvantage of DSP is considered to be high density, reaching up to 1.4 t/m 3 , which makes the material quite heavy. Square meter cement particle board weighs about 14.5 kg, which makes installation difficult. In addition, the bending strength of the plate is low, it can break. At the same time, the material is very resistant to longitudinal deformations, which makes it indispensable for strengthening the frames of houses.
The scope of DSP is very wide. They are used for insulation of buildings, for their internal and external cladding, in the manufacture of frame structures and various moisture-resistant partitions, in the production of sandwich panels. They can be used for interior walls and floors, as well as for the manufacture of fixed and removable formwork, as flooring under the roof or as window sills. Cost of standard size DSP sheets starts from 750 rubles.
Oriented strand board
Oriented strand board is a modern material used in construction and decoration. It consists of about 90% wood in the form of chips and chips, interconnected by waterproof synthetic resins. Each plate is formed by three or four layers of chips pressed under high temperatures and pressure, the length of which reaches 15 cm. The peculiarity of the material is that the direction of the chips in each layer is different, which allows the plates to acquire special strength.

The industry produces several types of oriented strand boards:
- OSB-1 have low moisture resistance and strength. They are used for interior work and for the production of furniture.
- OSB-2 is characterized by low moisture resistance and high strength. Well proved as overlappings, the bearing designs and internal partitions.
- OSB-3 are characterized by high moisture resistance and the same strength, therefore they are optimal for outdoor work.
- OSB-4 have high moisture resistance and ultra-high strength, which allows them to be used as load-bearing elements, roofs and walls.
In addition, oriented strand boards with a laminated or varnished surface are produced, which are indispensable, for example, for the repeated production of formwork. Plates are also produced with tongue-and-groove joints applied to the ends on two or four sides.
The main advantages of OSB are:
- High strength and resistance to all kinds of damage, due to design features material.
- Long, more than 50 years, service life, subject to tightness.
- Ease of installation and handling. The relatively low weight of the boards makes it possible to do without additional equipment when they are installed on the roof or walls. The material is easily sawn, drilled, etc. Chips, cracks and irregularities are practically not formed.
- Good resistance to various bioinfluences and air humidity.
- Affordable cost.
- Provide good sound insulation and heat retention.
- The large format of the sheets allows you to build a structure with a minimum number of joints.

The main drawback of the material is the presence of toxic substances in its composition. To avoid trouble when buying, you should clarify the environmental class of the board and never use OSB intended for outdoor use for other purposes. In addition, the plates are combustible and require preparatory measures before decorative finishing. In the absence of tightness, they can begin to absorb water, swell, as a result of which the structure is deformed and loses its strength characteristics.
Oriented strand boards are used for sheathing ceilings, walls and floors, arranging stairs and ceilings, manufacturing sandwich panels, building frame houses, and roofing. They are used during auxiliary works, such as the installation of scaffolding, formwork, etc., for the construction of auxiliary buildings, fences, street structures and in the form of structural elements of furniture. The cost of material from European manufacturers starts from 800 rubles. per sheet.
fibreboard
Fiber board is a material consisting of a fibrous mass obtained from wood or other cellulose-containing plant fibers, synthetic polymer resins, fillers, special additives and water. Fiberboard is produced in two main ways: dry, with the addition of synthetic resins to the crushed fibers, and wet, without the addition of chemical binders.

The method of formation and processing determines the division of fiberboards into several types.
Super hard
The density of this group of materials reaches 1100 kg/m 3 . They are characterized by high flexural and tensile strength. All this makes it possible to use superhard boards in the manufacture of external panel doors and balcony doors, for built-in furniture parts and as a structural and heat-insulating material for flooring. There are brands of this variety:
- ST - plates of increased hardness, the front surface is not ennobled.
- ST-S - increased hardness, the front layer is made using finely dispersed wood pulp.
Solid
The density of these materials is about 850 kg / m 3, they are also quite strong for bending and stretching. Several grades of solid fibreboard are available:
- T - sheets with a non-refined surface.
- T-C - the front side is made of finely dispersed wood pulp.
- T-P - the front side is tinted.
- T-SP - the front layer of fine wood pulp is tinted during the production process.
- T-V - increased moisture resistance and not ennobled front surface.
- T-SV - increased moisture resistance, the front surface is made of finely dispersed wood pulp.
The first four types are further subdivided into two quality groups, A and B. The division criterion is the level of physical and mechanical characteristics. Group A is somewhat superior in its parameters to group B. To give the plates a more attractive appearance, they can be subjected to various finishes. The material is painted with polyvinyl acetate water-based paints, which makes the surface matte, or enamels based on synthetic resins to obtain a semi-matt or mirror surface. In addition, in order to simulate various materials boards can be laminated with synthetic films with textured paper inside.

Solid matte fiberboards are used for cladding ceilings and walls in rooms with normal operating conditions. Glossy and semi-matte - as a wall finish for bathrooms, kitchens, panel doors. Special perforated panels can be used for ceiling cladding, which improves their soundproofing properties. Also, the material of the T-SV and TV brands can be used for flooring and in the construction of panel exterior and balcony doors.
Semi-solid
The material is better known as MDF. It is an abbreviation of the name "medium density fibreboard" in English. It is produced by dry pressing with the addition of carbamide resins modified with melamine, which significantly reduces the emission of formaldehyde and makes them more environmentally friendly. During the production process, MDF is given special properties: water resistance, fire resistance and biostability. The plates are durable, this indicator is 2 times higher than that of fiberboard. The density of the material is in the range from 600 to 800 kg/m 3 .
MDF is most often sold uncoated, with the exception of facade options, which requires additional finishing costs. Plates are used for interior decoration in the form of laminated flooring, wall panels, as well as in the manufacture of furniture. This is due to the low cost of MDF, its homogeneous structure and ease of processing. The boards lend themselves well to sawing, drilling, milling, etc.
Soft
The density of the material became the basis for their classification:
- Mark M-1 - plate density from 400 to 200 kg / m 3.
- Grade M-2 - the density of the material varies from 350 to 200 kg / m 3.
- Mark M-3 - the density is in the range from 200 to 100 kg / m 3.
Plates have lower bending and tensile strength. They are used as thermal insulation of floors, walls and ceilings. With appropriate processing, they are used as soundproofing and decorative material for finishing ceilings. During production, they can be decorated by applying a special layer consisting of crushed wood pulp with dye, mineral filler and glue. After drying, a paint and varnish coating is applied on top.

Common advantages for all varieties of fiberboard can be considered:
- long service life;
- high thermal insulation characteristics;
- low material cost;
- easy to process without changing the original structure.
The main drawback of the material is due to the peculiarities of its manufacture. This is a small thickness of the sheet, as a result of which fiberboard has significant restrictions on its use. In addition, the plates are quite sensitive to moisture. The cost of the material depends on the type, brand and other parameters and starts from 130 rubles.
Comparative characteristics of all wood-based panels are presented in the form of a table:
| OSB | |||||
| Advantages | Strength, wear resistance, ease of use and installation, low weight, dimensional stability and flexibility, low thermal conductivity, low cost. | High strength, superior to wood, water resistance, easy processing, low cost. | High strength, resistance to various damages, ease of installation and processing, durability, good warmth and sound insulation, low cost. | Strength, environmental friendliness, good sound insulation characteristics, ease of processing, biostability, durability. | High thermal insulation characteristics, ease of processing and installation, long service life, low cost, the possibility of a variety of finishes. |
| Flaws | Insufficient resistance to adverse conditions, vulnerability to moisture, which can penetrate deep into the material and destroy it, the presence of moderately toxic materials in the composition of plywood. | The presence of toxic substances in the composition of the material, some fragility, which does not allow for fine processing of parts, poor retention of screws. | The presence of toxic substances, the flammability of the plates. With insufficient sealing, water is “pulled”, which destroys the material and deforms the structure. | High density and high weight, which makes installation difficult. Low bending strength. | Insufficient moisture resistance, small sheet thickness, which causes restrictions on the use of the material. |
| Application area | Roofing, interior design, exterior decoration, flooring, formwork, etc. | Roofing, wall cladding, flooring, flooring, interior finishing, formwork, etc. | Roofing, sandwich panel production, wall, ceiling, floor cladding. Arrangement of ceilings and stairs. Carrying out auxiliary works, erection of fences, street structures, auxiliary buildings. | Insulation of buildings, exterior and interior decoration, production of moisture-resistant partitions, frame structures, production of sandwich panels, etc. | Heat and sound insulation of the roof, manufacturing floors, decoration and decoration of walls and ceilings, arrangement of floor coverings. |
| Price | Minimum from 310 rubles. | From 650 rub. per sheet. | From 800 rub. per sheet. | From 750 rub. per sheet. | From 130 rub. per sheet. |
Inna Yasinovskaya, rmnt.ru



